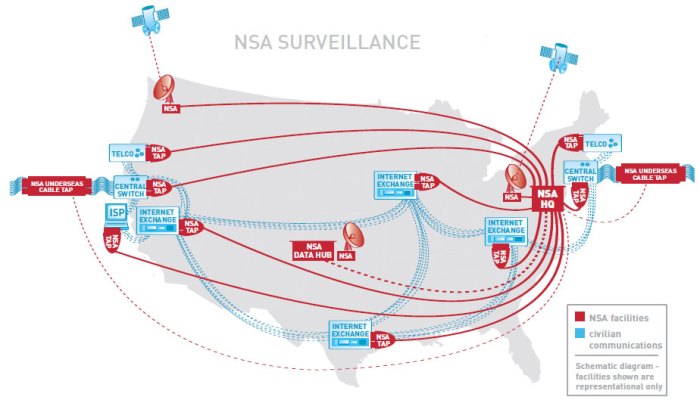
Nsa call records bulk collection usa freedom act – NSA call records bulk collection, USA Freedom Act – this legislation grapples with a fundamental conflict: national security versus individual privacy. The act sought to address concerns over the government’s broad powers to collect phone records, a practice that sparked intense debate and legal challenges. Understanding its provisions, the historical context, and the ongoing legal battles is crucial for grasping the complexities of surveillance in the 21st century.
The USA Freedom Act attempted to reform previous surveillance programs, aiming to strike a balance between protecting the nation and respecting citizens’ rights. This involved careful consideration of legal precedents, constitutional concerns, and the potential societal impact of such extensive data collection. The act’s success in achieving this balance remains a subject of debate and ongoing scrutiny.
Historical Context of Surveillance
The history of surveillance in the USA is a complex tapestry woven from evolving legal frameworks, technological advancements, and societal anxieties. From the earliest days of the republic, the government has sought to balance national security concerns with individual liberties, a struggle that continues to this day. This evolution has been marked by periods of intense surveillance, often spurred by perceived threats, followed by periods of reform and legal challenges.The pursuit of security has often outweighed concerns about privacy, leading to the development of increasingly sophisticated tools and methods for collecting and analyzing communications data.
This constant tension between national security and individual rights has shaped the legal and political landscape surrounding surveillance, leading to landmark court cases and legislative battles. The USA Freedom Act, a response to earlier surveillance programs, represents a significant attempt to address these concerns.
Evolution of Government Powers to Collect Communications Data
The collection of communications data has evolved dramatically throughout American history. Early forms of surveillance were largely reactive, responding to specific threats or suspected criminal activity. The development of telephone technology in the early 20th century, and later, radio and electronic communications, significantly expanded the potential for government surveillance. These technological advancements, coupled with changing social contexts and perceptions of national security, created a need for new legal frameworks to address the growing power of surveillance.
Key Legal and Political Debates Surrounding Surveillance
Legal and political debates surrounding surveillance have focused on the balance between national security and individual liberties. Proponents of robust surveillance argue that it is essential for preventing terrorism and other serious crimes, while opponents emphasize the potential for abuse and the erosion of privacy. These debates often involve differing interpretations of the Constitution, particularly the Fourth Amendment’s protection against unreasonable searches and seizures.
Examples of Significant Court Cases and Legislation Related to Wiretapping and Electronic Surveillance
Landmark court cases like
- Katz v. United States* (1967) and
- United States v. Jones* (2012) fundamentally altered the legal landscape of electronic surveillance. These rulings established crucial precedents regarding the application of the Fourth Amendment to modern technologies. Significant legislation, such as the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) of 1978, aimed to establish legal parameters for electronic surveillance in national security contexts.
The USA Freedom Act in Relation to Previous Surveillance Programs
The USA Freedom Act was enacted in 2015 as a response to the controversial National Security Agency (NSA) bulk collection program. The act sought to limit the government’s ability to collect data on millions of Americans without individualized suspicion. The USA Freedom Act, in many ways, attempted to rebalance the powers of surveillance in the wake of concerns raised by previous practices.
The act significantly modified the earlier Patriot Act provisions and established new limitations on data collection.
