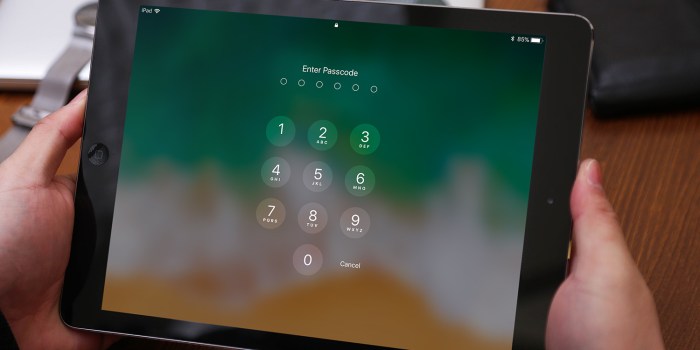
iOS 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint change is a crucial aspect of maintaining device security. This guide dives deep into understanding trusted devices, how fingerprint passcodes are implemented, and the steps to safely change them. We’ll explore various scenarios requiring a change, troubleshooting common issues, and security best practices. This detailed look covers everything from the fundamentals to advanced considerations, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently manage your iOS 11 device security.
Changing a fingerprint passcode on a trusted device in iOS 11 requires careful attention to detail. The process involves verifying your identity, following specific steps, and understanding potential errors. This article provides a comprehensive walkthrough, comparing trusted device passcode changes to non-trusted device changes for a clearer understanding.
Introduction to Trusted Device Passcodes on iOS 11
Trusted devices in iOS 11 are a crucial security feature designed to enhance the protection of user data. They allow users to perform sensitive actions, like accessing certain app features or making purchases, without having to re-enter their primary device passcode every time. This streamlined approach significantly improves user experience while maintaining a high level of security. This system leverages the concept of trust between a primary device and a secondary “trusted” device.The implementation of passcodes for trusted devices in iOS 11 involves a cryptographic mechanism.
When a user designates a device as trusted, a unique cryptographic key pair is generated. This key pair is used to encrypt and authenticate communication between the primary and trusted devices. This process ensures that only authorized devices can access sensitive information or perform specific actions. The primary device retains the private key, while the trusted device holds the public key.
This separation of keys is critical to maintaining the security of the user’s data.
Trusted Device Passcode Implementation Details
The security of trusted devices relies heavily on the robust implementation of passcodes. A secure passcode is a fundamental element of this implementation. The system verifies that the passcode entered on the trusted device matches the one stored on the primary device, ensuring that only the intended user can access the trusted device. This verification process utilizes cryptographic hashing to protect the integrity of the passcode.
Importance of Trusted Devices in Maintaining Device Security
Trusted devices are essential in strengthening overall device security. They provide a convenient way for users to access their accounts and data without the hassle of constantly entering their primary device passcode. This streamlined approach not only enhances user experience but also minimizes the risk of unauthorized access. For instance, if a user frequently uses a secondary device for banking or shopping, trusted device passcodes eliminate the need for repeatedly entering the primary device’s complex passcode, thereby reducing the risk of human error and typos.
Types of Passcodes Supported
The system supports various passcode types, allowing users to choose the method they find most secure and convenient. These include numerical passcodes, alphanumeric passcodes, and even complex passcodes incorporating symbols. The complexity of the passcode directly impacts the security of the trusted device. The more complex the passcode, the harder it is for unauthorized individuals to guess it.
Security Implications of Relying on Trusted Devices
While trusted devices enhance convenience, relying on them also carries potential security implications. A compromised trusted device could potentially expose the user’s data. This is why it’s crucial for users to maintain the security of all their devices. Regularly updating the software on both the primary and trusted devices is vital to patch any vulnerabilities. Furthermore, users should avoid sharing their passcodes or using easily guessable passwords for their trusted devices.
Scenarios Requiring Trusted Device Passcode Changes
Several situations might necessitate a change to a trusted device’s passcode. A lost or stolen trusted device demands immediate passcode change to prevent unauthorized access. Similarly, if a user suspects their passcode has been compromised, a change is necessary. Furthermore, a change might be required after a significant period of inactivity on the trusted device to ensure security.
Changing your iOS 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint can be a bit tricky, but it’s important for security. This is especially relevant when considering the safety measures of ride-sharing services like Uber, which are constantly evolving. For example, ensuring your phone’s security is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to your account and potentially compromising your safety during rides.
Uber rideshare safety transportation details best practices for safe travel, but ultimately, secure device management remains key to a secure experience. So, take the time to adjust your passcode and fingerprint for a more secure mobile experience.
Finally, changes are recommended if the user wishes to improve the complexity of the passcode for enhanced security.
