Zoom fatigue is more intense for women than men heres why – Zoom fatigue is more intense for women than men, here’s why. This isn’t just about feeling tired after a virtual meeting; it delves into the complex interplay of social expectations, communication styles, and even potential biological factors. We’ll explore how women and men experience virtual meetings differently, and uncover the reasons behind this disparity.
The article will delve into the reasons behind this difference, examining social expectations, cultural norms, and potential biological factors. We’ll also offer practical strategies to alleviate zoom fatigue for everyone, regardless of gender, and highlight the need for further research to fully understand this phenomenon.
Defining Zoom Fatigue
Zoom fatigue, a modern phenomenon, describes the overwhelming exhaustion and mental drain experienced after extended periods of virtual meetings. This fatigue isn’t simply tiredness; it’s a complex interplay of factors related to the unique characteristics of online communication. It manifests in various ways, impacting individuals’ productivity and well-being.
Understanding Zoom Fatigue, Zoom fatigue is more intense for women than men heres why
Zoom fatigue is more than just feeling tired after a meeting. It encompasses a constellation of symptoms, affecting cognitive and emotional well-being. Individuals experiencing Zoom fatigue often report feeling mentally drained, stressed, and unable to focus on tasks after virtual meetings. This exhaustion can manifest in physical symptoms, such as headaches, eye strain, and even muscle tension. The constant state of alertness required to participate in virtual meetings, coupled with the lack of non-verbal cues and the need for constant self-monitoring, contributes to this feeling of being drained.
Zoom fatigue seems to hit women harder than men, and it’s got me thinking about the social connections I’ve missed. It’s not just about the endless meetings; it’s about the loss of casual interactions and the comforting hum of background noise, like I used to experience at my bar maverick site. I miss the sounds, the playlists, the people talking, the feeling of community – it’s all part of what I crave.
i miss my bar maverick site sounds playlist people talking. This longing, this yearning for those pre-pandemic connections, likely contributes to the heightened sense of exhaustion women feel during virtual interactions. Maybe it’s because women are often expected to manage more responsibilities, both in the home and the work place, during these virtual meetings.
Symptoms of Zoom Fatigue
The symptoms of Zoom fatigue vary from person to person, but some common indicators include:
- Reduced cognitive function: Difficulty concentrating, remembering information, and making decisions after a meeting.
- Emotional exhaustion: Feeling overwhelmed, stressed, or anxious after a virtual meeting.
- Physical discomfort: Headaches, eye strain, neck pain, or muscle tension due to prolonged screen time and maintaining posture.
- Decreased productivity: Difficulty focusing on work tasks and reduced efficiency following a virtual meeting.
- Social disconnect: Feeling isolated or disconnected from colleagues despite being in virtual contact. This is often due to the lack of casual interaction and non-verbal cues, creating a disconnect from the social element of work.
These symptoms highlight the multifaceted nature of Zoom fatigue, encompassing not just physical tiredness, but also cognitive and emotional strain.
Factors Contributing to Zoom Fatigue
Several factors contribute to Zoom fatigue, often interacting in complex ways.
- Constant screen time: Prolonged exposure to screens, particularly during meetings, can lead to eye strain, headaches, and difficulty focusing.
- Lack of non-verbal cues: Virtual meetings often lack the subtle cues and body language that help us understand others’ emotions and intentions in person, requiring constant mental effort to interpret the interaction. This constant mental effort is taxing.
- Distractions: Home environments often have more distractions than traditional workspaces, such as family members, pets, or household chores. This makes it harder to fully focus on the meeting.
- Meeting etiquette: The lack of established meeting norms and protocols in virtual settings can lead to unproductive discussions, endless introductions, or poorly structured meetings. This can lead to frustration and cognitive load.
- Technical issues: Unexpected interruptions, poor audio quality, or video glitches can disrupt the flow of the meeting, causing frustration and making it difficult to concentrate.
These factors, both internal and external, combine to create the feeling of being overwhelmed and drained after a virtual meeting.
