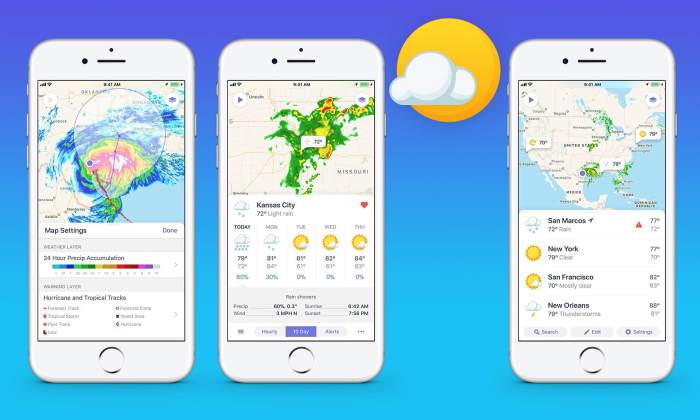
Weather up atlas calendar event forecast price is a comprehensive guide exploring how weather impacts various aspects of our lives, from planning events to predicting price fluctuations. This deep dive into weather forecasting, visualization, and integration with calendars will help you understand how to make informed decisions in a world affected by ever-changing conditions.
We’ll examine the different types of weather forecasts, how they are generated, and how their accuracy varies across time scales. We’ll see how an atlas can visualize weather patterns geographically, how a calendar can integrate these forecasts to help schedule events, and how these tools can be used to anticipate and adapt to weather-related price changes.
Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts are essential for a multitude of activities, from planning outdoor events to ensuring the safety of travelers. Understanding how these predictions are generated and the limitations involved is crucial for using them effectively. Different types of forecasts cater to varying needs, offering insights into the weather at different scales and time horizons.
Types of Weather Forecasts, Weather up atlas calendar event forecast price
Weather forecasts are categorized based on the time period they cover and the geographic area they encompass. Short-term forecasts provide predictions for a few hours to a few days, while long-term forecasts extend to several weeks or even months. Regional forecasts concentrate on a specific geographic area, like a state or country, while global forecasts cover the entire Earth.
These diverse types address various needs, from local farmers planning their crops to global airline companies routing their flights.
Methods for Generating Weather Forecasts
Generating weather forecasts involves sophisticated methods. Numerical weather prediction (NWP) is a common approach. NWP uses complex computer models to simulate the atmosphere’s behavior based on initial conditions and physical laws. Statistical models are also employed, combining historical weather data with statistical techniques to predict future conditions. These methods, while powerful, have inherent limitations due to the complexity of the atmosphere and the inherent uncertainties in initial conditions.
Common Elements in Weather Forecast Formats
Weather forecasts, regardless of the specific type, often include similar elements. A typical forecast will specify the expected temperature, precipitation (rain, snow, etc.), wind speed and direction, and any potential severe weather events. Additionally, forecasts typically include the time period covered by the prediction, such as “today,” “this weekend,” or “next week.” The inclusion of these consistent elements ensures clarity and accessibility for users.
Accuracy Comparison of Forecast Types
| Forecast Type | Short-Term (0-3 days) | Medium-Term (3-10 days) | Long-Term (10+ days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional | Generally high accuracy | Moderate accuracy | Low accuracy |
| Global | Moderate accuracy | Lower accuracy than regional | Very low accuracy |
The table above demonstrates the general trend in forecast accuracy across different time horizons and geographic scales. Short-term forecasts are usually more accurate due to better understanding of atmospheric conditions. As the time horizon extends, the accuracy degrades, reflecting the increasing complexity and uncertainties in the atmospheric system.
Factors Influencing Forecast Accuracy
Several factors impact the accuracy of weather forecasts. Initial conditions, representing the state of the atmosphere at the start of the forecast period, are crucial. Even small errors in these conditions can propagate and lead to significant inaccuracies in the forecast. The complexity of the atmosphere, with its diverse and interconnected processes, poses a challenge. Unforeseen weather events, like sudden shifts in pressure systems, can also disrupt the accuracy of forecasts.
The sophistication of the models used, along with the computing power available, significantly influence the accuracy and reliability of the forecasts.
Atlas and Calendar Integration
Integrating weather data into an atlas and calendar offers a powerful tool for planning and preparation. By visualizing weather patterns geographically and scheduling activities based on forecasts, individuals and organizations can optimize their time and resources. This approach can be particularly beneficial for outdoor activities, travel planning, and agricultural practices.
