Why AI and automation offer hope for cybersecurity? This exploration delves into how artificial intelligence and automation are revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering proactive solutions to emerging threats. We’ll examine AI-powered threat detection, automated security tasks, and enhanced security postures through data analysis, all while exploring the challenges and considerations involved in this transformative shift.
Imagine a world where cybersecurity threats are anticipated and neutralized before they even emerge. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns indicative of potential attacks, allowing for proactive measures. Automation tools can streamline routine security tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic initiatives. This paradigm shift promises a more robust and resilient digital landscape.
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Prevention
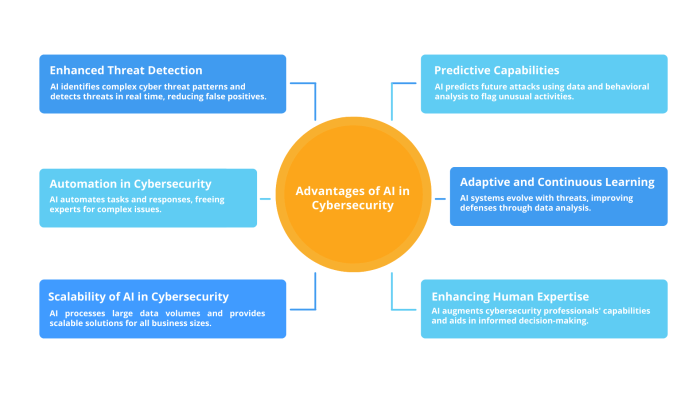
AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering a powerful arsenal against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Traditional methods often struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of attack techniques. AI’s ability to learn, adapt, and identify subtle patterns in vast datasets gives it a significant advantage in detecting and responding to emerging threats.AI algorithms excel at analyzing massive amounts of data, identifying anomalies, and adapting to new attack vectors, making them ideal for threat detection and prevention.
This surpasses the capabilities of human analysts, who are limited by time and cognitive capacity.
AI Models for Threat Detection
Various AI models are employed in cybersecurity, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Machine learning, a cornerstone of AI, is used to identify patterns in network traffic and user behavior. Deep learning, a more complex form of machine learning, can analyze intricate data relationships and recognize complex attack patterns. Behavioral analytics leverages past user activity to detect deviations that could signal malicious intent.
Comparing AI-Based Threat Detection Systems
| AI Model | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Relatively easier to implement and maintain, effective for identifying known threats, good for large datasets. | Can struggle with complex, evolving threats, may require significant labeled data for training, less accurate in identifying novel attacks. |
| Deep Learning | Highly effective at identifying complex patterns and anomalies, can learn from unstructured data like images and audio, more accurate in identifying novel attacks. | More computationally intensive, requires large datasets for training, harder to interpret the decision-making process. |
| Behavioral Analytics | Effective at detecting insider threats and malicious activity by analyzing user behavior, can detect unusual login patterns and data access attempts. | Requires extensive historical data, can be prone to false positives, might struggle with unexpected user behavior changes. |
Predictive and Preventative Capabilities
AI can predict and prevent cyberattacks by analyzing network traffic and user behavior for patterns and anomalies. For instance, if a user’s login attempts are unusually frequent or from an unusual location, the system can flag this as suspicious and take preventive measures, such as blocking the access.
Automating Incident Response
AI plays a crucial role in automating incident response. Once a threat is detected, AI can trigger automated responses, such as isolating infected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and initiating remediation procedures. This drastically reduces the time it takes to contain and recover from a cyberattack, minimizing damage and downtime. For example, an AI system can automatically isolate a compromised server, prevent further data breaches, and initiate a restoration process, greatly minimizing the impact of a breach.
“AI-driven incident response reduces recovery time by automating critical tasks, minimizing damage and maximizing operational efficiency.”
Automated Security Tasks

Automating security tasks is crucial for modern cybersecurity. It frees up valuable human resources, allowing cybersecurity professionals to shift their focus from repetitive, time-consuming tasks to strategic initiatives like threat intelligence analysis and incident response planning. This shift in focus leads to improved efficiency, reduced errors, and a more proactive approach to security.Automation streamlines processes, making vulnerability scanning, patching, and security monitoring more efficient and effective.