Comparing In-Person and Virtual Meetings
| Feature | In-Person Meetings | Virtual Meetings | Potential Causes of Fatigue ||——————-|—————————————————-|——————————————————–|—————————–|| Environment | Familiar, physical space, conducive to focus | Home or other personal space, potentially distracting | Distractions, lack of physical space || Engagement | Physical presence, non-verbal cues | Reliance on visual cues, reduced nonverbal cues | Mental effort to interpret, social isolation || Interaction | Direct interaction, casual conversation | Formalized interaction, potentially less relaxed | Social disconnect, formal tone || Structure | Established routines, clear expectations | Varying structures, potential for disorganization | Lack of structure, meeting etiquette || Technology | No reliance on technology, minimal technical issues | Reliance on technology, potential technical issues | Technical difficulties, screen fatigue |This table highlights the key differences between in-person and virtual meetings and how these differences contribute to the experience of fatigue.
Ever wondered why zoom fatigue seems to hit women harder than men? It’s a complex issue, but it often boils down to the extra burden of childcare and household responsibilities that women disproportionately shoulder. Fortunately, if your electronics are giving you a headache, ubreakifix now offers walk-in surface repairs to help you get back on track.
This extra pressure during virtual meetings likely contributes to the higher levels of reported zoom fatigue in women. The ongoing pressure of juggling work and personal demands during these virtual interactions undoubtedly plays a significant role.
Gender Differences in Meeting Experiences
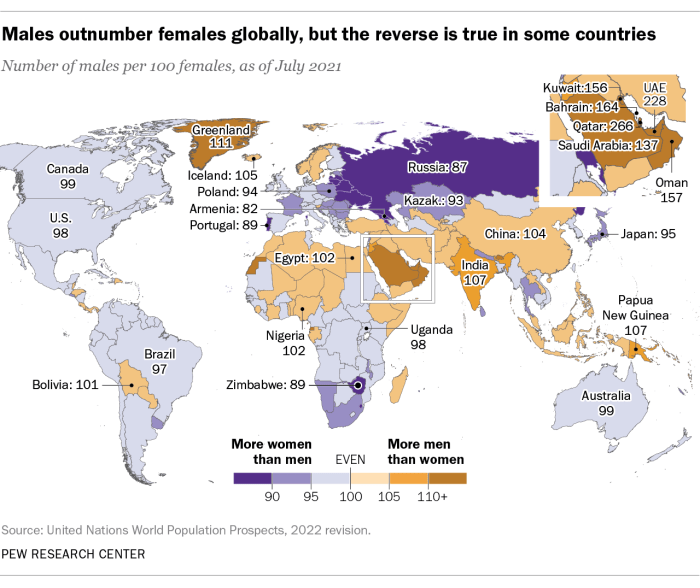
Zoom fatigue, a pervasive feeling of exhaustion and disconnect from virtual meetings, disproportionately affects women. While the reasons are multifaceted, understanding the nuances of gendered meeting experiences in virtual settings is crucial for fostering more inclusive and productive online interactions. This exploration dives into the potential social and cultural factors influencing women’s experiences, examines how expectations and roles shape fatigue levels, and highlights differences in communication styles.The experience of virtual meetings is not a gender-neutral space.
Social and cultural expectations often place different demands on women and men, leading to varying levels of fatigue. These differences are deeply ingrained in societal norms and influence how individuals perceive and participate in virtual interactions. Understanding these dynamics is key to addressing the issue of gender disparity in Zoom fatigue.
Meeting Experience Differences
Different expectations and roles assigned to women and men can significantly impact their virtual meeting experiences. Women are often expected to take on more supporting roles, such as actively listening and summarizing discussions, while men might be perceived as more authoritative, speaking more frequently and taking a leading role. These expectations contribute to the varying levels of fatigue, with women often feeling overwhelmed by the constant need to participate in a supportive role.
This is further complicated by the pressure to maintain a professional and engaging presence throughout the meeting, which can be especially challenging for women who may also juggle household responsibilities.
Social and Cultural Factors
Several social and cultural factors can influence the virtual meeting experiences of women. Traditional gender roles often dictate that women prioritize others’ needs and emotions, leading to a higher level of emotional labor in virtual meetings. This involves actively listening, empathizing, and responding to others’ needs, which can be mentally taxing, particularly when coupled with a sense of responsibility to present a professional demeanor.
Cultural norms surrounding communication styles also play a significant role. In some cultures, women may be less inclined to interrupt or challenge others in virtual meetings, potentially leading to a feeling of being unheard or undervalued. These factors, when combined with existing societal expectations, can contribute to the higher levels of Zoom fatigue experienced by women.
