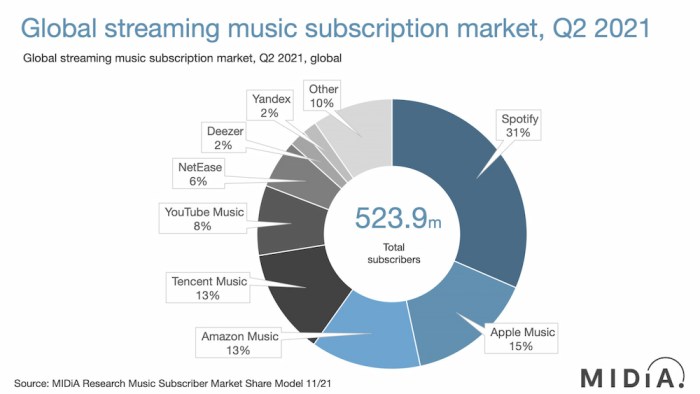
Music industry apple spotify paid streaming sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail. From the evolution of paid streaming services, to the head-to-head comparison of Apple Music and Spotify, and the impact on artists and labels, this exploration dives deep into the financial and technological intricacies of the modern music industry.
We’ll also consider the future of music streaming, the consumer experience, and the role of technology in this digital age of music.
The shift from physical media to digital downloads, and then to paid streaming, has profoundly reshaped how music is consumed and monetized. Understanding the revenue models of these platforms, and the impact on artists and labels, is crucial to grasping the current state of the music industry. This examination will delve into the key developments, the strengths and weaknesses of competing services, and the strategies employed by both Apple and Spotify to dominate the market.
The Evolution of Paid Streaming
The music industry has undergone a dramatic transformation from the physical realm of vinyl records and CDs to the digital age of downloads and streaming. This shift has been fueled by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences, ultimately reshaping how we consume and experience music. The transition to paid streaming services represents a significant turning point in this evolution, fundamentally altering revenue models and the very structure of the industry.The shift from physical media to digital downloads laid the groundwork for the streaming revolution.
Initially, digital downloads offered convenience and accessibility but lacked the integrated listening experience that streaming provided. The emergence of paid streaming services addressed this gap, offering users a vast library of music on-demand for a monthly fee.
The music industry’s shift to paid streaming services like Apple Music and Spotify is interesting. It’s a huge change, and it’s definitely impacting artists and listeners alike. Meanwhile, Amazon’s decision to drop mask mandates for fully vaccinated warehouse workers ( amazon wont require masks for fully vaccinated warehouse workers ) raises questions about workplace safety in a post-pandemic world.
Ultimately, these kinds of decisions will likely continue to influence how we consume music and other products in the years ahead.
Historical Context of Music Distribution
The music industry’s journey from physical media to digital downloads is marked by several key developments. Early music distribution relied heavily on physical formats like vinyl records and cassette tapes. The advent of CDs marked a significant leap forward in audio quality and convenience. The rise of the internet and MP3 downloads introduced a new era of accessibility and affordability, though often bypassing traditional revenue streams for artists.
Timeline of Key Developments in Paid Music Streaming
The transition to paid streaming services wasn’t instantaneous. Several key milestones shaped the current landscape.
- The early 2000s witnessed the rise of online music stores, offering digital downloads. These platforms, while not streaming services, began to shift the focus from physical to digital formats. Early adopters started to see the potential of digital distribution.
- The mid-2000s saw the emergence of streaming services, initially offering free access with limitations. These services laid the foundation for the paid models that followed. Users became accustomed to the convenience of on-demand listening.
- 2010-2015 marked the significant growth of paid streaming services, with Spotify and Apple Music leading the charge. These services attracted significant user bases, offering a substantial library of music for a monthly fee. Artists started to see increased revenue through streaming.
- The 2015-2020 period saw continued growth and innovation in streaming services. Features like personalized recommendations and curated playlists further enhanced user engagement and satisfaction. The focus shifted to user experience and retention.
- The current era is characterized by intense competition among streaming services, ongoing evolution in subscription models, and the continued impact on the music industry’s revenue structure.
Shift in Consumer Behavior Towards Paid Streaming
Consumer behavior has demonstrably shifted toward paid streaming subscriptions. Factors like convenience, accessibility, and the vast selection of music available have played a significant role. Users now expect a seamless and personalized listening experience, leading to a high demand for subscription-based services.
The music industry’s shift to paid streaming services like Apple Music and Spotify is definitely changing things. It’s interesting to see how this model is impacting artists and listeners alike. Speaking of deals, if you’re in the market for a new vacuum cleaner, check out this amazing offer: pay just 80 and bag this bargain cordless stick vacuum saving 110.