Visualizing Weather Patterns Geographically
An atlas, especially one with interactive features, can display weather patterns in a visually compelling way. Color-coded maps can illustrate temperature variations, precipitation zones, and wind patterns across a region. For instance, a map highlighting areas with high heat indices could be overlaid with a layer indicating the probability of thunderstorms. This visual representation allows users to quickly understand the spatial distribution of weather phenomena.
Scheduling Activities Based on Weather Predictions
Calendars can be enhanced by incorporating weather forecasts. This feature enables users to schedule outdoor activities, such as hiking or gardening, considering the expected weather conditions. If a user has a scheduled camping trip, they can check the weather forecast for the destination and adjust their packing list or even reschedule the trip if severe weather is anticipated.
Similarly, farmers can plan their planting and harvesting schedules based on projected rainfall and temperature data.
Checking the weather up Atlas calendar event forecast price is crucial, but sometimes I get sidetracked. Like, I was just researching the gboard split keyboard returns here and realized how much I need to know the upcoming event prices to plan my outings. Knowing the forecast is still key to making the best choices for outdoor events, though.
Examples of Weather Data Integration into a Calendar
A calendar event for a picnic could include a weather forecast for the specific location and date. This information could be presented as a visual graphic or a short text summary. Alternatively, a travel itinerary could be synced with a weather atlas to show expected conditions along the route. This feature could also display the likelihood of delays or cancellations due to adverse weather.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Calendar Weather Integration
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved planning and decision-making | Potential for over-reliance on predictions |
| Reduced risk of unpleasant weather surprises | Data accuracy and reliability can vary |
| Enhanced efficiency and resource optimization | Increased complexity in calendar interface |
| Increased awareness of weather patterns | Potential for user confusion with excessive data |
| Support for informed decisions in various sectors (tourism, agriculture, etc.) | Requires integration of multiple data sources and accurate data updates |
Informing Calendar Event Planning with Weather Data
Weather data from an atlas can significantly inform calendar event planning. For instance, a user planning a marathon in a mountainous region can use an atlas to identify areas prone to fog or high winds. This information, coupled with the calendar’s weather forecast, allows for adjustments to the event’s route or timing. Knowing the likelihood of rain or extreme temperatures enables proactive measures, such as setting up backup plans or providing appropriate gear recommendations to participants.
Similarly, a user planning a sailing trip can use the atlas to identify areas with strong currents and high wave predictions. This information, combined with the calendar’s weather forecast, allows for the adjustment of the sailing plan to minimize risk.
Event Forecasting: Weather Up Atlas Calendar Event Forecast Price

Weather forecasts are invaluable tools for event organizers, enabling them to anticipate and mitigate potential disruptions caused by adverse weather conditions. Accurate predictions allow for proactive planning, minimizing risks and maximizing the enjoyment of the event for attendees. By understanding the potential impact of various weather scenarios, organizers can make informed decisions regarding logistics, safety measures, and contingency plans.Accurate weather forecasting empowers event organizers to make informed decisions, proactively addressing potential problems.
This proactive approach not only enhances the safety and enjoyment of attendees but also minimizes financial losses and reputational damage.
Checking the weather up Atlas calendar for event forecasts and pricing is always a good idea, especially with the unpredictable nature of the weather. Interestingly, a recent discovery shows that the Pixel 6 is already being displayed at Google’s NYC store, pixel 6 already display googles nyc store which is a great sign for those planning their shopping trips.
This all helps in understanding the broader picture, and ultimately helps me decide when to check for the latest weather up Atlas calendar event forecast price updates.
Methods for Assessing Weather Disruption
Several methods are used to evaluate the potential disruption of weather on scheduled events. These range from simple qualitative assessments to complex quantitative models. A combination of these methods often yields the most reliable predictions. Qualitative assessments involve examining historical weather data for similar events, considering geographic location, and analyzing the specific weather patterns predicted. Quantitative methods use mathematical models to predict the likelihood and severity of weather events.
These methods often utilize sophisticated algorithms and large datasets to produce detailed forecasts.
Examples of Adjusting Plans Based on Forecasts
Event organizers can adapt their plans in numerous ways to account for potential weather disruptions. For instance, if a rain forecast is issued for a planned outdoor concert, organizers might move the event to an indoor venue, set up temporary shelters, or postpone the event to a later date. A sporting event might require adjusting playing times or moving the location to a covered facility.