Expectations and Roles Affecting Fatigue
Meeting expectations and roles play a vital part in shaping fatigue levels. Women often face a double burden in virtual settings, juggling work responsibilities and domestic tasks, leading to increased stress and fatigue. The expectation to be constantly available and engaged in virtual interactions can also contribute to the problem, particularly for women who often carry additional emotional labor in these contexts.
This can lead to burnout and a heightened sense of exhaustion compared to men who might experience less pressure in these roles.
Communication Styles and Fatigue
| Communication Style | Typical Behavior in Virtual Meetings | Potential Impact on Fatigue (Women/Men) |
|---|---|---|
| Passive | Avoids expressing opinions or taking initiative, listens attentively. | Potentially leads to feeling unheard or undervalued, which may increase fatigue for women due to the expectation to be supportive and nurturing. |
| Assertive | Expresses opinions clearly and confidently, actively participates in discussions. | Could contribute to higher levels of fatigue for both women and men, depending on the cultural context and meeting environment. |
| Aggressive | Interrupts others, dominates discussions, and expresses opinions forcefully. | Could lead to increased fatigue for both genders due to the potentially confrontational nature of the interactions. |
| Passive-Aggressive | Expresses dissatisfaction indirectly or subtly. | Potentially leads to increased frustration and fatigue for both women and men, as unspoken issues can hinder productive discussion. |
This table illustrates how different communication styles can affect fatigue levels in virtual meetings. The nuances of these styles and how they’re perceived, both by the individual and by others in the meeting, significantly contribute to the overall experience. The expectation of women to adopt certain styles can add to the burden and potentially increase their susceptibility to fatigue.
Potential Biological and Psychological Factors
Zoom fatigue, the overwhelming sense of exhaustion and mental strain associated with virtual meetings, is a complex phenomenon. While the reasons for its intensity varying between genders are multifaceted, understanding the potential biological and psychological factors can shed light on the disparity in experiences. This section explores the possible biological underpinnings, the role of psychological responses, and how societal expectations interact to contribute to the differing levels of fatigue.The experience of fatigue is often linked to neurobiological processes, and these can vary significantly between genders.
Hormonal fluctuations, sleep patterns, and even the inherent differences in brain structure and function can all play a role. Moreover, stress responses and emotional labor are crucial psychological elements that can significantly impact an individual’s perception of fatigue during virtual interactions. Women, often burdened with societal expectations of managing multiple roles and responsibilities, might be more susceptible to the pressures of emotional labor in virtual settings.
Potential Biological Factors
Biological differences between genders can influence fatigue levels during virtual meetings. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can impact energy levels and stress responses. Studies suggest that variations in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which regulates stress responses, might contribute to differing susceptibility to fatigue. Additionally, differences in sleep patterns and sleep quality between genders could play a role.
Potential Psychological Factors
Psychological factors like stress responses and emotional labor are significant contributors to the experience of fatigue. Stress responses, triggered by various factors including virtual meeting environments, can lead to increased feelings of exhaustion. Furthermore, emotional labor, the effort required to regulate and manage emotions during social interactions, is a key aspect of the virtual meeting experience. In virtual meetings, the lack of nonverbal cues can heighten the demands of emotional labor.
Emotional Labor and Societal Expectations
Societal expectations often place additional emotional labor burdens on women. Women may feel more pressure to maintain positive interactions, provide support, and be actively engaged in virtual meetings. This can lead to increased feelings of fatigue, as the effort required to regulate and manage emotions is substantial. Furthermore, women may feel compelled to address interruptions or concerns from other participants, even if it is not their responsibility, adding to their emotional labor burden.
Impact of Meeting Fatigue on Women
The interplay of biological and psychological factors, coupled with societal expectations, can create a unique experience of virtual meeting fatigue for women. The increased emotional labor demands, combined with potential hormonal variations and stress responses, could contribute to a heightened sense of exhaustion. Women might experience greater difficulty focusing, feel more overwhelmed, and have more challenges participating in virtual meetings compared to men.
Ever wonder why zoom fatigue seems to hit women harder than men? It’s a complex issue, but part of it boils down to the disproportionate amount of unpaid caregiving women often shoulder. Think about all the extra household tasks and childcare responsibilities that often fall on women. Freeing up some of that time with a premium robot vacuum like this one could really make a difference in reducing stress and allowing for more focused work time.
Ultimately, this extra burden contributes to the heightened sense of exhaustion and frustration felt by many women during virtual meetings.