It’s a steal! Ultimately, the future of music streaming is still unfolding, and it’ll be interesting to see how it evolves.
Comparison of Revenue Models of Different Streaming Services
Different streaming services employ various revenue models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
| Streaming Service | Revenue Model |
|---|---|
| Spotify | A combination of subscription fees and advertising revenue. |
| Apple Music | Primarily subscription-based, with potentially smaller advertising revenue. |
| Other services | Varying models, often including both subscription and advertising components. |
Impact of Apple Music and Spotify on the Music Industry’s Financial Structure
Apple Music and Spotify have profoundly impacted the music industry’s financial structure. They have provided a new revenue stream for artists, replacing the traditional methods of record sales and physical performances. However, the precise distribution of these revenues among artists and labels remains a subject of ongoing discussion.
“The transition to paid streaming has created a new ecosystem, demanding new strategies for revenue distribution and artist compensation.”
The shift towards paid streaming has led to significant changes in the industry’s economic dynamics. The debate around fair compensation and equitable revenue distribution continues to shape the future of the music industry.
Apple Music vs. Spotify
The music streaming landscape is dominated by two titans: Apple Music and Spotify. Both platforms offer a vast library of music, podcasts, and other audio content, but they differ significantly in their approaches, user experiences, and target audiences. This analysis delves into the key distinctions between these services, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and competitive strategies.Apple Music and Spotify, while both aiming for global reach, have tailored their services to different preferences.
Apple, with its focus on seamless integration into the wider Apple ecosystem, has sought to provide a user-friendly, holistic experience. Spotify, meanwhile, has built a robust platform with a broader appeal by emphasizing user personalization and a comprehensive feature set.
The music industry’s shift to paid streaming services like Apple Music and Spotify is fascinating. It’s a big change from the old days, and it’s interesting to see how companies are trying to adapt. However, the recent Sprint and Verizon mock pop-up shop, charging twice the price for similar products ( sprint verizon mock pop up shop twice the price ), raises questions about pricing strategies in other industries.
Ultimately, the future of music streaming models, especially the subscription-based ones, remains a significant factor in the overall music industry landscape.
Comparative Analysis of Strengths and Weaknesses
Apple Music’s strength lies in its tightly integrated design, functioning seamlessly within the Apple ecosystem. This integration, coupled with its curated playlists and focus on high-quality audio, appeals to users prioritizing a polished, user-friendly interface. However, its limited user base and potentially less extensive content library compared to Spotify represent weaknesses.Spotify’s strength is its vast library, encompassing a wide range of genres and artists.
Its extensive features, such as personalized recommendations and extensive podcast selections, cater to diverse user preferences. Yet, the complexity of the interface and potential for ad interruptions are drawbacks for some users.
Key Differentiators
The key differentiators between the platforms extend beyond their respective strengths and weaknesses. User interfaces, features, and artist partnerships play crucial roles in shaping each platform’s identity.
- User Interface: Apple Music’s interface prioritizes simplicity and aesthetic appeal, aiming for intuitive navigation. Spotify’s interface, while robust, can be more complex, demanding a greater learning curve for new users.
- Features: Apple Music emphasizes curated playlists and high-fidelity audio. Spotify boasts a comprehensive range of features, including personalized recommendations, podcast support, and social listening tools.
- Artist Partnerships: Both platforms have signed exclusive deals with artists and labels. Apple Music’s focus on exclusivity might limit the availability of some content, while Spotify’s broader reach can grant access to a wider range of musical selections.
Competitive Landscape and Strategies
Both platforms have adopted distinct strategies to gain market share. Apple Music leverages its ecosystem integration and premium offerings, targeting users who prioritize a streamlined experience. Spotify, in contrast, emphasizes its vast content library and comprehensive features, aiming for a broad appeal.
- Apple Music Strategy: Apple Music’s strategy revolves around seamless integration with other Apple products and services. This integrated approach enhances user experience and strengthens brand loyalty within the Apple ecosystem. This strategy also leverages Apple’s existing user base and brand recognition. This ecosystem approach also creates a positive feedback loop where the use of other Apple products encourages users to stay within the Apple ecosystem.
- Spotify Strategy: Spotify’s strategy focuses on providing a diverse content library and a broad range of features to cater to diverse user preferences. This includes personalized recommendations, podcasts, and social features, which attract a broader user base.
Exclusive Content Deals and Artist Support
The approach to exclusive content deals and artist support differs between the two platforms. Apple Music has secured exclusive deals with some artists and labels, while Spotify’s broader reach potentially allows for access to a wider selection of music.