Similarly, if a severe storm is predicted, organizers may implement safety protocols such as evacuations or crowd control measures.
Contingency Measures for Various Events
| Event Type | Potential Weather Conditions | Contingency Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Concert | Heavy Rain, Thunderstorms | Move event to indoor venue, provide temporary shelters, reschedule, postpone |
| Outdoor Sporting Event | High Winds, Heavy Snow | Adjust playing times, relocate to indoor facility, postpone or cancel, implement safety protocols |
| Festival | Extreme Heat, Severe Storms | Provide water stations, relocate activities to shaded areas, adjust schedules, implement emergency response plans |
| Outdoor Wedding | Heavy Rain, Strong Winds | Provide tents or indoor alternatives, adjust ceremony and reception schedules, postpone or cancel |
Potential Weather Risks for Outdoor Events
Identifying potential weather-related risks is crucial for effective planning. A comprehensive list of potential risks should consider various scenarios.
- Rain: Heavy downpours can lead to waterlogged grounds, impacting the safety of attendees and disrupting the flow of the event. This includes possible cancellation or postponement of the event.
- Strong Winds: High winds can cause damage to structures, equipment, and even personal safety. This includes the potential for equipment failure, venue damage, and attendee injury.
- Extreme Temperatures: Excessive heat or cold can impact attendee comfort and health. Extreme heat can lead to heat exhaustion or heat stroke, while extreme cold can lead to hypothermia. This requires provisions for attendee safety and event adjustments.
- Lightning: Lightning poses a serious safety risk during outdoor events. Event organizers need to have procedures in place to identify and avoid lightning strikes, and to advise attendees on safety protocols.
- Severe Storms: Storms can bring hail, tornadoes, and flooding, creating major disruptions to events. Event organizers need to have contingency plans to address these extreme weather events.
Price Impacts
Weather significantly impacts the cost of goods and services, affecting everything from agricultural produce to transportation. Understanding these effects is crucial for businesses and consumers alike, as it allows for better planning and adaptation to changing market conditions. The unpredictable nature of weather anomalies makes accurate forecasting of price changes an essential tool for navigating the economic landscape.The interplay between weather patterns and market prices is complex.
Extreme weather events, like droughts, floods, or intense heat waves, can disrupt supply chains, leading to shortages and price hikes. Conversely, favorable weather conditions can increase yields, potentially lowering prices. The impact is not uniform across all products, and the specific effects vary based on the type of product, the region, and the severity of the weather event.
Impact of Weather on Agricultural Products
Agricultural products are particularly vulnerable to weather fluctuations. Droughts can drastically reduce crop yields, leading to shortages and subsequently higher prices. Conversely, excessive rainfall can also damage crops, impacting the quantity available for market. These disruptions ripple through the supply chain, affecting processing facilities and retailers, ultimately impacting consumer prices. For example, a severe drought in a major wheat-producing region can cause a significant rise in bread prices due to reduced supply.
Similarly, floods can damage livestock, leading to price increases for meat products.
Impact of Weather on Transportation Costs
Weather conditions directly influence transportation costs. Heavy snowstorms, for instance, can halt road traffic, delaying deliveries and increasing transportation costs. Extreme heat can damage infrastructure, increasing repair costs and potentially disrupting supply chains. In these situations, logistics companies often need to implement alternative routes or strategies, which adds to the overall transportation expense. For instance, severe winter weather can significantly impact the cost of transporting perishable goods, as delays can lead to spoilage and loss.
Checking the weather up Atlas calendar for event forecasts and prices is always a good idea. Knowing the price fluctuations and potential events can help you plan accordingly. This week, though, I’m also excited about the upcoming Lamborghini Lanzador EV, which is slated to have a lamborghinis lanzador ev will have a significant impact on the automotive market.
Hopefully, this doesn’t affect the overall weather up Atlas calendar event forecast price too much. Let’s see how it plays out!
Impact of Weather on Energy Prices
Weather patterns play a crucial role in energy demand. Cold snaps, for example, increase energy consumption for heating, leading to higher electricity prices. Conversely, extremely hot weather can drive up demand for air conditioning, also contributing to higher energy costs. Weather forecasts can be utilized to predict energy demand fluctuations, allowing utilities to adjust their production schedules and potentially mitigate price spikes.