Table: Key Dates, Legislation, and Court Decisions Related to Surveillance
| Date | Legislation/Court Decision | Key Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| 1967 | *Katz v. United States* | Expanded the Fourth Amendment’s protection to electronic communications. |
| 1978 | Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) | Established procedures for electronic surveillance in national security investigations. |
| 2001 | USA Patriot Act | Expanded government surveillance powers, leading to concerns about civil liberties. |
| 2015 | USA Freedom Act | Limited bulk collection of telecommunication metadata, addressing concerns about the Patriot Act. |
| 2012 | *United States v. Jones* | Clarified the meaning of “search” in the context of GPS tracking. |
The USA Freedom Act

The USA Freedom Act, signed into law in 2015, aimed to address concerns surrounding the government’s bulk collection of telecommunications data. This legislation was a direct response to the revelations about the NSA’s surveillance programs, sparking significant debate about national security versus individual privacy. The act sought to strike a balance between these competing interests, limiting government access while maintaining the ability to conduct targeted surveillance in specific cases.The act significantly altered the landscape of government surveillance by imposing restrictions on bulk collection practices.
It recognized the need for reforms to address the perceived overreach of previous surveillance programs. These changes had a profound impact on the balance of power between the government and the citizenry in the digital age.
Provisions of the USA Freedom Act
The USA Freedom Act made several key changes to the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA). Crucially, it eliminated the bulk collection of phone records, a practice that had been criticized for its potential to violate privacy rights. This reform was a major step towards limiting the scope of government surveillance.
Addressing Concerns about Bulk Collection
The USA Freedom Act directly addressed concerns about bulk collection by transitioning from a system of indiscriminate data gathering to one focused on specific investigations. This shift was aimed at mitigating the risk of mass surveillance and focusing resources on cases with a legitimate need for intelligence gathering. The act required that requests for phone records be tied to specific investigations, thereby ensuring a more targeted and justified approach.
Key Differences from Previous Programs
Prior to the USA Freedom Act, the government’s surveillance programs often operated under broad, unchecked mandates, allowing for the collection of vast quantities of data without explicit legal justification. The act dramatically altered this by introducing specific legal standards and limitations on the types of data that could be collected. Instead of blanket collection, the USA Freedom Act mandated that surveillance requests be tailored to specific, legitimate investigative purposes.
Remember that NSA call records bulk collection in the USA sparked a lot of debate about freedom. While that’s a serious issue, it’s also worth checking your freezer for potentially recalled frozen pizzas, like those from Home Run Inn. Home Run Inn pizza recall check your freezer for these frozen meat pizzas might seem unrelated, but it highlights how important it is to stay informed about food safety, just as we should be aware of government surveillance practices.
Ultimately, both issues affect our rights and safety.
Comparison with Other Legislation
The USA Freedom Act has been compared to other legislation addressing government surveillance, particularly the FISA Amendments Act of 2008. While both aimed to regulate surveillance practices, the USA Freedom Act introduced more substantial changes in the way the government could access communications data. The key difference lies in the shift from bulk collection to targeted investigations. Other relevant legislation might include the Patriot Act and its amendments.
Comparison with these pieces of legislation would highlight the evolving nature of the balance between security and privacy.
Specific Sections and Implications
| Section | Implications |
|---|---|
| Section 702 | Allows the government to collect foreign intelligence information from US persons with a court order. This provision has been a source of debate, concerning the scope of the collection and potential for overreach. |
| Section 703 | Eliminates the bulk collection of telephony metadata. This is a significant change from previous practices and limits the ability of the government to collect this data without a specific court order. |
| Section 2 | Restricts the collection of phone records to instances with specific court orders, tied to legitimate investigations. This provision aimed to eliminate the broad, unfocused collection of data. |
Legal Challenges and Debates
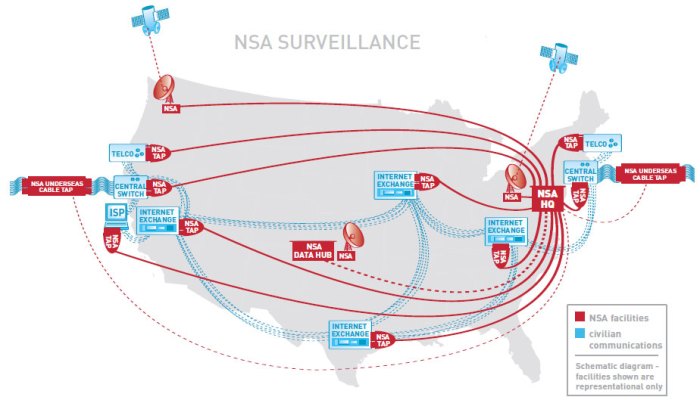
The USA Freedom Act, while intended to reform the bulk collection of telecommunication metadata, sparked immediate and ongoing legal challenges. These disputes revolved around the constitutionality of government surveillance powers and the balance between national security and individual liberties. The act’s impact on the legal landscape continues to be debated, with differing interpretations shaping its practical application.The legal battles surrounding the bulk collection of call records highlight the inherent tension between national security concerns and the protection of individual privacy rights.
