Mpls to sd wan migration – MPLS to SD-WAN migration is a crucial step for businesses looking to modernize their network infrastructure. This comprehensive guide explores the process, from understanding the benefits of SD-WAN to implementing the solution and monitoring its performance post-migration. We’ll cover everything from cost analysis to security considerations, offering a clear path for organizations seeking to transition from traditional MPLS to the agility and scalability of SD-WAN.
This guide will delve into the specifics of each stage of the migration, including detailed analysis of your current MPLS network, assessment of SD-WAN needs, planning a phased migration strategy, implementation steps, and ongoing post-migration maintenance. We’ll also touch upon the crucial aspects of security and cost-benefit analysis throughout the entire process. Get ready to unlock the potential of SD-WAN!
Introduction to SD-WAN and its benefits
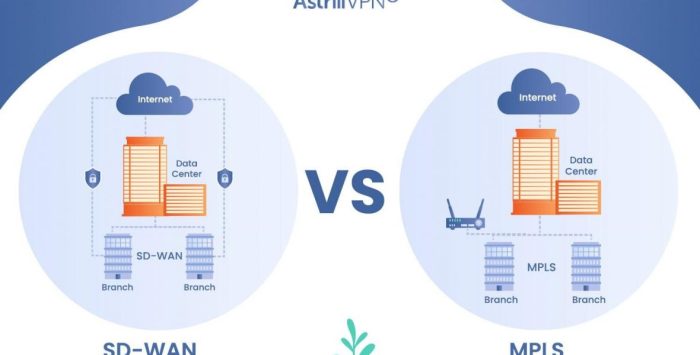
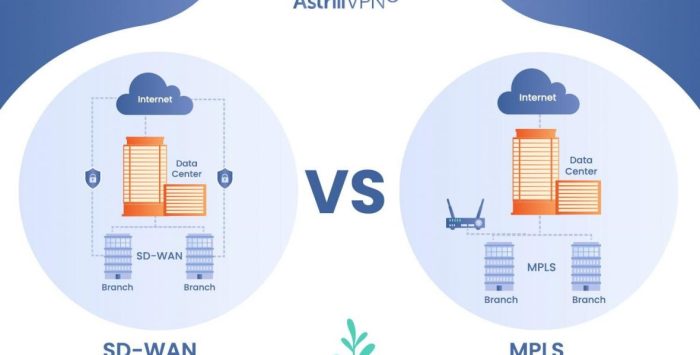
Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) are transforming how businesses connect their geographically dispersed locations. SD-WAN leverages software-based control to dynamically manage network traffic across various connections, including broadband internet, MPLS, and other options. This allows organizations to optimize network performance and costs in a more flexible and adaptable manner.SD-WAN offers a powerful alternative to traditional, dedicated MPLS networks by enabling businesses to take advantage of the cost-effectiveness and speed of modern internet connections while maintaining the security and reliability needed for critical applications.
This agility is a key differentiator in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Key Advantages of SD-WAN over MPLS
Traditional MPLS networks often impose inflexible, high upfront costs, and lack the agility needed to respond to changing business needs. SD-WAN’s programmability and dynamic routing capabilities provide significant advantages. Organizations gain greater control over network resources, allowing for optimal utilization and reduced costs. This flexibility is crucial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or those with fluctuating bandwidth requirements.
Business Drivers for Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN, Mpls to sd wan migration
Several key business drivers are fueling the shift from MPLS to SD-WAN. These include the desire for reduced network costs, improved application performance, enhanced network agility, and increased security. The cost savings associated with SD-WAN, often significantly lower than MPLS, are a major incentive for businesses looking to optimize their IT spending. Additionally, the ability to dynamically adjust bandwidth based on demand is particularly attractive for businesses with fluctuating needs.