Changing a Fingerprint Passcode on a Trusted Device
Modifying your fingerprint passcode on a trusted device allows for security updates and enhanced personal privacy. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your device’s security features. A well-managed passcode ensures only authorized users can access sensitive information.Changing a fingerprint passcode on a trusted iOS device is a straightforward process, but adhering to the correct steps is essential to avoid potential issues.
This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough, including verification methods and troubleshooting steps for common errors.
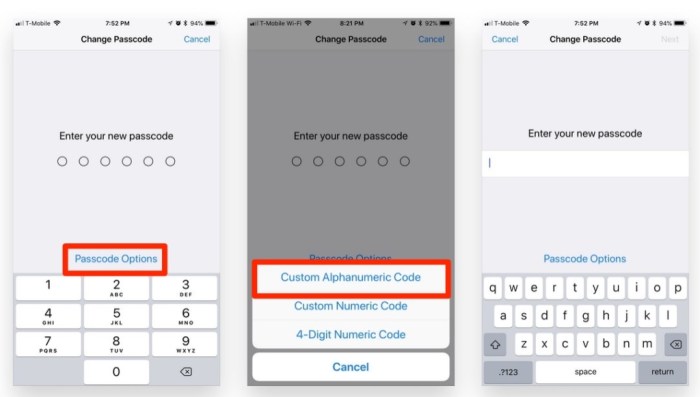
Steps for Changing a Fingerprint Passcode
This section Artikels the precise steps required to change your fingerprint passcode on a trusted iOS device. Following these steps diligently is key to preventing errors and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Launch Settings: Open the Settings app on your iOS device.
- Navigate to Passcode: Tap on “Face ID & Passcode” or “Touch ID & Passcode” depending on your device’s security features.
- Enter Existing Passcode: Enter your current passcode. This verifies your identity and grants access to the passcode change settings.
- Change Passcode: Select “Change Passcode” or a similar option within the Passcode settings.
- Create New Passcode: Enter your desired new passcode, then re-enter it to confirm.
- Confirm with Fingerprint: Authenticate the new passcode with your fingerprint or Face ID for added security.
- Verification: The system will confirm the new passcode change, ensuring the updated passcode is secure.
Verification Methods
Validating your identity during the passcode change process is paramount to preventing unauthorized access. The following methods are typically used:
- Current Passcode Entry: Entering your current passcode acts as a primary verification step, ensuring the user attempting to modify the passcode is the legitimate owner of the device.
- Fingerprint or Face ID Authentication: Using your registered biometric data (fingerprint or Face ID) adds a further layer of security. This biometrics-based verification method is critical for ensuring only the device owner can change the passcode.
Potential Errors and Troubleshooting
Several errors might occur during the passcode change process. Recognizing these errors and implementing appropriate troubleshooting steps is essential.
- Incorrect Passcode Entry: Repeated incorrect passcode entries can lead to temporary lockouts. If this happens, wait for the specified time period before attempting again.
- Biometric Verification Failure: If the fingerprint or Face ID fails to verify, check for obstructions or ensure proper placement for a successful authentication.
- Device Connectivity Issues: If the device experiences network or connectivity issues, it might disrupt the passcode change process. Ensure a stable internet connection.
- System Glitches: Occasional system glitches might affect the passcode change operation. Restarting the device could resolve such problems.
Comparison of Passcode Change Steps, Ios 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint change
| Feature | Trusted Device | Non-Trusted Device |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Access | Requires current passcode | May require activation lock bypass |
| Verification | Current passcode + Biometric | Usually only current passcode |
| Security | High, due to biometric validation | Medium, relies on passcode only |
Troubleshooting Issues with Passcode Changes
Changing a fingerprint passcode on a trusted device can sometimes present challenges. Understanding the potential problems and their solutions can significantly streamline the process and prevent frustration. This section dives into common issues, their causes, and effective troubleshooting strategies for iOS 11 trusted devices.
Common Passcode Change Issues
Troubleshooting passcode changes often involves identifying the root cause. These issues frequently stem from user errors, software glitches, or device limitations.
Changing your iOS 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint can be a bit tricky, but it’s crucial for security. Recent updates, like those for the Tile scan secure feature app, have highlighted the importance of regularly reviewing app permissions and potential unwanted tracking tags. For example, checking out the latest on tile scan secure feature app unwanted tracking tags update will help you stay on top of these issues.
Ultimately, remembering to keep your iOS 11 trusted device passcode secure is a key part of your overall digital safety strategy.
- Incorrect Passcode Entry: Repeated incorrect passcode entries can lead to temporary or permanent device lockouts. This is often due to typos, hasty input, or insufficient light/reflection on the sensor.
- Fingerprint Sensor Issues: Problems with the fingerprint sensor, such as smudges, dirt, or moisture, can prevent accurate recognition. The sensor’s quality can also affect the outcome.
- Device Software Glitches: Temporary software glitches can disrupt the passcode change process. This could manifest as freezing, errors during the process, or unexpected device restarts.