AI and automation hold real promise for bolstering cybersecurity defenses. Imagine a system that can instantly identify and neutralize threats faster than any human could, and that’s precisely what these technologies can do. With the recent Spotify launch of a hub for shows like Squid Game and Bridgerton and your other favorite Netflix shows here , it’s clear that innovation is rapidly changing the way we consume entertainment.
This same kind of rapid evolution in technology is vital for cybersecurity, providing a much-needed edge in the ongoing battle against cybercriminals.
This enhanced efficiency allows for faster identification and resolution of security issues, leading to a stronger overall security posture. AI-powered tools further amplify these benefits by automating even more complex tasks, often with greater accuracy and speed.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
Cybersecurity professionals often spend considerable time on repetitive tasks like vulnerability scanning, log analysis, and patch management. Automation tools can significantly reduce this workload, allowing them to dedicate more time to higher-level strategic activities. This shift towards strategic thinking is essential for staying ahead of evolving threats.
Improving Efficiency and Effectiveness
Automation significantly improves the efficiency and effectiveness of vulnerability scanning, patching, and security monitoring. Automated vulnerability scanners can quickly identify weaknesses in systems, reducing the time needed for manual assessments. Similarly, automated patching systems can deploy security updates more efficiently and consistently, minimizing the risk of exposure to known vulnerabilities. Automated security monitoring tools can provide continuous surveillance, alerting administrators to potential threats in real-time.
Comparison of Automation Tools and Platforms, Why ai and automation offer hope for cybersecurity
Various tools and platforms offer automation capabilities for different aspects of cybersecurity. Some popular options include:
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools: Nessus, OpenVAS, QualysGuard. These tools automate the process of identifying vulnerabilities in systems and applications. Each tool offers a different set of features and functionalities, catering to diverse needs and budgets. For example, Nessus is known for its comprehensive vulnerability database and powerful scanning capabilities.
- Patch Management Systems: Puppet, Ansible, Chef. These tools automate the deployment of security patches across various systems. They streamline the process of identifying required updates, testing compatibility, and applying them consistently.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Splunk, ArcSight, QRadar. These systems automate the collection, analysis, and correlation of security logs, providing valuable insights into potential threats. Each SIEM offers a unique approach to data processing and visualization, supporting different analytical needs.
Streamlined Workflow for Automated Security Tasks
Organizing automated security tasks into a streamlined workflow is crucial for maximum effectiveness. A typical workflow might involve:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Automated scanning identifies potential vulnerabilities.
- Risk Prioritization: Automated tools analyze the severity and impact of identified vulnerabilities.
- Patch Deployment: Automated systems deploy security patches to affected systems.
- Security Monitoring: Automated tools monitor systems for suspicious activity and generate alerts.
- Incident Response: Automated tools aid in incident response by providing context and streamlining the investigation process.
AI-Powered Automation in Security Tasks
AI-powered tools are increasingly used to automate security tasks, offering improved accuracy and speed. For example, AI can be used to:
- Analyze Network Traffic: AI algorithms can identify malicious patterns in network traffic with higher accuracy than traditional methods, enabling faster threat detection and response.
- Detect Insider Threats: AI can identify anomalies in user behavior that might indicate insider threats, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
- Automate Incident Response: AI can automatically triage security alerts, prioritize incidents, and even initiate some response actions, significantly reducing response time.
Enhanced Security Posture Through Data Analysis
AI and automation are revolutionizing cybersecurity, not just by detecting threats, but also by proactively identifying potential vulnerabilities. A crucial aspect of this proactive approach is analyzing vast datasets to gain a deeper understanding of security risks. By leveraging the power of data analysis, organizations can uncover hidden patterns and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed, leading to a significantly enhanced security posture.Data analysis is the cornerstone of a proactive cybersecurity strategy.
By scrutinizing various data points, AI can identify trends, anomalies, and correlations that could indicate malicious activity or system weaknesses. This allows security teams to anticipate and mitigate threats before they materialize.