Comparison of MPLS and SD-WAN
The table below highlights a comparative analysis of MPLS and SD-WAN in terms of cost, performance, and scalability.
| Feature | MPLS | SD-WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High upfront costs, predictable but potentially inflexible. Long-term contracts can be expensive to adjust. | Lower upfront costs, greater flexibility in adjusting bandwidth and contracts. More cost-effective for fluctuating bandwidth needs. |
| Performance | Generally high performance due to dedicated circuits. Performance can vary based on network congestion, but less variability than SD-WAN. | Performance depends on the internet connection quality. However, SD-WAN can optimize traffic flow and ensure application performance. |
| Scalability | Scalability can be challenging and costly to adjust. Requires significant investment for expansion. | Scalability is easier and more cost-effective due to the dynamic nature of the network. Adding new locations or bandwidth is more agile and less expensive. |
Evaluating the MPLS Network
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN requires a deep understanding of your existing network’s strengths and weaknesses. A thorough evaluation of your MPLS infrastructure is crucial for identifying potential bottlenecks and limitations that could hinder a smooth transition or create unforeseen issues in the SD-WAN deployment. This assessment is a critical step in ensuring that the migration aligns with your business needs and objectives.A comprehensive evaluation of your MPLS network helps in proactively addressing potential issues and planning for a successful migration.
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is becoming increasingly crucial for businesses. The recent shift towards remote work, exemplified by the coronavirus-driven remote work policies at companies like Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter, and Seattle-based tech firms, has accelerated the need for more flexible and adaptable networking solutions. This need for enhanced network agility, especially considering the remote work trends seen at coronavirus Amazon Google Facebook Microsoft Twitter Seattle staff remote work , has highlighted the limitations of traditional MPLS.
SD-WAN’s dynamic routing and cost-effectiveness make it a powerful solution for this evolving business landscape. Ultimately, a smooth MPLS to SD-WAN transition is key for staying competitive.
This proactive approach minimizes risks and maximizes the benefits of the SD-WAN deployment. It also helps in determining the optimal configuration and features for the new SD-WAN solution.
Potential Bottlenecks and Limitations
MPLS networks, while reliable, can have inherent limitations. Identifying these bottlenecks is key to planning a smooth migration. Potential issues include bandwidth limitations, high costs, and inflexibility in adapting to changing network demands. Geographic constraints can also be a significant factor, as MPLS connectivity may not be readily available or cost-effective in all locations. Over-reliance on a single vendor or provider for services could also present challenges during the transition to SD-WAN.
Importance of Network Traffic Analysis
Network traffic analysis is essential for assessing migration readiness. Understanding current traffic patterns, volumes, and types of applications using the network allows for accurate capacity planning and selection of the right SD-WAN solution. Analyzing historical data reveals seasonal variations and predictable spikes in traffic, helping in projecting future needs. Identifying bandwidth-intensive applications is vital to ensure the SD-WAN can handle the anticipated load.
Steps for a Thorough MPLS Network Assessment
A thorough assessment involves several key steps:
- Inventory of Existing Network Infrastructure: This includes a detailed listing of all MPLS circuits, routers, switches, and other network equipment. This inventory should include the bandwidth capacity, contract terms, and service level agreements (SLAs) for each circuit.
- Traffic Analysis and Reporting: This involves gathering data on network traffic patterns over a defined period. This data should include the volume of traffic, the types of applications generating traffic, and the locations of the traffic sources and destinations. Detailed reporting tools are essential to capture this information.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM): This step focuses on measuring the performance of applications that rely on the MPLS network. Monitoring response times, latency, and packet loss is essential to understanding the current performance of applications and to ensure the SD-WAN can deliver equivalent or improved performance.
- Cost Analysis: A thorough cost analysis should compare the current MPLS costs with potential SD-WAN solutions. This should include the cost of the SD-WAN infrastructure, the cost of any new hardware or software, and the ongoing operational costs.
- Vendor Evaluation: A thorough evaluation of current and potential SD-WAN vendors should be undertaken to ensure they can meet the identified needs of the organization.
Checklist for Evaluating the Current MPLS Network Infrastructure
This checklist provides a structured approach to assessing the MPLS network:
| Category | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Network Connectivity |
|
| Network Traffic |
|
| Cost and Operational Aspects |
|
Assessing SD-WAN Needs
Choosing the right SD-WAN solution is crucial for a successful migration. It’s not just about picking a vendor; it’s about aligning the solution with your specific business needs and future growth. This involves careful consideration of your current network, anticipated traffic patterns, and potential use cases. A well-defined SD-WAN strategy ensures optimal performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Key Factors in SD-WAN Solution Selection
Several key factors influence the optimal SD-WAN solution. These include network topology, existing infrastructure, anticipated traffic volumes, and security requirements. Understanding these elements is vital for achieving a seamless migration and realizing the benefits of SD-WAN. A thorough evaluation will guide you towards a solution that best meets your needs.
