Toyota eyes china for its own version of full self driving – Toyota eyes China for its own version of full self-driving, setting the stage for a fascinating exploration of the company’s strategy in the world’s largest auto market. Toyota’s current presence in China, its historical relationship with the Chinese market, and recent announcements about autonomous driving technology will be examined. The potential motivations for developing a China-specific autonomous driving system, alongside comparisons to Toyota’s approach in other markets, will be explored.
This includes potential partnerships and collaborations for this cutting-edge technology.
This in-depth look delves into the current state of full self-driving technology adoption in China, considering the regulatory landscape and the challenges and opportunities involved. The role of infrastructure development, comparisons with other countries’ technological advancements, and the impact of government policies will be discussed. Finally, Toyota’s potential China-specific approach, including potential strategies, benefits, drawbacks, and cultural considerations, will be evaluated, alongside successful localization strategies in other industries.
Toyota’s Strategy in China

Toyota’s presence in the vast and dynamic Chinese automotive market is substantial, marked by a long history of adaptation and a commitment to navigating the complexities of this key global market. The company’s recent announcements about developing a dedicated autonomous driving system tailored for China suggest a strategic shift, potentially reflecting a nuanced understanding of the unique opportunities and challenges presented by the Chinese market.Toyota’s sustained investment and growth in China underscore its recognition of the significant potential within the country’s burgeoning automotive sector.
Their strategic approach seems to be a blend of adapting to local preferences while also leveraging their global expertise.
Toyota’s Current Presence and Market Share in China
Toyota enjoys a prominent position in the Chinese market, holding a significant market share. Their extensive dealer network and established brand recognition contribute to their strong presence. Specific market share figures fluctuate, but Toyota consistently ranks among the top automakers in China, demonstrating a considerable foothold in the country.
Toyota’s Historical Relationship with the Chinese Automotive Market
Toyota’s journey in China has been characterized by a long-term commitment to the market, including substantial investments in manufacturing facilities and joint ventures. This historical engagement reflects a recognition of the country’s growing economic power and its pivotal role in the global automotive landscape. Early ventures focused on building local production capacity and adapting models to meet Chinese consumer preferences.
Toyota’s Recent Announcements and Statements Regarding Autonomous Driving Technology
Recent statements from Toyota suggest a commitment to developing autonomous driving technologies tailored for specific markets, including China. These announcements highlight a potential shift towards a more regionally focused approach to autonomous driving development, acknowledging that local regulations, infrastructure, and consumer preferences might necessitate unique solutions. Notably, they have not yet disclosed precise technical specifications or timelines for this China-specific autonomous driving program.
Toyota’s Potential Motivations for Developing a China-Specific Autonomous Driving System
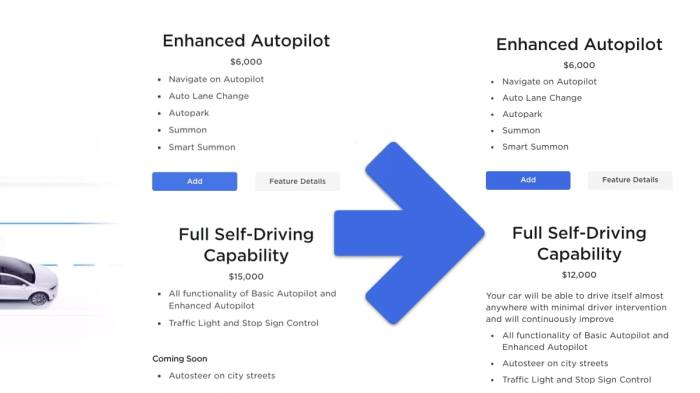
Several factors likely motivate Toyota to develop a China-specific autonomous driving system. The growing demand for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous features in China could drive the need for a system tailored to specific local conditions. Regulatory differences, infrastructure specifics, and unique consumer expectations could further necessitate a customized approach. This approach allows Toyota to effectively respond to local demands, potentially differentiating their offerings from competitors.
Comparison of Toyota’s Approach to Autonomous Driving Development in China with its Approach in Other Markets
Toyota’s approach in China may differ from its strategy in other markets. For instance, the regulatory landscape, technological infrastructure, and consumer preferences in China could vary considerably from other countries. This variation likely necessitates a distinct development strategy. Their strategy in China may involve a collaborative approach, integrating input from local partners, and focusing on adapting technology to meet unique market requirements.
This potentially includes navigating the intricacies of Chinese infrastructure and regulations.