Predicting Price Changes Using Weather Forecasts
Weather forecasts provide valuable insights into potential price fluctuations. By anticipating potential weather anomalies, businesses can prepare for supply chain disruptions and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly. For example, if a forecast predicts a severe drought in a major agricultural region, producers can start looking for alternative sources of supply or implement strategies to conserve water. This anticipatory approach can help mitigate the negative impact of extreme weather on prices.
Table Comparing Weather Event Impacts
| Weather Event | Agricultural Products (e.g., Wheat) | Transportation Costs (e.g., Trucking) | Energy Prices (e.g., Electricity) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drought | Reduced yield, higher prices | Increased fuel consumption, higher costs | Increased demand, potentially higher prices |
| Flood | Crop damage, higher prices | Road closures, delays, higher costs | No direct impact, but indirectly can affect demand |
| Severe Cold Snap | No direct impact, but increased demand for heating | Increased fuel consumption, higher costs | Increased demand, potentially higher prices |
Role of Supply Chains in Price Fluctuations
Supply chains act as conduits for weather-related price fluctuations. When weather events disrupt production or transportation, the effects propagate through the supply chain, impacting various stages from the farm to the consumer. A disruption at one point can trigger a cascade of price increases along the entire chain. For example, a flood in a region producing a crucial component for electronics manufacturing can lead to shortages, triggering price hikes for the finished products.
Supply chain resilience and adaptability are crucial in mitigating the impact of weather-related price volatility.
Visualizations
Weather patterns, agricultural prices, and event planning are intricately linked. Visual representations are crucial for understanding these connections and predicting future trends. Effective visualizations can highlight patterns, correlations, and potential risks, empowering informed decision-making across various sectors.
Atlas-Style Map of Regional Weather Patterns
Visualizing weather patterns across a region using an atlas-style map is a powerful tool. The map should display different weather parameters, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind speed, over a specific geographic area. Color-coding or gradient shading can be used to represent variations in each parameter, enabling quick visual comparisons and identification of regional differences. For instance, a red hue could highlight high-temperature zones, while a blue hue could indicate areas experiencing heavy rainfall.
Such a visualization is highly beneficial for farmers in understanding regional weather impacts on crops.
Correlation Graph Between Weather and Agricultural Product Prices
A graph showcasing the correlation between weather patterns and agricultural product prices is essential. This graph can plot the price of a particular crop against various weather indicators like temperature, rainfall, and sunshine hours over a defined period. A scatter plot, for example, can visually demonstrate the relationship. Points clustered closely along a line would suggest a strong correlation, while points scattered randomly would indicate a weak or non-existent correlation.
A positive correlation would be indicated by higher prices correlating with hotter temperatures or lower rainfall in certain regions, whereas negative correlations would indicate a reverse relationship.
Diagram of Weather Data Integration into Calendar Event Planning
A diagram illustrating the integration of weather data into a calendar event planning process is valuable. This diagram should depict a workflow that incorporates weather forecasts into event scheduling. For instance, a flow chart might start with a weather forecast input, followed by an analysis of the forecast’s impact on the event (e.g., potential rain delays). Subsequent steps would include contingency planning, event rescheduling if necessary, and communication of any changes to attendees.
The diagram should clearly show how weather data influences each step in the event planning process.
Chart Illustrating Weather Type Impact on Event Attendance
A chart illustrating the impact of different weather types on event attendance is a useful tool. The chart should categorize different weather types (e.g., sunny, rainy, windy, snowy) and display the corresponding average attendance rates for events held under those conditions. This data can be collected from historical event records. The chart could use bar graphs, line graphs, or pie charts to represent the data.
For example, a chart might show significantly lower attendance for events held during periods of heavy rain compared to sunny days.
Timeline of Weather and Price Fluctuations for a Specific Product
A timeline displaying the historical relationship between weather and price fluctuations for a specific product, like wheat, is a valuable tool for trend analysis. The timeline should plot the price of wheat over a certain period (e.g., 10 years) and overlay it with weather data, such as rainfall and temperature data. This visual representation allows for a clear understanding of how weather events have impacted wheat prices historically.
Data points that align with extreme weather events (droughts, floods) would be particularly noticeable.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding weather up atlas calendar event forecast price empowers us to plan more effectively, mitigate risks, and make better decisions based on anticipated conditions. By combining sophisticated forecasting with visualization and calendar integration, we can anticipate the impact of weather on our events and even the prices of goods and services. The information presented here is designed to help you anticipate and adapt to the ever-changing weather landscape.