- Network Topology: Evaluating your current network’s architecture, including the number of sites and their geographical distribution, is essential. This assessment helps determine the best SD-WAN deployment model (e.g., hub-and-spoke, mesh). A hub-and-spoke model is often preferred for centralizing traffic and optimizing performance for geographically distributed sites. The mesh model, on the other hand, provides higher redundancy and flexibility for a more complex network configuration.
- Existing Infrastructure: Compatibility with existing routers, firewalls, and other network devices is critical. SD-WAN solutions need to integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure for a smooth transition.
- Anticipated Traffic Volumes: Future growth and traffic patterns should be considered. Accurate forecasting ensures that the chosen SD-WAN solution can handle anticipated increases in bandwidth demands and data volumes.
- Security Requirements: Security considerations are paramount. Features like encryption, access control, and intrusion detection should be evaluated to meet the specific security needs of your organization.
Defining Bandwidth and Performance Requirements
Accurate bandwidth and performance estimations are crucial for a successful SD-WAN deployment. This involves analyzing existing traffic patterns, identifying peak usage times, and forecasting future growth. By understanding the anticipated traffic volumes, you can select an SD-WAN solution with the necessary capacity.
- Traffic Analysis: Analyzing historical data to understand traffic patterns, including peak usage times and typical data volumes, is essential. This allows for the accurate calculation of bandwidth needs.
- Performance Requirements: Defining specific performance metrics (e.g., latency, jitter, packet loss) is crucial. These metrics should be aligned with the specific requirements of your applications and services.
- Future Projections: Projecting future traffic growth is essential for ensuring that the chosen SD-WAN solution can handle anticipated increases in bandwidth demands. Using historical data, market trends, and business projections, these forecasts can be made.
Identifying Potential SD-WAN Use Cases
Identifying suitable SD-WAN use cases helps tailor the solution to specific business needs. A clear understanding of application requirements and potential benefits guides the selection process. This enables optimization of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Branch Office Connectivity: SD-WAN excels in connecting branch offices to the central network. This allows for optimized data transfer, reducing latency and enhancing productivity. This is a common use case for businesses with geographically distributed locations.
- Remote Worker Access: SD-WAN facilitates secure and high-performance connections for remote workers, ensuring reliable access to corporate resources.
- Cloud Application Access: SD-WAN optimizes connections to cloud applications and services, providing improved performance and reliability for critical business functions.
Characteristics of Different SD-WAN Use Cases
Different SD-WAN use cases have varying performance requirements. Understanding these differences is vital for selecting the right solution.
| Use Case | Performance Requirements |
|---|---|
| Branch Office Connectivity | Low latency, high bandwidth, reliable connectivity |
| Remote Worker Access | High reliability, consistent performance, secure connectivity |
| Cloud Application Access | Low latency, high bandwidth, optimized performance for cloud applications |
| Video Conferencing | Ultra-low latency, minimal jitter, high bandwidth |
Migration Planning and Strategy
Successfully migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN requires a meticulous plan. A well-defined strategy, encompassing phased implementation, robust security measures, and comprehensive testing, is crucial for a smooth transition and minimal disruption to business operations. This involves understanding the nuances of your current MPLS network, identifying specific SD-WAN needs, and carefully planning the steps required for a successful migration.
Developing a Migration Plan
A comprehensive migration plan Artikels the steps involved in transitioning from MPLS to SD-WAN. This plan should detail the timeline, resources required, and potential risks associated with the migration. Critical elements include defining clear objectives, identifying key stakeholders, and creating a communication strategy to keep all parties informed throughout the process. Detailed network documentation is also essential for accurate assessment and future reference.
Phased Approach to Migration
A phased approach to migration is highly recommended. This minimizes disruption to existing operations and allows for gradual integration of the SD-WAN solution. A typical phased approach involves migrating specific applications or locations at a time. This enables thorough testing and validation of the SD-WAN solution in a controlled environment before extending its usage across the entire network.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount during the migration process. Comprehensive security measures need to be implemented throughout the migration to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. This includes robust encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems for the SD-WAN infrastructure. Careful consideration must be given to security protocols, policies, and compliance requirements to ensure alignment with industry best practices and regulatory standards.