Toyota’s looking to China for its own take on full self-driving, which is pretty interesting. While they’re focusing on that, don’t forget to check out some of the surprising health benefits of Halloween treats like pumpkins! This article highlights how even those seasonal goodies can be good for you. Ultimately, though, Toyota’s China-focused self-driving initiative is a significant development in the automotive industry.
Potential Partnerships and Collaborations in China for This Technology
Toyota’s potential collaborations in China could involve partnerships with local technology companies, government entities, or other automotive manufacturers. These partnerships could leverage local expertise, facilitate access to necessary resources, and enable the rapid development and deployment of the autonomous driving system in the Chinese market. Examples of such collaborations in other sectors showcase the benefits of integrating local knowledge and expertise into global projects.
A strong partnership network can expedite the development process and enhance the technology’s overall effectiveness in the Chinese market.
Full Self-Driving Technology in China
Toyota’s foray into the Chinese market, including their development of a localized version of full self-driving technology, reflects the immense potential and challenges presented by the Chinese automotive sector. The country’s rapid technological advancements and substantial infrastructure development are driving a burgeoning demand for autonomous driving features. However, navigating the complexities of the regulatory environment and consumer acceptance remains crucial for success.The current state of full self-driving technology in China is marked by significant progress but also notable limitations.
Pilot programs and limited-functionality autonomous features are becoming increasingly prevalent in specific areas, indicating a growing awareness and interest in the technology. However, widespread adoption is still nascent, largely due to ongoing regulatory considerations and the necessity for further infrastructure development.
Current State of Adoption
China has witnessed a steady rise in the development and deployment of autonomous driving features. This has been driven by a combination of government incentives, private investment, and technological advancements. While specific models and levels of autonomy vary, companies are actively exploring and implementing Level 2 and 3 autonomous driving systems in certain vehicles. This includes features like adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assist, and automated parking.
However, fully autonomous driving, often categorized as Level 4 or 5, remains largely experimental and restricted to limited areas.
Regulatory Landscape
China’s regulatory landscape for autonomous vehicles is evolving rapidly. The government has implemented a series of policies and regulations to foster innovation and safety in this emerging technology. These regulations generally aim to balance the need for innovation with the requirement for stringent safety standards and public confidence. Specific requirements concerning data privacy, vehicle testing procedures, and liability in case of accidents are actively being defined.
The government’s focus on safety and public acceptance will be critical in shaping the future of autonomous vehicles in the country.
Challenges and Opportunities
Introducing full self-driving technology in China presents both significant challenges and promising opportunities. The vastness of the country and the diversity of road conditions present unique testing and deployment obstacles. Furthermore, public acceptance and trust in the technology are crucial for successful adoption. Addressing these issues will require ongoing efforts from both the government and the private sector to foster trust and confidence in the technology.
Conversely, the immense market size and the rapidly developing infrastructure offer substantial opportunities for companies to introduce and implement innovative solutions. The potential for creating a comprehensive autonomous driving ecosystem is considerable.
Infrastructure Development
The development of robust infrastructure is essential to support the implementation of full self-driving technology. This includes the integration of intelligent transportation systems, the establishment of standardized road markings and traffic signals, and the creation of robust communication networks for vehicles. The availability of high-quality, reliable, and consistent infrastructure will be a key factor in determining the success of full self-driving technology.
Improvements in real-time traffic data collection and distribution will allow autonomous vehicles to navigate complex traffic conditions more efficiently.
Comparison with Other Countries
China’s technological advancements in full self-driving are rapidly catching up with those of other leading countries. While the US and Europe have a longer history of research and development, China’s emphasis on large-scale deployment and infrastructure development is creating a unique dynamic. China’s focus on the practical application of the technology, coupled with its vast market, is creating a compelling environment for innovation and competition.
The comparison highlights the unique advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
Potential Impact of Government Policies
Government policies play a critical role in shaping the adoption of full self-driving technology in China. Incentives for research and development, supportive regulations, and investment in infrastructure will all contribute to the development and adoption of this technology. The policies can influence the rate of adoption, the types of autonomous features that become prevalent, and the overall public perception of the technology.
The government’s strategic vision will significantly influence the future trajectory of autonomous vehicles in China.
Toyota’s China-Specific Approach
Toyota’s entry into the Chinese market for full self-driving technology necessitates a nuanced approach. The sheer size and complexity of the Chinese market, coupled with its unique technological landscape and cultural nuances, demand a tailored strategy to achieve success. This strategy must go beyond simply replicating existing global models.The Chinese market presents both opportunities and challenges for Toyota’s full self-driving ambitions.
Government support for autonomous vehicle development, a burgeoning middle class with a growing interest in advanced technologies, and the country’s massive infrastructure create favorable conditions. However, competition is fierce, regulatory frameworks are still evolving, and cultural expectations about technology adoption require careful consideration.