Arguments for and against the practice often hinge on the interpretation of constitutional protections, particularly the Fourth Amendment’s prohibition against unreasonable searches and seizures.
Constitutional Concerns
The Fourth Amendment safeguards against unreasonable searches and seizures, requiring warrants based on probable cause. Opponents of bulk collection argued that the government’s practice violated this principle by collecting vast amounts of data without individualized suspicion, effectively conducting mass surveillance. This broad collection of information, they contended, could potentially lead to chilling effects on free speech and association.
The government’s counter-arguments focused on the need for such programs in combating terrorism and national security threats, arguing that the collection of metadata is a reasonable measure in the face of evolving threats.
Arguments for and Against Bulk Collection
- Arguments for bulk collection often emphasized the potential for identifying patterns and connections that might reveal terrorist plots or other criminal activity. Proponents argued that this data collection was crucial for preventing attacks and protecting national security, citing the potential for identifying individuals involved in future criminal activity.
- Arguments against bulk collection centered on the violation of individual privacy rights. Critics argued that the government’s access to vast amounts of personal data, without individualized suspicion, could lead to abuses of power and an erosion of civil liberties. They highlighted the potential for misuse of the data and the lack of transparency in its collection and use.
Role of the Courts in Interpreting Surveillance Programs
Courts play a crucial role in balancing competing interests in surveillance cases. Their decisions shape the legality and parameters of government surveillance programs, interpreting constitutional protections in the context of evolving technological advancements and security threats. The courts must weigh the potential benefits of surveillance against the potential harms to individual liberties and privacy. These decisions are often complex and require careful consideration of the facts and arguments presented by both sides.
USA Freedom Act’s Interpretation and Challenges, Nsa call records bulk collection usa freedom act
The USA Freedom Act, while aiming to reform the bulk collection program, faced challenges in its interpretation and application. Courts grappled with defining the scope of permissible surveillance activities and the extent to which the act truly restricted the government’s power. Challenges arose regarding the act’s limitations on data collection, its impact on law enforcement, and the balance between national security and individual liberties.
Key Legal Arguments and Counterarguments
| Legal Argument | Counterargument |
|---|---|
| Bulk collection of call records violates the Fourth Amendment’s prohibition against unreasonable searches and seizures because it lacks individualized suspicion. | The collection of metadata is a reasonable measure in the face of evolving threats to national security, enabling the identification of patterns and connections that might reveal terrorist plots. |
| The government’s access to vast amounts of personal data without individualized suspicion raises concerns about potential abuses of power and erosion of civil liberties. | Such surveillance is a necessary tool for protecting the public from terrorist attacks and other national security threats. |
| The USA Freedom Act’s limitations on data collection are insufficient to fully protect individual privacy rights. | The act represents a significant step towards balancing national security needs with individual liberties, providing necessary reforms while maintaining vital investigative capabilities. |
Public Opinion and Societal Impact
The USA Freedom Act, while intended to address concerns about government surveillance, sparked a complex and multifaceted response from the public. Public reaction to prior surveillance programs, like those authorized under the Patriot Act, played a significant role in shaping the debate surrounding the Freedom Act. Understanding this public sentiment is crucial to grasping the societal impact of these policies on civil liberties and trust in government.The debate over privacy rights versus national security remains a persistent tension.