Thorough security audits should be conducted at each phase to identify and address any vulnerabilities.
Testing the SD-WAN Solution
Thorough testing of the SD-WAN solution before deployment is crucial. This allows for identification and resolution of potential issues before a full-scale migration. Testing should cover various scenarios, including network performance under load, security measures, and integration with existing applications. This process involves simulating real-world traffic patterns and evaluating the solution’s ability to handle various demands. Critical success factors in the testing phase are identifying potential bottlenecks, optimizing performance, and resolving any compatibility issues.
Migration Phases and Timelines
The following table Artikels a possible phased approach to the migration process, along with estimated timelines. This framework is a template and needs to be tailored to the specific needs of each organization. Factors such as network complexity, number of locations, and the scope of applications to be migrated will influence the specifics of the timeline.
| Phase | Description | Timeline (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Planning and Assessment | Detailed network assessment, SD-WAN selection, security strategy development. | 4-6 weeks |
| Phase 2: Proof of Concept (PoC) | Pilot deployment in a controlled environment, testing of key applications and network components. | 2-4 weeks |
| Phase 3: Gradual Rollout | Phased migration of selected locations or applications, with continuous monitoring and adjustments. | 8-12 weeks |
| Phase 4: Full Deployment and Optimization | Complete transition to SD-WAN, optimization of network performance, and final security hardening. | 4-6 weeks |
Implementing the SD-WAN Solution
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning and execution. The implementation phase focuses on deploying the SD-WAN solution, configuring devices, integrating with existing systems, and establishing robust monitoring and troubleshooting procedures. A well-executed implementation will ensure a seamless transition and maximize the benefits of the new network.
Deploying the SD-WAN Solution
The deployment process typically involves several stages, starting with the selection and procurement of the necessary hardware and software components. This includes SD-WAN gateways, network management platforms, and security appliances. Careful consideration of the network topology, traffic patterns, and security requirements is critical during this phase. Following best practices in device selection and configuration is essential for optimal performance and scalability.
Configuring SD-WAN Devices
Proper configuration of SD-WAN devices is crucial for a successful deployment. This involves defining network policies, routing protocols, and security settings. Configuration tools often offer wizards and templates to streamline the process, enabling faster implementation. The configurations should be reviewed and validated thoroughly to ensure they align with the defined network architecture and traffic patterns. Thorough testing and validation of the configuration before deployment is paramount to prevent unexpected issues.
Integrating with Existing Applications and Systems
A key aspect of the implementation is seamlessly integrating the SD-WAN solution with existing applications and systems. This involves identifying the applications that will utilize the new network and configuring them to leverage the SD-WAN’s capabilities. Careful mapping of existing applications to the SD-WAN network is necessary for proper traffic routing and optimization. For example, VoIP applications might require specific settings for quality of service (QoS) to ensure optimal call quality.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Monitoring and troubleshooting the SD-WAN deployment is vital for ongoing performance and security. Comprehensive monitoring tools are essential to track key metrics such as latency, throughput, and packet loss. Early identification and resolution of issues are critical for minimizing disruptions to applications and services. Establish a robust alerting system to notify administrators of potential problems. A detailed log file analysis and monitoring tools are indispensable for troubleshooting and performance optimization.
Integrating Legacy Applications
Legacy applications often require specific configurations to function optimally on the SD-WAN network. This involves identifying the applications requiring integration and determining the necessary adjustments. For instance, legacy applications relying on specific protocols might need to be configured to use SD-WAN gateways. Careful consideration of the application’s dependencies is necessary for a smooth transition. It is essential to create detailed documentation of the integration steps and any necessary configuration changes to ensure future maintainability.
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is often about reducing costs and improving network agility, but recent events like T-Mobile’s reversal of forced plan migrations ( t mobile walks back forced plan migration wont make people switch plans after all ) highlight how customer experience can impact the success of such transitions. Ultimately, a smooth and user-friendly experience is key to any successful network migration, including the complex process of transitioning from MPLS to SD-WAN.