- Exclusive Content: Apple Music has secured exclusive content deals, which can limit access for some users, while Spotify has often aimed for broader licensing agreements.
- Artist Support: Both platforms offer artist support through various programs and initiatives, although the specific details and approaches may differ.
Pricing Models, User Base, and Target Audience
The following table contrasts the pricing models, user base, and target audience for both platforms.
| Feature | Apple Music | Spotify |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Tiered subscriptions with different features and benefits | Tiered subscriptions with different features and benefits; also offers a freemium model |
| User Base | Concentrated within the Apple ecosystem | Large and diverse global user base |
| Target Audience | Users prioritizing seamless integration and a polished experience within the Apple ecosystem | Users seeking a vast music library, diverse features, and a personalized listening experience |
Impact on Artists and Labels
The transition to paid streaming has fundamentally reshaped the income streams for artists and record labels, introducing new complexities and challenges. While the potential for increased revenue is significant, the intricacies of revenue-sharing models and the evolving industry landscape require careful adaptation. Artists and labels must navigate these changes to maximize their earnings and maintain their position in the music industry.The shift from free, ad-supported models to paid streaming has introduced new revenue streams for artists and labels, but the distribution of these earnings is not always straightforward.
Understanding the nuances of these models is crucial for maximizing income and ensuring a sustainable future. Different revenue-sharing structures impact artists and labels differently, often creating disparities in earnings depending on factors like artist popularity, label size, and streaming platform policies.
Revenue-Sharing Models
The revenue-sharing models implemented by streaming platforms vary significantly. A crucial aspect is the percentage split between the platform, the label, and the artist. These percentages are often negotiated and vary depending on the artist’s popularity and the label’s size. This variable distribution makes predicting income a complex task. Streaming platforms typically have a substantial portion of the revenue, while the label and the artist share the remaining amount.
Implications of Revenue-Sharing Models
Different revenue-sharing models have varying implications for artists and labels. For example, a model where a larger percentage of revenue goes to the platform might result in lower earnings for both artists and labels, especially for independent artists. Conversely, models with more equitable splits might offer better opportunities for independent artists to earn a living. The overall effect on income is not always predictable and depends heavily on the specific contract terms and the artist’s popularity.
Artist Adaptation Strategies
Artists and labels can adapt to the changing industry landscape by diversifying their income streams, leveraging digital marketing strategies, and fostering relationships with fans. A key aspect of this adaptation involves embracing new technologies and strategies, such as using social media to build direct relationships with fans and exploring merchandise sales to complement streaming income. Building a strong online presence is essential for visibility and fostering engagement with a wider audience.
Independent Artists in the Paid Streaming Era
Independent artists face unique challenges in the paid streaming era. Their smaller budgets and limited resources often mean they struggle to compete with major label artists, who can leverage larger marketing budgets and established fan bases. Building a loyal fanbase, promoting their music effectively, and securing favorable agreements with streaming platforms are critical for independent artists to thrive.
Artist Agreements
| Agreement Type | Key Clauses |
|---|---|
| Exclusive Record Deal | Granting exclusive rights to a record label for a specified period. Often includes clauses regarding royalties, distribution, and marketing. |
| Independent Artist Agreement | Typically focused on licensing and distribution rights. Includes clauses on revenue sharing, usage rights, and termination clauses. |
| Streaming-Specific Agreements | Often focused on revenue sharing from streaming platforms. Clauses specify the percentage of revenue going to the artist and label. |
| Performance Agreements | Cover live performances and related merchandise sales. Includes clauses about royalty percentages, stage management, and potential income streams. |
Independent artists may find it more challenging to negotiate favorable terms in these agreements due to a lack of leverage.
The Future of Music Streaming
The music streaming landscape is poised for significant evolution over the next five years. The current dominance of established platforms like Apple Music and Spotify is likely to be challenged by emerging technologies and evolving listener preferences. Understanding these shifts is crucial for artists, labels, and streaming services to adapt and thrive in the future.
Projected Trajectory of the Music Streaming Industry
The music streaming industry will likely continue its growth trajectory, but with a shift in focus. Increased competition and evolving listener expectations will drive a more personalized and interactive user experience. Subscription-based models will remain dominant, but subscription fatigue could lead to innovative payment models, potentially incorporating freemium options or dynamic pricing.
Potential Disruptions and Emerging Trends
Several trends could disrupt the current music streaming model. The rise of audio-focused social media platforms, offering unique music discovery experiences, will influence listener habits. Personalized recommendations based on sophisticated algorithms will become even more sophisticated, enhancing the user experience. Integration of immersive audio technologies like spatial audio and 3D audio will enhance the listening experience and drive user engagement.