Analyzing Logs, Events, and Threat Intelligence
Analyzing security logs, system events, and threat intelligence feeds is critical for identifying potential vulnerabilities. AI algorithms can sift through these massive datasets, identifying patterns that human analysts might miss. For example, a sudden spike in failed login attempts from a specific IP address, coupled with unusual network traffic patterns, might indicate a targeted attack. Similarly, anomalies in user behavior, such as unusually high file downloads or access to sensitive data, could signal compromised accounts or insider threats.
The ability to correlate these events across different data sources provides a more comprehensive picture of the security landscape.
Identifying Hidden Patterns
AI algorithms excel at identifying hidden patterns in data that are often imperceptible to human analysts. These patterns can manifest as unusual access requests, atypical file modifications, or deviations from established user behavior. For instance, an organization might notice a recurring pattern of unusual data exfiltration attempts during specific hours of the day. This insight allows security teams to implement targeted security controls and monitor the situation closely.
Similarly, unusual relationships between user actions and system events can reveal hidden vulnerabilities or potential entry points for attackers. This ability to recognize subtle deviations from the norm is crucial for proactively identifying and addressing security risks.
Data Sources for Improved Security Posture
A multitude of data sources can be leveraged to improve security posture. These include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems: These systems collect and analyze logs from various security devices, providing a comprehensive view of security events.
- Network traffic logs: These logs provide insights into network activity, enabling the identification of unusual patterns and potential intrusions.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) data: EDR solutions collect data from individual endpoints, offering granular insights into user and application behavior.
- Threat intelligence feeds: These feeds provide real-time information on emerging threats and vulnerabilities, enabling proactive security measures.
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) data: UEBA solutions analyze user and entity behavior to identify deviations from established patterns, potentially signaling malicious activity.
Combining data from these diverse sources allows for a more holistic understanding of the security landscape, leading to a more robust security posture.
Benefits of Data Analysis for Proactive Cybersecurity
The table below highlights the benefits of leveraging data analysis for proactive cybersecurity measures:
| Data Analysis Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Early Threat Detection | Identifying anomalies and patterns indicative of potential threats before they escalate into major incidents. |
| Vulnerability Identification | Uncovering hidden vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems and processes, enabling timely remediation. |
| Improved Incident Response | Gaining valuable insights to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of incident response procedures. |
| Reduced Attack Surface | Identifying and mitigating potential attack vectors to minimize the risk of successful cyberattacks. |
| Proactive Security Measures | Implementing targeted security controls and monitoring strategies based on analyzed data. |
Proactive Security Measures
AI and automation are not just reactive tools in cybersecurity; they empower proactive measures that anticipate and mitigate threats before they cause significant damage. By analyzing vast datasets and identifying patterns, AI systems can predict potential vulnerabilities and suggest preventative actions. This proactive approach is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, where adversaries are constantly innovating their tactics.AI’s predictive capabilities extend beyond simply recognizing known threats.
By learning from historical data and real-time events, AI can identify emerging patterns and potential attack vectors that haven’t been seen before. This adaptability is essential in safeguarding against zero-day exploits and other novel threats.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
AI systems are not static; they constantly learn and adapt to new threats. Machine learning algorithms analyze new attack patterns, identifying anomalies and suspicious behavior. This continuous learning process allows AI to stay ahead of evolving threats, updating its detection capabilities and response strategies in real time. For example, an AI system detecting a new phishing campaign can immediately flag similar emails and block them, preventing potential compromises.
Enhancing Security of Cloud Environments
Cloud environments, with their dynamic nature and dispersed resources, present unique security challenges. AI and automation can significantly improve cloud security by automating tasks like user access management, threat detection, and vulnerability scanning. This allows security teams to focus on more complex and strategic tasks. For instance, AI-powered tools can automatically identify unusual access patterns in a cloud environment, alerting security personnel to potential breaches before data is compromised.