Post-Migration Considerations

Successfully migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is a significant achievement, but the journey doesn’t end there. Post-migration, meticulous monitoring and ongoing optimization are crucial for realizing the full potential of your SD-WAN deployment and ensuring a smooth transition. This phase requires a proactive approach to address potential issues and maximize performance.Post-migration, maintaining a vigilant eye on the SD-WAN network is paramount to ensuring optimal performance and quickly identifying and resolving any issues.
A proactive approach to monitoring and maintenance is essential to maximizing ROI and preventing disruptions.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Effective SD-WAN management hinges on continuous monitoring. Real-time data analysis is essential for identifying trends, anomalies, and performance bottlenecks. This enables proactive intervention, preventing potential issues from escalating into major disruptions. Comprehensive monitoring tools should track key metrics such as latency, bandwidth utilization, packet loss, and application performance. This allows for immediate identification of any performance degradation.
Regularly scheduled reports and alerts are critical for keeping stakeholders informed and enabling swift responses to potential problems.
Optimizing SD-WAN Performance
Several methods can optimize SD-WAN performance post-migration. Fine-tuning the network’s configuration, including adjusting bandwidth allocation, prioritizing applications, and optimizing routing protocols, is critical. Regularly evaluating and adjusting these parameters ensures the network meets evolving demands. Utilizing the SD-WAN’s built-in analytics and reporting features to understand traffic patterns and application behavior allows for intelligent resource allocation and optimization.
This proactive approach minimizes bottlenecks and ensures optimal application performance.
Addressing Potential Issues
Post-migration, it’s inevitable that some issues may arise. A well-defined troubleshooting plan is essential. Proactive monitoring allows for early detection and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime and impact on business operations. This includes establishing clear communication channels, training staff on troubleshooting procedures, and establishing a robust incident response plan. Documentation of procedures is crucial for consistency and efficiency in handling issues.
Metrics for Post-Migration Success
Tracking specific metrics is critical to assess the success of the SD-WAN migration. These metrics should reflect the network’s performance, application performance, and user experience. Metrics such as average latency, packet loss rate, bandwidth utilization, application response times, and user satisfaction scores provide valuable insights into the network’s health and effectiveness.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Post-Migration Monitoring
| KPI | Description | Target Value | Measurement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Latency | Average time taken for data packets to travel across the network. | Less than 50ms | Hourly |
| Packet Loss Rate | Percentage of data packets lost during transmission. | Less than 1% | Daily |
| Bandwidth Utilization | Percentage of available bandwidth used by the network. | Under 80% | Hourly |
| Application Response Time | Time taken for applications to respond to user requests. | Less than 2 seconds | Hourly |
| User Satisfaction Score | Measure of user experience on the SD-WAN. | Above 90% | Weekly |
Security Considerations in SD-WAN Migration
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN presents exciting opportunities for improved network performance and cost savings, but it also introduces new security challenges. Understanding these implications and proactively implementing robust security measures is crucial for a successful and secure SD-WAN deployment. A thorough assessment of existing security protocols and a well-defined security strategy are essential to maintain the same level of data protection and confidentiality as the previous MPLS network.SD-WAN’s distributed nature, with its diverse range of devices and network paths, necessitates a shift in security thinking.
Traditional perimeter-based security models might not fully address the expanded attack surface. Implementing layered security across the entire SD-WAN environment, from the edge devices to the cloud, is vital. This includes employing network security controls like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure access solutions.
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is a big deal, and it’s often a complex process. Thinking about upgrading your tech, especially if you’re looking for cost-effective solutions? Well, you might be interested to know that Apple’s M2 MacBook Pro is seeing its first-ever discount, with a cool $200 savings! Check out this deal. It’s all about streamlining operations, and finding the right tech tools for the job, which can be equally important for the smooth transition to a new SD-WAN infrastructure.
Hopefully, that discount will make the transition even more affordable.
Security Implications of SD-WAN Migration
The distributed nature of SD-WAN, using potentially less secure public internet paths, significantly broadens the attack surface. A compromised device or vulnerable connection point in the network can expose sensitive data to malicious actors. Moreover, the increased reliance on cloud services and remote access can introduce new vulnerabilities if not carefully managed. The potential for data breaches and disruptions is heightened, especially if the security measures implemented during the migration are not comprehensive and carefully planned.