Impact of New Technologies on the Music Streaming Model
New technologies will significantly impact the music streaming model. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) will enhance personalized recommendations, curate playlists based on complex user data, and potentially even generate new music genres. The growing adoption of blockchain technology could provide artists with more control over their music distribution and royalties. The metaverse could potentially create new virtual concert experiences and immersive music consumption environments.
Strategies to Maintain Listener Engagement and Subscription Growth
Maintaining listener engagement and subscription growth will require a multi-faceted approach. Streaming services will need to offer exclusive content, artist collaborations, and immersive listening experiences to retain subscribers. Providing personalized playlists, tailored to individual listener preferences, will be crucial. Actively fostering community and interaction among listeners will be essential to building loyalty and driving engagement.
Potential Future Revenue Streams for Music Companies, Music industry apple spotify paid streaming
| Revenue Stream | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Subscription Fees | Core revenue source for streaming services. | Will likely remain a significant source of income, but faces competition and evolving payment models. |
| Artist-Specific Bundles/Packages | Exclusive content, artist collaborations, and VIP access. | Provides artists with direct revenue and strengthens their connection with listeners. |
| Brand Sponsorships and Advertising | Integrating relevant advertising into the streaming platform. | Could generate substantial revenue but must be implemented carefully to avoid negatively impacting user experience. |
| Merchandise and Physical Products | Allowing artists to sell physical merchandise, such as albums, vinyl records, or concert tickets. | Provides a physical outlet for music consumption, especially for fans who prefer physical products. |
| Virtual Concerts and Events | Hosting live concerts and other events within the metaverse or streaming platform. | Creates new revenue opportunities and provides a unique way for artists to interact with fans. |
| Data and Analytics Services | Providing data and analytics to artists and labels. | Could be a lucrative service for music industry players. |
Consumer Experience and Preferences
Choosing a music streaming service is a deeply personal decision, influenced by a multitude of factors. Beyond the sheer volume of music available, users prioritize ease of use, personalized recommendations, and the overall feeling the platform evokes. The battle for subscribers hinges on delivering a superior experience that resonates with individual preferences and evolving musical tastes.The streaming landscape is constantly shifting, with new features and functionalities emerging regularly.
This dynamic environment necessitates a keen understanding of user needs and a commitment to continuous improvement. Platforms that adapt to evolving trends and proactively address user feedback are better positioned to thrive in this competitive market.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choice
User choice in music streaming services is a complex interplay of several factors. Price is a key consideration, especially for budget-conscious consumers. The sheer volume of music available plays a significant role, and the ability to discover new artists and genres is another critical factor. Convenience, ease of use, and a seamless user interface are highly valued.
Importance of User Experience and Interface Design
A user-friendly interface is paramount in retaining subscribers. Intuitive navigation, clear categorization, and aesthetically pleasing design contribute significantly to a positive user experience. A well-designed platform allows users to easily find what they want, explore new music, and enjoy their streaming experience without frustration. Streamlined search functionality, clear album and artist pages, and intuitive playlist creation tools are vital components of a robust user experience.
Role of Curated Playlists and Personalized Recommendations
Curated playlists and personalized recommendations are powerful tools for engaging users. Expertly crafted playlists offer a curated experience, introducing users to diverse genres and artists. Personalized recommendations, based on listening history and preferences, can be highly effective in introducing new music and expanding musical horizons. The accuracy and relevance of these recommendations directly impact user satisfaction and platform loyalty.
Impact of Emerging Music Genres and Trends
Emerging music genres and trends have a significant impact on streaming services. The rise of genres like K-Pop, Latin trap, and alternative rock, for example, has driven demand for platforms that cater to these genres. Streaming services that proactively adapt to these trends and incorporate them into their playlists and recommendations can attract a broader user base. Platforms that are slow to respond may lose ground to those that embrace these evolving tastes.
User Feedback on Different Streaming Platforms
| Streaming Platform | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Music | High-quality audio, excellent curated playlists, seamless integration with Apple ecosystem. | Limited discovery options, sometimes slow loading times, lack of certain genres. |
| Spotify | Vast library of music, extensive personalized recommendations, affordable subscription options, excellent user interface. | Occasional issues with audio quality, ads, and limited offline functionality. |
| Tidal | High-quality audio, focus on high-fidelity music, diverse artist features. | Higher price point, smaller user base, limited accessibility to some genres. |
| Amazon Music | Extensive library, seamless integration with Amazon ecosystem, good value for money. | Limited discovery options, occasional technical issues, lack of personalized features. |
This table provides a snapshot of user experiences across various platforms. The specific feedback varies widely depending on individual preferences and usage patterns. However, it demonstrates the diverse nature of user experiences and the importance of catering to specific needs and expectations.