Balancing the need for security against the fundamental right to privacy is a continuous challenge for policymakers and citizens alike. Public trust in government’s ability to strike this balance directly impacts the effectiveness and acceptance of surveillance programs.
Public Reaction to Surveillance Programs
Public opinion on surveillance programs has consistently been mixed, with strong concerns about potential abuses of power alongside arguments for the necessity of these measures in combating terrorism. Initial reactions to the Patriot Act, for example, showed a wide range of opinions. While some argued that the Act was crucial for national security, others voiced serious concerns about its potential impact on civil liberties.
These concerns continued and evolved with subsequent surveillance programs, including those authorized under the USA Freedom Act. The media played a critical role in shaping public perceptions and disseminating information, sometimes amplifying concerns and sometimes presenting more nuanced perspectives.
Debate Regarding Privacy Rights and National Security
The debate regarding privacy rights and national security is a complex one. Proponents of robust surveillance measures often emphasize the importance of national security in combating terrorism and other threats. They argue that certain measures are necessary to protect the public from harm. Conversely, advocates for stronger privacy protections highlight the potential for misuse of surveillance powers and the importance of safeguarding individual liberties.
The fear of government overreach and the potential for discriminatory targeting are frequently raised.
Speaking of privacy, the NSA’s bulk collection of call records under the USA Freedom Act is a fascinating topic. While I’m certainly not an expert, it seems like a pretty big deal. Meanwhile, all these new trailers for movies like Serpent, Infinity Train, and the upcoming Falcon and Winter Soldier are really exciting! new trailers serpent infinity train vanquish falcon winter soldier netflix marvel disney hbo are dominating my feed right now, but the whole debate around government surveillance still keeps me thinking about the USA Freedom Act and its impact on our freedoms.
Hopefully, we’ll see some positive changes soon.
Impact on Civil Liberties and Public Trust
Surveillance programs have undeniably affected civil liberties and public trust. For example, the perception of government intrusion into personal lives has led to a decline in trust in government institutions. The fear of being monitored can lead to self-censorship and limit free expression. Specific instances, such as the targeting of particular communities or groups, have further exacerbated these concerns.
The USA Freedom Act attempted to address some of these concerns by limiting bulk collection of data, but its impact on public trust remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Societal Impact of the USA Freedom Act and Previous Surveillance Efforts
The societal impact of the USA Freedom Act and prior surveillance efforts has been significant, touching upon various aspects of daily life. The act’s provisions on data collection and usage have influenced how individuals perceive their privacy in digital spaces. Concerns about the government’s ability to access personal data have led to increased awareness and concern about online security.
Different Perspectives on Surveillance and the USA Freedom Act
| Perspective | Arguments | Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Pro-Surveillance | Surveillance is necessary for national security, combating terrorism, and maintaining public safety. | Potential for misuse, targeting of innocent individuals, and erosion of civil liberties. |
| Pro-Privacy | Privacy is a fundamental right, and surveillance can lead to self-censorship and stifle free expression. | Potential for insufficient oversight of surveillance programs, leading to abuse of power. |
| Neutral/Balanced | Finding a balance between national security and individual privacy is crucial. | Need for robust oversight mechanisms and transparency to prevent abuse of surveillance powers. |
Impact on National Security
The debate surrounding surveillance programs, particularly in the context of national security, is deeply complex. Proponents argue that robust surveillance is crucial for preventing terrorist attacks and maintaining public safety. Conversely, critics express concern over potential abuses of power and the erosion of civil liberties. This discussion delves into the arguments for and against surveillance, examining its effectiveness, the impact of legislation like the USA Freedom Act, and the potential for government overreach.The justification for surveillance programs often centers on the perceived need to identify and neutralize potential threats.
Proponents claim that these programs allow law enforcement agencies to gather crucial intelligence that can thwart terrorist plots and other acts of violence. The effectiveness of these programs, however, remains a subject of ongoing scrutiny and debate.
Arguments for the Necessity of Surveillance
The argument for surveillance programs hinges on the notion that they provide crucial intelligence for preventing terrorism and other threats. Proponents emphasize that such programs allow law enforcement to identify patterns, predict potential attacks, and gather information that would otherwise remain hidden. They highlight cases where intelligence gleaned from surveillance led to the disruption of terrorist plots.