Strategies for Securing the SD-WAN Network
A multi-layered approach is paramount. This involves a combination of network-level security, application-level security, and user-level security measures. Protecting the network itself requires strong access controls, intrusion prevention systems, and robust firewalls. Securing applications requires implementing encryption and access controls for specific applications and data. User authentication and authorization policies are critical to prevent unauthorized access.
Security Protocols and Measures to Protect Data
Implementing strong encryption protocols like IPSec or TLS is essential to safeguard data traversing the SD-WAN network. Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions should be integrated to detect and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network. Zero-trust security models, which verify every user and device, offer a robust defense against unauthorized access. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical to identify and address weaknesses proactively.
Comprehensive Security Checklist for SD-WAN Implementation
- Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to isolate different parts of the SD-WAN network. This limits the impact of a security breach to a specific segment, preventing its spread across the entire network.
- Firewall Configuration: Ensure firewalls are correctly configured to control traffic flow, blocking unauthorized access and enforcing security policies. This includes configuring firewall rules to prevent malicious traffic and to control access to sensitive resources.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS solutions to monitor network traffic for malicious activity and automatically block threats.
- Endpoint Security: Implement strong endpoint security measures on all devices connected to the SD-WAN network, such as antivirus and anti-malware software, and enforce security policies on them.
- Access Control: Implement strong access controls to restrict access to network resources based on user roles and permissions. This involves user authentication, authorization, and access management. Multi-factor authentication is highly recommended.
Different Security Approaches to Securing a SD-WAN Environment
- Zero Trust Security: This approach assumes no implicit trust in any user, device, or network resource, requiring verification of every access attempt. This is particularly valuable for SD-WAN’s distributed architecture.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): This strategy helps in maintaining a consistent security posture across cloud environments. It ensures that the SD-WAN’s cloud services adhere to the organization’s security policies.
- Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP): This approach creates a virtual perimeter around applications and data, allowing only authorized users and devices to access them, regardless of their location. It helps in securing access to cloud resources.
Cost Analysis and ROI
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN is an exciting prospect, but the financial implications are crucial to understand. A thorough cost analysis and a clear ROI calculation are essential for making an informed decision. This involves understanding the initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and potential savings to determine the overall value proposition.This section dives deep into the financial aspects of the migration, providing insights into cost implications, ROI calculation methodologies, and real-world examples to demonstrate the potential savings and factors influencing the total cost of ownership.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of the financial landscape is key to ensuring a successful SD-WAN implementation.
Cost Implications of the Migration
The migration to SD-WAN involves both upfront and ongoing costs. Upfront costs encompass the purchase of new SD-WAN equipment, software licenses, and potential consulting fees for the implementation process. Ongoing costs include subscription fees for SD-WAN services, network management, and maintenance. Careful planning and budgeting for these costs are critical to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the ROI for an SD-WAN migration involves comparing the costs of the existing MPLS network with the anticipated costs of the SD-WAN solution over a specific timeframe. The formula for ROI is generally: (Total Savings – Total Costs) / Total Costs. This calculation quantifies the financial benefit derived from the investment in SD-WAN.
Examples of Cost Savings with SD-WAN
SD-WAN can significantly reduce costs in several areas. Reduced bandwidth costs are often a major factor, as SD-WAN allows for more efficient use of available bandwidth and can often optimize bandwidth consumption. Furthermore, reduced long-distance data transmission costs can lead to substantial savings, especially for organizations with geographically dispersed locations. Additionally, optimized network management and reduced operational expenses can contribute to significant savings.
Factors Affecting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of SD-WAN
Several factors influence the overall cost of ownership of an SD-WAN solution. These include the size and complexity of the network, the number of locations involved, the type of SD-WAN services chosen, and the level of ongoing maintenance and support required. Network complexity and the number of locations play a significant role in determining the complexity and cost of the migration process.
Moreover, choosing the right SD-WAN service provider, understanding the specific requirements, and having a comprehensive support strategy are critical for managing TCO.