Enhancing Security of IoT Devices
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices creates a vast attack surface. AI can help to secure these devices by identifying vulnerabilities and implementing proactive security measures. By analyzing data from various IoT devices, AI systems can spot anomalous behavior, detect potential malware infections, and automatically patch known vulnerabilities. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of a widespread attack through a compromised IoT device.
Proactive Security Measures Facilitation
AI and automation facilitate a wide range of proactive security measures.
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: AI can automate vulnerability scans across networks and systems, identifying potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. This proactive approach allows for timely patching and mitigation.
- Anomaly Detection: AI can detect anomalies in system behavior, alerting security personnel to potential threats that might otherwise go unnoticed. This involves identifying deviations from expected patterns, which can signal malicious activity.
- Predictive Threat Modeling: AI can analyze historical data and current trends to predict potential threats and vulnerabilities. This allows for proactive security measures to be implemented before an attack occurs.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can automate incident response processes, including isolating compromised systems, containing the spread of malware, and restoring services. This significantly reduces response time and minimizes damage.
Prioritizing Vulnerabilities
AI can identify and prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. By assessing the likelihood of exploitation and the potential damage, AI can rank vulnerabilities according to severity. This enables security teams to focus their resources on the most critical issues first, maximizing the impact of security investments. For instance, a vulnerability in a critical infrastructure component might be prioritized higher than a vulnerability in a less important system.
Improved Security for Specific Industries
AI and automation are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Their effectiveness in cybersecurity hinges on tailoring them to the unique needs and challenges of specific industries. This requires understanding the specific threats, vulnerabilities, and regulatory frameworks each sector faces. By analyzing these factors, we can develop targeted security strategies that are far more effective than generic approaches.Tailored AI and automation solutions are crucial for robust cybersecurity across various industries.
AI and automation are promising for cybersecurity because they can identify and respond to threats faster than humans. While we’re focusing on tech, don’t forget to grab a massive 40% off these adorable sports-themed dog clothes at Petco! take a massive 40 off these adorable sports themed dog clothes at petco This enhanced speed and efficiency could dramatically reduce the time it takes to mitigate attacks, making the digital world a safer place for everyone.
Ultimately, this powerful combination is key to a stronger online defense.
Understanding the specific security needs and challenges for each sector enables the development of targeted solutions. This approach yields a higher return on investment compared to a blanket approach.
AI and automation hold promise for cybersecurity, offering a potential solution to the ever-growing threat landscape. Think about how human error, fatigue, and simple lack of time can lead to security breaches – automation can help mitigate this. Just as a comparison study like the Theranos one, highlighting the unreliability of some diagnostic labs ( theranos comparison study labcorp quest diagnostics not reliable ), demonstrates a need for better systems, AI-powered security tools can automate threat detection and response, offering a much-needed layer of protection.
This automated approach to security offers a way to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are prime targets for cyberattacks due to the sensitive data they handle. They face the constant threat of fraud, data breaches, and financial theft. Specific security needs include robust authentication, real-time transaction monitoring, and sophisticated fraud detection systems. AI can play a pivotal role in detecting anomalies in transaction patterns, identifying potential fraudsters, and preventing unauthorized access.
For instance, machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets of transactions to identify suspicious activity in real-time, alerting security teams to potential threats before they escalate.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry faces the challenge of protecting patient data, complying with stringent regulations like HIPAA, and safeguarding sensitive medical records. AI can be used to automate the identification of suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data breaches, and enhance data encryption protocols. For example, AI-powered systems can analyze medical images for anomalies or detect patterns that suggest potential fraudulent claims.
This is particularly important in preventing cyberattacks that compromise patient confidentiality.
Government
Government agencies often deal with highly sensitive information, including national security data and citizen records. They need to maintain strict confidentiality and integrity. AI and automation can aid in identifying and mitigating threats, monitoring for unusual activity, and automating compliance checks. For example, automated systems can scan incoming communications for potential threats, identify anomalies in access patterns, and ensure adherence to data privacy regulations.