Potential Strategy for Developing and Introducing Full Self-Driving Technology in China
Toyota can leverage its existing presence and strong brand recognition in China to establish a localized full self-driving system. This could involve partnering with Chinese tech companies for localized data collection, development, and manufacturing. A key aspect of this approach is adapting the technology to specific Chinese road conditions, traffic patterns, and infrastructure limitations. Furthermore, integrating the system with existing Chinese navigation and mapping systems will be crucial.
By building trust and fostering a positive relationship with the Chinese market, Toyota can address any regulatory hurdles more effectively.
Comparison of Potential Toyota Strategy with Competitors
| Feature | Toyota | Tesla | Baidu |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localization Strategy | Partner with Chinese tech companies, adapt to local conditions | Limited localization, prioritizing global standardization | Strong emphasis on local data and infrastructure integration |
| Data Collection Focus | Emphasis on Chinese road conditions and traffic patterns | Global data collection, potentially less focused on Chinese specifics | Leveraging massive amounts of Chinese data |
| Manufacturing Approach | Potentially establish joint ventures for manufacturing in China | Manufacturing in China but less localized than some competitors | Significant manufacturing presence in China |
| Regulatory Compliance | Proactive engagement with Chinese authorities, focusing on regulatory alignment | Potentially slower adaptation to evolving regulations | Close ties with Chinese authorities |
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of a Localized Full Self-Driving System in China
- Benefits: A localized system can better adapt to China’s unique road conditions, traffic patterns, and infrastructure, potentially improving safety and efficiency. This tailored approach can build stronger trust and a positive reputation within the Chinese market. The localized system can also contribute to China’s broader autonomous vehicle ecosystem.
- Drawbacks: Developing a localized system requires significant investment in resources and time. There is also a risk that local regulations or technological standards could change, potentially impacting the system’s long-term viability. Maintaining compatibility across multiple platforms and regions might present a challenge.
Successful Localization Strategies in Other Industries in China
- Example 1: Mobile Phone Manufacturers: Companies like Xiaomi and Huawei have successfully adapted their products and services to Chinese preferences by tailoring their software and user interfaces. They understand the cultural context and consumer preferences, which are key to their success.
- Example 2: E-commerce Platforms: Alibaba and JD.com have successfully adapted their platforms to meet the specific needs of Chinese consumers. This includes features like mobile payment integration and tailored logistics solutions. They have established a strong user base through localized strategies.
Potential Impact on Toyota’s Global Image
A successful localization strategy in China could significantly enhance Toyota’s image as a company that understands and responds to local market needs. It could also attract more investment and attention from global markets. Conversely, a poorly executed localization strategy could damage Toyota’s reputation and brand image.
Cultural Considerations Influencing the Success of a Localized Approach
Understanding and respecting Chinese cultural norms and values are crucial for success. This includes adapting marketing campaigns, product features, and customer service to align with local customs. For example, focusing on safety and reliability, aspects that resonate strongly in the Chinese market, is essential.
Potential Market Impact: Toyota Eyes China For Its Own Version Of Full Self Driving
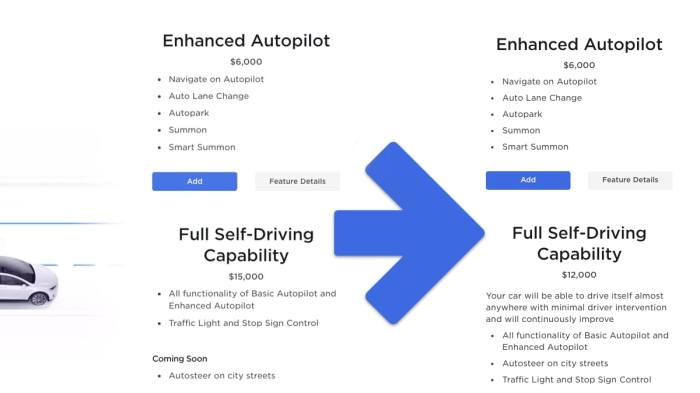
Toyota’s foray into full self-driving technology in China promises a significant shift in the automotive landscape. The move reflects a calculated strategy to capitalize on the burgeoning Chinese market and its rapidly evolving consumer preferences. This analysis explores the potential market response, focusing on consumer behavior, competitive reactions, and the broader implications for the Chinese automotive industry.The Chinese market is particularly receptive to innovative technologies, and Toyota’s commitment to full self-driving could generate substantial consumer interest.