Table of Biological and Psychological Theories Related to Meeting Fatigue
| Theory | Biological Aspect | Psychological Aspect | Potential Impact on Women |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Fluctuations | Variations in estrogen and progesterone levels | Increased emotional reactivity, fluctuations in mood | Potentially heightened susceptibility to fatigue, increased difficulty regulating emotions. |
| HPA Axis Activity | Differences in stress response regulation | Increased cortisol levels, heightened anxiety | Potential for greater vulnerability to stress-related fatigue, increased emotional exhaustion. |
| Sleep Patterns | Differences in sleep quality and duration | Reduced cognitive function, increased irritability | Increased risk of fatigue due to disrupted sleep patterns, impacting concentration in meetings. |
| Emotional Labor | Effort to regulate emotions | Increased stress, feelings of exhaustion | Higher burden of emotional labor, leading to more pronounced fatigue, especially in virtual meetings. |
| Social Roles and Expectations | Societal pressures on women | Increased emotional burden, expectations of support | Potential for increased emotional labor, leading to higher fatigue levels in virtual environments. |
Social and Cultural Influences
Zoom fatigue, while a universal experience, appears to disproportionately affect women. Beyond the biological and psychological factors, societal expectations and cultural norms play a significant role in shaping women’s virtual meeting experiences. These influences often contribute to a higher level of stress and fatigue, stemming from the pressure to conform to specific communication styles and present a particular image.The digital space, while intended for connection, can inadvertently amplify pre-existing societal pressures on women to be perfect, poised, and attentive.
This pressure, often absent or less pronounced in face-to-face interactions, can be particularly intense during virtual meetings, leading to a higher level of anxiety and self-consciousness.
Societal Expectations and Polished Image
Women are frequently socialized to prioritize politeness, attentiveness, and emotional regulation in social interactions. This often translates to a higher expectation for maintaining composure and a polished image, even in virtual settings. The feeling that every action is under scrutiny and judged can contribute to feelings of inadequacy and ultimately, greater fatigue. For example, women may feel compelled to meticulously prepare for meetings, ensuring their background is impeccable and their attire is professional, even when it’s a casual meeting.
This heightened sense of performance pressure can lead to a higher level of mental and emotional expenditure.
Gendered Communication Styles
Different communication styles are often associated with gender roles. Women are sometimes expected to be more collaborative and supportive, taking turns and actively listening. This expectation can lead to feeling obligated to contribute in a particular way, potentially leading to a greater sense of responsibility and workload during virtual meetings. Conversely, men might be perceived as having more freedom to express their opinions and ideas, even interrupting more frequently, without being judged in the same way.
This difference can contribute to a sense of imbalance and increased workload for women, further intensifying the fatigue.
Cultural Variations in Virtual Meetings
Cultural norms regarding communication styles, active participation, and even the perception of time in virtual meetings can significantly influence fatigue levels. Different cultures may have varying expectations about turn-taking, the use of nonverbal cues, and the appropriateness of interrupting.
| Culture | Typical Approach to Virtual Meetings | Potential Impact on Fatigue Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Individualistic Cultures (e.g., US, UK) | Direct communication, active participation encouraged, less emphasis on nonverbal cues. | Potential for heightened pressure to contribute and maintain a polished image. May experience fatigue from needing to continuously participate. |
| Collectivistic Cultures (e.g., Japan, South Korea) | Indirect communication, emphasis on maintaining harmony, less active participation from individuals, respect for hierarchy. | Potential for fatigue from the need to carefully consider the impact of words and actions, as well as navigate cultural expectations about participation. |
| High-Context Cultures (e.g., many Latin American cultures) | Emphasis on nonverbal cues, relationship-building, and indirect communication. | Potential for fatigue from needing to interpret subtle cues and maintain rapport, potentially leading to a higher level of mental effort. |
Illustrative Examples of Differences
Zoom fatigue, a phenomenon impacting both men and women, often manifests differently. While both genders experience the mental strain of constant virtual interaction, women frequently report more intense fatigue due to a confluence of social, psychological, and biological factors. This stems from societal expectations, emotional labor, and often overlapping responsibilities. Understanding these differences is crucial to fostering more inclusive and supportive virtual environments.
Scenarios of Increased Zoom Fatigue for Women
Societal expectations often place disproportionate burdens on women, leading to heightened Zoom fatigue. Consider a working mother who juggles childcare responsibilities while participating in back-to-back virtual meetings. This scenario is likely to induce greater fatigue in her compared to a male counterpart without similar responsibilities. The constant pressure to multitask and maintain a polished virtual persona while managing family demands can be overwhelming.