Comparative Analysis of Security Needs and Challenges
| Industry | Key Security Needs | Major Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Institutions | Fraud detection, transaction monitoring, robust authentication | Sophisticated fraud attempts, regulatory compliance |
| Healthcare | Patient data protection, compliance with HIPAA, secure data storage | Data breaches, regulatory pressures, evolving threats |
| Government | National security, data confidentiality, compliance with regulations | Advanced persistent threats, insider threats, data breaches |
Specific Security Solutions
AI and automation solutions tailored for specific industries often involve custom-built systems that integrate with existing security infrastructure. For instance, financial institutions may leverage AI-powered fraud detection systems, while healthcare organizations may use AI to enhance data encryption and compliance monitoring. This involves implementing machine learning models, natural language processing (NLP), and other advanced technologies to create custom security solutions.
Industries Benefiting Most from AI and Automation
Industries with large datasets, complex processes, and high-value assets stand to gain the most from AI and automation in cybersecurity. These include financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies, as these sectors handle substantial amounts of sensitive data.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI and automation offer exciting possibilities for enhancing cybersecurity, their implementation comes with inherent challenges. Blindly adopting these technologies without careful consideration can lead to unforeseen vulnerabilities and ethical dilemmas. A proactive approach, understanding potential pitfalls, and prioritizing human oversight are crucial for successful integration.
Potential Implementation Challenges
The transition to AI-powered security necessitates significant infrastructure adjustments and resource allocation. Organizations must evaluate their existing security infrastructure, identify data silos, and invest in the necessary hardware and software to support the new technologies. This process requires careful planning, budgeting, and the allocation of skilled personnel to manage the transition effectively. Furthermore, the integration of AI systems with existing security tools and protocols can be complex, requiring careful configuration and testing to avoid conflicts and disruptions.
Successfully implementing AI in security requires a thorough understanding of the entire ecosystem, from data collection to threat analysis.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Biases
AI systems, particularly those trained on historical data, can inherit and perpetuate biases present in the data. This can lead to inaccurate threat detection or even discrimination against certain groups. For example, a facial recognition system trained primarily on images of a specific demographic might perform poorly on individuals from other groups. Ethical considerations, therefore, require careful attention to the data used for training and ongoing monitoring of the system’s performance across diverse populations.
Continuous auditing and adjustments to the training data are crucial to mitigate potential biases.
Importance of Human Oversight in AI-Driven Systems
AI systems, while powerful, are not infallible. Human oversight is essential to validate AI-generated alerts, interpret complex threat patterns, and make critical decisions in ambiguous situations. Human analysts bring contextual understanding and judgment that AI systems lack. This collaborative approach, combining AI’s speed and analytical capabilities with human intuition and critical thinking, ensures more effective and comprehensive security.
A system relying solely on AI for decision-making is inherently vulnerable.
Training and Development of Cybersecurity Professionals
The emergence of AI in cybersecurity necessitates a shift in the skills needed for cybersecurity professionals. Existing professionals need ongoing training and development to understand how AI tools function, interpret their outputs, and integrate them into their workflows. New cybersecurity roles focused on AI management and oversight will also emerge. Continuous learning and adaptation are vital to maintain a competitive edge in this evolving field.
This includes training in data analysis, machine learning principles, and ethical considerations surrounding AI.
Protecting AI Systems from Cyberattacks
AI systems themselves are susceptible to cyberattacks. Malicious actors can attempt to manipulate or compromise AI algorithms to produce false positives, mask malicious activities, or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Robust security measures, including intrusion detection systems, access controls, and regular security audits, are necessary to safeguard these systems from attacks. This includes hardening the infrastructure supporting the AI, encrypting sensitive data, and implementing secure coding practices for AI development.
Protecting the AI systems is as important as protecting the data they are designed to secure.
Concluding Remarks: Why Ai And Automation Offer Hope For Cybersecurity
In conclusion, AI and automation are not just tools; they are the catalysts for a new era in cybersecurity. By leveraging the power of these technologies, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, predict and prevent attacks, and respond to incidents more effectively. While challenges and ethical considerations remain, the potential benefits of AI and automation are undeniable, offering hope for a future where cybersecurity is a proactive, rather than reactive, endeavor.