Early adoption rates, especially among tech-savvy millennials and Gen Z, are expected to be high, potentially influencing broader market trends.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences
Consumer response to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving features has been overwhelmingly positive in other markets. In China, where the middle class is expanding rapidly and technological adoption is high, this positive response is anticipated to be even more pronounced. Increased convenience and safety are expected to be key drivers for consumer adoption. Consumers may prioritize features like hands-free driving, parking assistance, and enhanced safety capabilities when making purchasing decisions.
Toyota’s focusing on China for its own self-driving tech, which is pretty interesting. Speaking of interesting, if you’re looking for some spooky movies to stream this Halloween, check out these are best spooky movies stream halloween. It seems like a logical move for Toyota to target the massive Chinese market for their self-driving ambitions.
This will likely lead to a higher premium being placed on vehicles with such advanced features, impacting the overall price range for vehicles.
Potential Competitors and Their Reactions
Major competitors like Tesla, BMW, and local Chinese brands like BYD and NIO will likely react to Toyota’s initiative. They might respond by introducing their own full self-driving packages, potentially adjusting pricing strategies or launching aggressive marketing campaigns. Some may seek collaborations or partnerships to accelerate their development and market penetration in the sector. Competition in this space will intensify, pushing companies to innovate and deliver compelling value propositions.
Long-Term Effects on the Chinese Automotive Market
Toyota’s move will likely accelerate the adoption of full self-driving technology in the Chinese automotive market. This will trigger a domino effect, driving innovation and forcing other players to adapt. The Chinese automotive market will become a testing ground for advanced driver-assistance systems, leading to potential improvements in road infrastructure and safety standards. The emergence of a competitive landscape could lead to more competitive pricing and wider availability of such technologies.
Impact on Jobs and Employment
The transition to fully autonomous vehicles will likely lead to shifts in job roles within the automotive industry. While some jobs in traditional vehicle manufacturing might be lost, new roles in software development, AI engineering, and autonomous vehicle maintenance will emerge. China’s large and skilled workforce will play a crucial role in adapting to these changes. Governments and educational institutions will need to proactively adapt their training programs to meet the changing needs of the market.
Comparison with Other Industry Trends in China
Toyota’s full self-driving initiative aligns with broader trends in China, such as the government’s emphasis on technological advancement and the increasing demand for smart and connected vehicles. The rise of e-commerce and digital services is also influencing consumer expectations, driving the need for innovative features like autonomous driving. The convergence of these trends will likely accelerate the transformation of the automotive industry in China.
Technological Aspects
Toyota’s foray into China’s autonomous driving market necessitates a deep understanding of the region’s unique technological landscape. This involves careful consideration of existing infrastructure, potential regulatory hurdles, and the specific needs of Chinese drivers. The company must develop a system that balances cutting-edge technology with adaptability to the particularities of the Chinese market.
Specific Technologies for a China-Focused System
Toyota’s China-specific full self-driving system will likely leverage a suite of advanced technologies. These technologies will likely include sophisticated sensor fusion, incorporating data from multiple sources like LiDAR, radar, and cameras. The precise configuration will depend on Toyota’s assessment of optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in the Chinese environment.
Potential Advancements in Autonomous Driving
Significant advancements are anticipated in autonomous driving technology. These include improvements in sensor accuracy, particularly in challenging environments like urban congestion and varying weather conditions. Further developments in AI algorithms will enable more sophisticated real-time decision-making, leading to smoother and safer driving experiences. For example, advancements in deep learning could enhance object recognition and predictive modeling, allowing for proactive responses to potential hazards.
Key Technological Components
A robust full self-driving system requires several crucial components. These components include high-resolution mapping systems, capable of capturing and updating detailed information about the Chinese road network. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) will form the foundation for gradual integration of autonomy. Robust communication systems will be essential for enabling vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, facilitating seamless interaction with other vehicles and infrastructure.
Integration with Existing Chinese Infrastructure
Toyota’s system must be compatible with China’s existing infrastructure. This includes adapting to diverse road conditions, traffic patterns, and regulatory frameworks. For instance, integration with existing traffic light systems and road markings is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Moreover, the system will need to account for potential variations in infrastructure quality across different regions of China.
Toyota’s focus on China for its own self-driving tech is intriguing. It seems like a smart move, considering the massive market there. Interestingly, this development might be spurred by advancements in software development, like Microsoft’s recent announcement of Visual Studio coming to macOS. Microsoft Visual Studio coming to Mac could potentially streamline the creation of the complex algorithms needed for autonomous vehicles.
This could ultimately speed up Toyota’s progress in bringing its own self-driving cars to market in China.