Social Expectations Impacting Women’s Contributions
Women often face social expectations to be more agreeable and supportive in virtual meetings. They might feel pressured to actively participate and offer input, but simultaneously avoid appearing overly assertive or aggressive. This can create a tension that leads to mental exhaustion. For example, in a virtual brainstorming session, a woman might hesitate to voice a strong opinion, even if she has a valuable insight, out of fear of being perceived negatively.
Conversely, a man might feel more comfortable voicing a potentially controversial opinion without the same level of apprehension.
Emotional Labor in Virtual Settings
The concept of emotional labor, which involves managing and regulating emotions to conform to social expectations, is particularly significant in virtual environments. Women frequently shoulder a greater burden of emotional labor in virtual meetings. This might involve actively listening to colleagues, ensuring everyone feels included, and mediating potential conflicts. While these contributions are vital, they can be mentally taxing and lead to greater fatigue.
Table Comparing Meeting Scenarios
| Scenario | Woman | Man | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meeting 1: Project Brainstorming | Feels pressured to offer input, but worries about appearing too assertive. May hesitate to speak up, even with a good idea. | More comfortable voicing opinions, even if they are controversial. | Societal expectations around assertiveness often affect women more. |
| Meeting 2: Problem Solving | Takes on the role of mediator, ensuring all voices are heard and respected. | Might focus more on the technical aspects of the problem, less on facilitating discussion. | Emotional labor to ensure inclusivity and harmony. |
| Meeting 3: Client Presentation | More concerned about projecting professionalism and positivity, even if feeling stressed. | Might present information in a more direct manner. | Women are often perceived as more empathetic and collaborative in virtual settings. |
| Meeting 4: Team Meeting | Responsible for managing logistics and schedules, alongside other responsibilities. | Might focus more on the task at hand, delegating scheduling details. | Women are often the primary organizers in virtual settings. |
Practical Strategies to Reduce Zoom Fatigue: Zoom Fatigue Is More Intense For Women Than Men Heres Why
Zoom fatigue, a pervasive issue in today’s virtual work environment, impacts individuals in various ways. It’s more than just feeling tired; it encompasses a range of mental and emotional strain associated with prolonged online interactions. Strategies for mitigating this fatigue are crucial for maintaining productivity and well-being in the digital age. By understanding the factors contributing to Zoom fatigue and implementing effective strategies, individuals can create more positive and productive virtual meeting experiences.
Creating a Supportive Virtual Meeting Environment
Virtual meetings, while essential, can sometimes feel overwhelming due to constant screen time and the lack of spontaneous interactions. Creating a supportive environment can significantly reduce fatigue for all participants. This involves optimizing the meeting space and structure to facilitate meaningful engagement.
- Establish Clear Meeting Agendas and Objectives: Pre-meeting communication about the agenda and specific objectives provides attendees with a clear framework. This reduces uncertainty and ensures that everyone is aware of the purpose and expected outcomes. This also reduces the feeling of being pulled in multiple directions.
- Optimize Meeting Structure: Break down large meetings into smaller, focused sessions, if possible. Utilize collaborative tools to encourage participation and engagement, like polls or breakout rooms. Regular short breaks can prevent mental fatigue. Implementing short breaks between meetings and sessions can also help prevent exhaustion.
- Encourage Active Participation and Engagement: Don’t rely solely on presentations. Encourage questions, discussions, and active participation to keep attendees engaged. Even short periods of interaction can revitalize and improve concentration.
Managing Expectations and Workloads
Managing expectations and workload is vital to prevent burnout, both during and after virtual meetings. Unrealistic expectations, coupled with overwhelming workloads, can contribute significantly to Zoom fatigue.
- Setting Realistic Meeting Lengths and Frequency: Evaluate the necessity of each meeting. If a meeting can be accomplished through email or a short chat, consider these alternatives. Limiting the duration of meetings to the essential time required can prevent fatigue. Consider reducing meeting frequency if possible, delegating tasks or combining them.
- Prioritizing Tasks and Time Management: Establish clear priorities and allocate appropriate time for virtual meetings and other tasks. Plan breaks and downtime to allow for mental restoration. Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance helps maintain focus and prevent feeling overwhelmed.
- Maintaining Work-Life Balance: Establish clear boundaries between work and personal time. Designate specific workspaces and avoid blurring the lines between work and personal life. This includes scheduling time for relaxation and activities outside of work.