Effectiveness of Surveillance Programs in Preventing Terrorism
Assessing the effectiveness of surveillance programs in preventing terrorism is inherently difficult. While instances of thwarted plots exist, definitively attributing their prevention to surveillance alone is challenging. The lack of publicly available data makes it hard to gauge the true extent of their impact. Furthermore, the evolving nature of terrorism makes it hard to predict or anticipate emerging threats.
The effectiveness of surveillance is therefore a contested and complex issue.
Impact of the USA Freedom Act on Law Enforcement Investigations
The USA Freedom Act significantly altered the landscape of surveillance by placing restrictions on bulk collection of telecommunication metadata. While this aimed to balance national security concerns with civil liberties, the precise impact on the ability of law enforcement to investigate potential threats is still being evaluated. The Act’s limitations on the collection of data have undeniably impacted investigation methods.
The NSA’s bulk collection of call records in the USA, under the Freedom Act, raised serious privacy concerns. While you’re gearing up for winter sports, remember that similar issues of government surveillance are always worth considering. Luckily, you can get some great deals on winter gear, like snowboards and skis, at the Evo Summer Sunset Sale , with up to 50% off.
Ultimately, balancing individual liberties with national security remains a crucial debate, just like choosing the perfect winter gear.
Law enforcement agencies now face new challenges in accessing the intelligence that may have been previously readily available.
Potential Risks of Government Overreach in Surveillance
The potential for government overreach in surveillance programs is a significant concern. Critics argue that the collection and use of personal data can lead to the erosion of civil liberties and privacy rights. Historical precedents of government abuses in the name of national security further underscore these concerns. The risk of misusing collected information, targeting innocent individuals, or establishing a surveillance state are all potential outcomes of unchecked surveillance powers.
Comparison of Stated Goals and Actual Outcomes of Surveillance Programs
| Stated Goal | Actual Outcome |
|---|---|
| Prevent terrorist attacks | Mixed results; some instances of thwarted plots, but difficult to isolate the impact of surveillance. |
| Gather intelligence on potential threats | Intelligence gathered, but the extent to which it prevented attacks is hard to measure and remains debatable. |
| Enhance public safety | Potential for enhanced public safety, but also potential for misuse and violations of civil liberties. |
Alternative Surveillance Methods and Technologies: Nsa Call Records Bulk Collection Usa Freedom Act
The USA Freedom Act, while a step towards limiting bulk collection, still leaves room for debate regarding surveillance practices. Alternative methods are crucial for striking a balance between national security and individual privacy. This section explores potential alternatives, emerging technologies, and the role of data minimization in modern intelligence gathering.The traditional model of bulk data collection, while seemingly efficient, often leads to an overabundance of irrelevant information, making targeted intelligence gathering challenging.
Modern surveillance must adapt to the changing landscape of data and technology to remain effective and ethical.
Alternative Intelligence Gathering Methods
The shift towards targeted collection requires a re-evaluation of existing intelligence-gathering methods. Agencies can focus on specific individuals or groups based on reasonable suspicion, rather than indiscriminately collecting vast amounts of data. This shift necessitates a strong legal framework for determining “reasonable suspicion.”
- Metadata Analysis: Examining metadata, such as call records or email headers, can provide valuable insights into communication patterns without accessing the full content of the communication. This method allows for a focused analysis of interactions without violating privacy.
- Signal Intelligence (SIGINT): Intercepting electronic communications and signals can reveal critical information. SIGINT is often more effective when paired with other methods for verification and contextualization. Sophisticated techniques for deciphering encrypted communications also exist.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): Utilizing human sources, including informants and agents, remains a vital tool. Careful vetting and management of these sources are crucial for maintaining their reliability and preventing compromise.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): Gathering information from publicly available sources, such as news articles, social media, and government documents, is a crucial component of modern intelligence gathering. This approach requires advanced analysis techniques to extract relevant data.