Table of Key Technological Considerations
| Component | Description | China-Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Sensors (LiDAR, Radar, Cameras) | Detect and perceive the surrounding environment | Need to be robust in diverse weather conditions and lighting, especially prevalent in urban areas. |
| Mapping Systems | Create and maintain high-resolution maps | Must account for varying road conditions, infrastructure updates, and unique traffic patterns. |
| AI Algorithms | Process sensor data and make driving decisions | Needs to adapt to diverse traffic behaviors and cultural factors. |
| V2X Communication | Enable communication between vehicles and infrastructure | Must be compatible with China’s existing V2X standards and infrastructure. |
| Safety Systems | Implement redundant safety mechanisms | Compliance with stringent Chinese safety regulations is paramount. |
Limitations and Potential Solutions
Current autonomous driving technology faces limitations, such as the complexity of handling unexpected events and the need for continuous data updates. Solutions to these limitations include ongoing development of more robust AI algorithms and improved sensor technologies. Further research and development efforts are needed to create a fully reliable and adaptable autonomous driving system that meets the diverse conditions of China’s road network.
For example, the development of algorithms capable of adapting to unusual driving situations, such as sudden lane changes by motorcycles, is a crucial area of focus.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Navigating the autonomous vehicle landscape in China presents a unique set of regulatory and legal challenges for Toyota. The country’s evolving legal framework for autonomous driving systems, coupled with its specific approach to technology adoption, requires careful consideration. Toyota must understand the potential hurdles and risks, and develop strategies to mitigate them. A comprehensive understanding of the regulatory environment is critical for successful market entry and long-term viability.The Chinese government is actively developing and implementing regulations for autonomous vehicles.
This includes establishing safety standards, data privacy policies, and liability frameworks. Toyota needs to proactively engage with these evolving regulations to ensure its full self-driving system aligns with Chinese legal requirements and expectations.
Relevant Regulations and Legal Frameworks
China’s regulations for autonomous vehicles are still under development. Existing laws and regulations concerning road safety, transportation, and data security are being adapted to accommodate the increasing complexity of autonomous driving technology. Specific regulations related to the testing, deployment, and operation of autonomous vehicles are emerging, creating a dynamic regulatory environment.
Potential Legal Hurdles and Risks, Toyota eyes china for its own version of full self driving
One major hurdle is the lack of a comprehensive legal framework specifically tailored to full self-driving systems. This creates ambiguity regarding liability in case of accidents involving autonomous vehicles. Determining fault in incidents where human intervention is minimal poses significant legal challenges. Furthermore, data privacy regulations and security requirements for the collection and use of vehicle data need to be carefully addressed.
Similar challenges have emerged in other countries, such as the US and Europe, highlighting the global nature of these issues.
Toyota’s Navigational Strategy
To navigate this complex landscape, Toyota needs a multi-faceted approach. This includes actively participating in regulatory discussions and consultations, collaborating with government agencies and industry stakeholders, and establishing robust safety protocols and data security measures. Examples of companies successfully navigating similar regulatory environments include those in the aviation and aerospace industries, which often face stringent safety and security regulations.
Their strategies, including rigorous testing and safety protocols, can serve as a valuable model for Toyota.
Impact of Legal Disputes or Safety Concerns
Legal disputes or safety concerns stemming from autonomous vehicle accidents could have a significant impact on public perception and market acceptance. Negative publicity and public distrust could hinder Toyota’s ability to gain consumer trust and market share. The public’s reaction to incidents involving autonomous vehicles is often emotionally charged, making damage control essential. Companies in other industries, like pharmaceuticals or nuclear energy, have learned the importance of managing public perception during crises.
Timeline of Regulatory Developments and Toyota’s Potential Response
| Regulatory Development | Potential Toyota Response |
|---|---|
| Drafting of specific regulations for autonomous driving | Engage with regulatory bodies, provide input, and adapt technology to comply. |
| Implementation of safety standards for autonomous vehicles | Invest in rigorous testing and safety protocols, partnering with Chinese testing centers. |
| Establishment of data privacy and security policies | Implement robust data encryption and security measures, comply with Chinese data privacy laws. |
| Formulation of liability frameworks | Develop clear protocols for incident reporting and liability, engage with legal experts. |
| Public consultation and feedback | Actively engage with the public, address concerns, and build trust. |
Epilogue
Toyota’s potential move into China’s full self-driving market presents a compelling case study for the automotive industry. The analysis considers market impact, technological aspects, regulatory considerations, and the potential long-term effects on the Chinese automotive market and employment. The potential impact on Toyota’s global image and the comparisons to other industry trends in China will be highlighted. This exploration concludes with a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing Toyota’s strategy and its possible implications for the future of autonomous driving in the world’s most populous nation.