The Role of Technology in Paid Streaming
The music streaming industry is deeply intertwined with technological advancements. From the initial development of digital audio formats to the sophisticated algorithms powering recommendation engines, technology underpins the entire ecosystem. Understanding the technical underpinnings is crucial to grasping the evolution and future of paid streaming services.The constant push for better audio quality, seamless user experiences, and efficient data management drives innovation in the field.
The streaming experience is a complex interplay of algorithms, infrastructure, and user interface design, all converging to deliver music to listeners globally.
Technical Aspects of Streaming Music
The process of streaming music involves compressing audio data to manageable sizes for efficient transmission over the internet. Various compression algorithms are employed, impacting audio quality. MP3, AAC, and more recently, lossless formats like FLAC, are common choices. These algorithms trade off file size for fidelity. Lower-bitrate formats, while more space-efficient, introduce audible artifacts.
Higher-bitrate formats, while preserving more sonic detail, require more storage and bandwidth.Data transfer protocols are essential for efficient delivery. Streaming services leverage protocols like HTTP and TCP to ensure reliable and rapid transmission of audio data to users. These protocols handle packet loss, network congestion, and other factors that might disrupt the playback. Efficient data management is key to maintaining a smooth user experience.
Importance of Infrastructure and Server Capacity
Maintaining a reliable streaming service demands robust infrastructure and substantial server capacity. Music streaming services must handle a massive volume of data requests simultaneously. This necessitates powerful servers, high-bandwidth networks, and redundant systems to prevent outages. Scalability is crucial to accommodate growth in user base and demand. Significant investments are made in infrastructure to ensure consistent service, especially during peak usage times.
Advancements in Audio Quality and User Experience
Technological advancements continuously enhance audio quality and user experience. High-resolution audio formats, such as 24-bit/96kHz, offer superior fidelity compared to standard formats. These higher-quality formats demand more bandwidth but deliver a richer, more immersive listening experience. Improved compression algorithms and efficient data transfer methods allow for these higher resolutions while maintaining seamless playback. Advanced audio processing techniques also improve clarity and reduce distortion, further enhancing the user experience.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Music Recommendation Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a significant role in personalized music recommendations. These systems analyze vast amounts of user data, including listening history, preferences, and interactions with playlists, to curate tailored suggestions. Algorithms learn user patterns, predict preferences, and suggest new music based on similarities to previously enjoyed tracks. AI-driven systems enhance user engagement and discoverability, leading to more diverse and personalized listening experiences.
Technical Specifications of Different Streaming Formats
| Format | Bitrate (kbps) | Audio Quality | File Size | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP3 | 128-320 | Lossy | Smaller | General streaming, portability |
| AAC | 128-320 | Lossy | Comparable to MP3 | Commonly used in mobile devices, higher compression |
| FLAC | Variable | Lossless | Larger | High-fidelity listening, archival purposes |
| WAV | Variable | Lossless | Largest | Professional audio, highest quality |
The table above provides a basic overview of different streaming formats. The choice of format depends on the balance between quality, size, and bandwidth constraints.
Wrap-Up: Music Industry Apple Spotify Paid Streaming
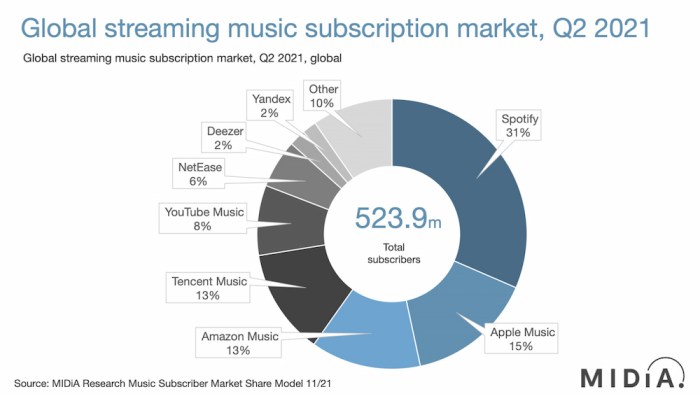
In conclusion, the music industry’s transition to paid streaming has been a dynamic and complex journey. The rise of Apple Music and Spotify has fundamentally altered the landscape, impacting artists, labels, and consumers alike. The future of music streaming, though uncertain, promises further innovation and challenges. This evolution underscores the crucial role of technology in shaping the way we experience and consume music, and it remains a fascinating area to observe as the industry continues to adapt.