Emerging Technologies Affecting Surveillance Practices
The rapid evolution of technology demands vigilance in adapting surveillance strategies. New technologies can provide novel methods of gathering and analyzing information.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI can be used to identify patterns in vast datasets that would be impossible for humans to discern. AI can analyze patterns in communication, financial transactions, and online behavior to identify potential threats. However, biases in the data used to train AI algorithms can create unfair or inaccurate results. Careful consideration of ethical implications and safeguards against bias are critical.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Data Analysis: The proliferation of connected devices generates a wealth of data about individuals’ routines and behaviors. This data can be valuable for surveillance but also raises significant privacy concerns. Stricter regulations and data minimization policies are crucial to avoid the potential for misuse.
- Advanced Encryption Techniques: New encryption methods are constantly emerging, making interception more difficult. However, advancements in decryption techniques often keep pace. This necessitates a continuous evolution of surveillance strategies.
Data Minimization and Targeted Collection
The focus on data minimization in surveillance practices is crucial for preserving privacy.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the data necessary to achieve a specific intelligence objective is essential. This reduces the risk of over-collection and inappropriate use of data.
- Targeted Collection: Focus on specific individuals or groups based on credible evidence, not broad categories or demographics. This reduces the potential for discrimination and unwarranted surveillance.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) offer methods to improve privacy while enabling surveillance.
- Differential Privacy: Adding noise to data can protect individual privacy while still allowing for aggregate analysis. This technique can be used to anonymize data sets and make it more difficult to identify specific individuals within the data.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Data can be encrypted in a way that allows computations to be performed on the encrypted data without decrypting it. This allows for analysis of encrypted data while preserving privacy. This method could allow for targeted data analysis without compromising privacy.
International Comparisons
Global surveillance practices vary significantly, reflecting diverse legal frameworks, societal values, and historical contexts. Understanding these differences is crucial for evaluating the US approach to balancing national security and privacy. Comparing these systems allows us to identify potential benefits and pitfalls in each approach.The US model, shaped by the Fourth Amendment and ongoing legal battles, often contrasts with systems in other countries.
These other systems might prioritize national security more explicitly, or rely on different levels of judicial oversight. Examining these alternatives offers insights into the trade-offs inherent in managing security and freedom.
Surveillance Practices in Other Countries
Different nations have developed diverse approaches to surveillance, often reflecting their unique political and social structures. For instance, some countries employ widespread surveillance of communications data as a routine part of national security efforts, while others emphasize targeted surveillance based on specific threats. The methods and tools used also differ significantly.
Similarities and Differences Between US and Other Nations’ Surveillance Programs
Comparing US surveillance programs to those in other countries reveals both similarities and significant differences. One similarity is the inherent tension between national security and individual liberties. However, the specific legal frameworks, levels of judicial oversight, and public perceptions surrounding surveillance differ substantially.
Balancing National Security and Privacy in Other Countries
The approaches to balancing national security and privacy differ dramatically across countries. Some nations, for instance, prioritize national security over individual privacy rights, while others adopt a more cautious approach that emphasizes safeguards for fundamental freedoms. These differences highlight the varied ways societies grapple with these competing values.
Role of International Cooperation and Agreements in Surveillance
International cooperation plays a vital role in surveillance efforts, though the extent and nature of these collaborations vary considerably. There are instances of international agreements facilitating data sharing and cooperation between intelligence agencies, while others focus on information exchange for specific purposes, such as combating terrorism or cybercrime. These agreements often involve a complex web of bilateral and multilateral treaties.
Table of Key Differences in Surveillance Policies
| Country | Surveillance Policy Focus | Level of Judicial Oversight | Public Perception | Key Legal Framework |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Balancing national security with privacy rights | Significant judicial oversight, ongoing debate | Mixed public opinion | Fourth Amendment, USA Freedom Act |
| China | National security prioritized | Limited judicial oversight | National security concerns outweigh individual rights | National Security Law |
| United Kingdom | Balancing national security and privacy | Significant judicial oversight, though often subject to government influence | Mixed public opinion, with ongoing debate | Human Rights Act |
| Germany | Strong emphasis on privacy protection | Robust judicial oversight | Strong public concern about surveillance | Basic Law |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the NSA call records bulk collection and the USA Freedom Act represent a significant turning point in the ongoing debate about government surveillance and privacy rights. The act’s provisions, legal challenges, and public reaction have highlighted the intricate relationship between national security, civil liberties, and the ever-evolving landscape of technology. The future of surveillance and its impact on our lives remain a topic of crucial discussion.