Comparing MPLS and SD-WAN Costs (3-Year Projection)
This table illustrates a hypothetical comparison of MPLS and SD-WAN costs over a three-year period, demonstrating the potential savings achievable with SD-WAN. These costs are illustrative and should be tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of the organization.
| Year | MPLS Cost | SD-WAN Cost | Cost Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $150,000 | $120,000 | $30,000 |
| 2 | $155,000 | $125,000 | $30,000 |
| 3 | $160,000 | $130,000 | $30,000 |
| Total | $465,000 | $375,000 | $90,000 |
Illustrative Scenarios
Migrating from a legacy MPLS network to a more flexible and scalable SD-WAN solution is a significant undertaking. Understanding the potential challenges and successes through real-world examples and hypothetical scenarios provides invaluable insight. These scenarios highlight the diverse applications of SD-WAN and the key considerations for a successful migration.This section delves into practical applications of SD-WAN, demonstrating its impact on business operations.
We will explore case studies, technical aspects, and the critical role of careful planning in achieving a smooth transition.
A Successful MPLS to SD-WAN Migration Case Study
A large retail chain, experiencing increasing latency and bandwidth limitations on its MPLS network, migrated to an SD-WAN solution. The company’s initial concerns centered around the complexity of the migration process and potential disruptions to its operations. The team addressed these concerns by thoroughly planning the migration, conducting extensive testing, and implementing a phased rollout. This approach minimized downtime and allowed for ongoing monitoring and adjustments during the transition.
The migration involved replacing the MPLS network with a hybrid SD-WAN solution that leveraged both cloud and on-premises resources. This approach provided greater flexibility in handling fluctuating bandwidth demands and optimizing network performance based on real-time traffic patterns. The results included a 20% reduction in network latency and a 15% improvement in application response times, significantly enhancing customer experience.
SD-WAN Impact on Application Performance
SD-WAN’s ability to dynamically route traffic across multiple connections has a profound impact on application performance. Consider a scenario where a company has geographically dispersed offices. An application, such as video conferencing, experiences high latency over the MPLS connection during peak hours. By migrating to SD-WAN, the network intelligently selects the optimal path based on factors like bandwidth availability and latency.
This ensures consistent and reliable application performance across all locations, regardless of network congestion. The impact is particularly noticeable in applications with real-time requirements, where consistent low latency is paramount. For example, a call center experiencing audio delays with customers would benefit significantly from SD-WAN’s dynamic routing capabilities.
Hypothetical Migration Journey: TechCo
TechCo, a software development company with offices in three cities, faced increasing costs and declining performance with its legacy MPLS network. Their initial steps included evaluating their current network infrastructure, identifying application performance bottlenecks, and assessing the potential of SD-WAN. They then defined clear migration goals, including a 15% reduction in network costs and a 10% improvement in application responsiveness.
The migration strategy included a phased rollout, beginning with the least critical location and gradually expanding to others. This approach allowed for a controlled testing environment and minimized potential service disruptions. Crucial technical aspects included implementing a network segmentation strategy, ensuring security protocols were in place, and incorporating a robust monitoring and management system. The successful implementation required careful consideration of the existing network architecture, the specific needs of applications, and the security requirements.
Technical Aspects of the Migration and Success Factors
Successful SD-WAN migrations hinge on meticulous planning and execution. Critical technical aspects include:
- Network Architecture Assessment: A comprehensive analysis of the current network architecture is essential to determine the optimal SD-WAN deployment model, including hybrid, cloud-based, or on-premises options. A detailed assessment of existing network topology, devices, and applications will reveal potential challenges and opportunities.
- Application Performance Testing: Thorough testing of critical applications is paramount to identify potential performance bottlenecks and ensure a seamless transition. Simulating various traffic patterns, network conditions, and user loads is critical for verifying optimal performance.
- Security Considerations: Implementing robust security protocols is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining network integrity. SD-WAN solutions often incorporate advanced security features, such as encryption and access control, to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Phased Rollout: A phased rollout strategy is highly recommended, starting with pilot locations and gradually expanding to other sites. This approach allows for controlled testing and adjustments, minimizing potential service disruptions.
Ending Remarks: Mpls To Sd Wan Migration
Migrating from MPLS to SD-WAN presents a significant opportunity for businesses to enhance their network capabilities. This guide has provided a thorough roadmap, encompassing various crucial aspects from initial evaluation to ongoing optimization. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and strategies associated with this transition, organizations can confidently embrace the advantages of SD-WAN, optimizing their network performance and achieving significant cost savings and improved scalability.