Practical Tips for All Participants
Implementing practical strategies can help all participants navigate the virtual meeting space effectively.
| Action | Benefit | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Minimize Distractions | Reduced mental strain and improved focus | Identify and eliminate potential distractions in your workspace. Inform others of your meeting time to minimize interruptions. |
| Prepare in Advance | Increased efficiency and reduced stress | Review the meeting agenda, gather necessary materials, and prepare your questions beforehand. This reduces the feeling of being unprepared and increases focus during the meeting. |
| Utilize Technology Effectively | Improved communication and collaboration | Familiarize yourself with the meeting platform’s features and tools to optimize participation. Use mute and unmute functions effectively. |
| Communicate Needs | Enhanced support and understanding | Clearly communicate any needs or preferences for virtual meetings to your colleagues. This can improve the meeting experience and support for all involved. |
Further Research Needed
Unveiling the intricacies of gendered experiences with Zoom fatigue requires a deeper dive into the underlying factors. While existing research provides valuable insights, gaps remain in our understanding of the nuanced interplay between biological, psychological, social, and cultural influences. Further research can illuminate these complexities, leading to more targeted interventions and a more inclusive approach to remote work.
Exploring Biological Mechanisms
Understanding the biological underpinnings of gender differences in Zoom fatigue is crucial. Research should investigate potential hormonal variations and their correlation with stress responses during virtual meetings. This could involve longitudinal studies tracking hormonal levels and meeting experiences over time, controlling for other factors such as personality traits or social support networks. Specific physiological responses, like heart rate variability and cortisol levels, during virtual interactions deserve examination to assess their potential connection with gendered experiences of fatigue.
Examining Psychological Processes
Psychological factors, including perceived social pressure, self-presentation concerns, and emotional regulation strategies, need further investigation. Studies should examine how these factors vary across genders in the context of virtual meetings. Qualitative research methods, such as interviews and focus groups, can provide rich insights into the subjective experiences of individuals. This research could also analyze the influence of gendered expectations and stereotypes on self-perceived performance and meeting participation.
Investigating Social and Cultural Influences
Social and cultural norms significantly impact how individuals perceive and react to virtual meetings. Comparative studies across diverse cultures can reveal how societal expectations regarding communication styles and roles affect the experience of Zoom fatigue. Examining the impact of gendered communication norms in virtual environments is critical. These investigations can involve ethnographic studies or large-scale surveys to capture a broader range of perspectives.
Analyzing the influence of family responsibilities and childcare duties on meeting participation and fatigue levels across genders is essential.
Developing Research Methodologies
Future research needs to employ a combination of quantitative and qualitative methodologies to gain a comprehensive understanding. This approach can involve large-scale surveys to collect data on meeting experiences, alongside in-depth interviews to explore the underlying reasons for reported fatigue. Using physiological measures like heart rate variability or skin conductance, combined with self-reported measures of stress and fatigue, could provide a more holistic picture of the impact of virtual meetings.
Table of Potential Research Questions
| Research Area | Research Questions |
|---|---|
| Biological Mechanisms | How do hormonal fluctuations relate to Zoom fatigue experiences among men and women? What physiological indicators (e.g., heart rate variability, cortisol levels) correlate with gender differences in meeting fatigue? |
| Psychological Processes | How do perceived social pressures and self-presentation concerns vary between genders in virtual meetings? How do coping mechanisms for stress differ in virtual environments based on gender? |
| Social and Cultural Influences | How do cultural norms regarding communication styles and roles impact gendered experiences of Zoom fatigue? How do family responsibilities and childcare duties influence meeting participation and fatigue levels for men and women? |
| Methodological Approaches | How can mixed-methods approaches (e.g., combining surveys and interviews) provide a more comprehensive understanding of gendered Zoom fatigue experiences? What are the ethical considerations for incorporating physiological measures in studies of virtual meeting fatigue? |
Summary
In conclusion, the intensity of Zoom fatigue appears to vary significantly between women and men. This difference stems from a combination of social and cultural expectations, communication styles, and potential psychological and biological factors. Understanding these nuances is crucial to creating more inclusive and effective virtual meeting environments. The key takeaway is that reducing Zoom fatigue for everyone requires addressing the unique challenges faced by both genders.
More research is needed to fully comprehend the complex factors at play and develop tailored strategies for mitigating this issue.