- Low Battery Levels: A low battery can cause the device to shut down during the passcode change process, leading to incomplete updates and issues.
- Incompatible Accessories: Certain accessories or cases might interfere with the fingerprint sensor, making accurate readings impossible.
- System Conflicts: Conflicts with other applications or system services can cause unpredictable behavior during passcode changes.
Troubleshooting Strategies
Effective solutions for these issues often depend on the specific problem. The troubleshooting steps are presented in a logical order.
- Incorrect Passcode Entry: Ensure adequate lighting, input the passcode slowly, and check for typos. If the issue persists, try restarting the device. As a last resort, contact Apple Support for advanced solutions.
- Fingerprint Sensor Issues: Clean the sensor gently with a soft, lint-free cloth. Ensure the sensor is dry and clear of debris. If the problem persists, check for incompatible accessories or cases that might be interfering.
- Device Software Glitches: Restart the device. If the issue persists, consider restoring the device to its factory settings. This is a drastic measure but can solve systemic issues.
- Low Battery Levels: Connect the device to a power source to ensure sufficient battery power during the passcode change process. If the problem persists, seek help from a technician.
- Incompatible Accessories: Temporarily remove any accessories or cases that might be interfering with the sensor. If the issue is resolved, you need to consider replacing the accessories or cases.
- System Conflicts: Close any running applications that might be consuming system resources. Restart the device, and if the issue continues, consider contacting Apple Support.
Best Practices for Preventing Passcode Change Problems
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the chances of encountering passcode change issues.
- Regular Device Maintenance: Keep the fingerprint sensor clean to maintain its functionality. Regular cleaning prevents smudges and dirt from accumulating.
- Stable Power Supply: Avoid using the device while the battery is low to prevent unexpected shutdowns during passcode changes.
- Software Updates: Keep the device’s software up to date to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Careful Passcode Input: Ensure the passcode is entered correctly and slowly to avoid typos.
Troubleshooting Summary Table
| Issue | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Passcode Entry | Typos, insufficient light, hasty input | Re-enter the passcode carefully, ensure sufficient light, restart device if needed |
| Fingerprint Sensor Issues | Smudges, dirt, moisture, incompatible accessories | Clean the sensor, remove interfering accessories, restart device |
| Device Software Glitches | System conflicts, temporary glitches | Restart the device, restore to factory settings if necessary |
| Low Battery Levels | Insufficient power | Connect to a power source |
| Incompatible Accessories | Interference with the sensor | Remove accessories, check for compatibility |
| System Conflicts | Application conflicts, resource contention | Close unnecessary apps, restart the device |
Security Considerations and Best Practices: Ios 11 Trusted Device Passcode Fingerprint Change
Protecting your trusted devices and the associated passcodes is paramount. This involves understanding potential vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures during passcode changes. A strong security posture for trusted devices hinges on vigilance and proactive measures. Ignoring these can lead to compromised data and unauthorized access.Changing a trusted device’s passcode is a critical security operation. It’s crucial to understand the security considerations and best practices to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your data.
This includes recognizing potential risks, implementing preventative measures, and understanding the security protocols employed during the process.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities and Risks
Security vulnerabilities can arise during passcode changes. Compromised devices or inadequate precautions during the change process can expose sensitive data. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors, resulting in unauthorized access. For example, if a user reuses the same password across multiple devices or fails to follow recommended security practices, the risk of a breach increases significantly.
Measures to Enhance Security During Passcode Changes
Several measures can enhance security during passcode changes. These include using strong, unique passcodes, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating passcodes. Implementing these measures helps fortify the security posture of the device and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
Security Protocols Employed During Passcode Change Process
Security protocols employed during the passcode change process are designed to safeguard the integrity of the data. These protocols often include encryption and authentication mechanisms to verify the user’s identity. For example, multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than one form of verification to confirm the user’s identity.
Importance of Regularly Reviewing and Updating Passcodes
Regularly reviewing and updating passcodes is essential. This proactive measure helps to ensure that the passcode remains strong and difficult to crack. Over time, passcodes can become susceptible to attacks if they are not updated. This can result in compromising the security of the trusted device.
Comparison of Security Methods for Trusted Device Management
Different security methods exist for managing trusted devices. These methods range from simple passcodes to more complex multi-factor authentication systems. The choice of method depends on the level of security required and the specific needs of the user. Stronger methods, like multi-factor authentication, offer enhanced protection against unauthorized access. This often comes at the cost of increased complexity in the setup and use.
Examples include security keys, biometrics, or hardware tokens. The most effective approach is a combination of strong passcodes, biometric authentication, and two-factor authentication.
Alternative Methods for Accessing Trusted Devices
Accessing your trusted iOS 11 devices shouldn’t always rely solely on passcodes or fingerprints. Alternative methods provide backup security and convenience, particularly in scenarios where primary authentication fails or is inconvenient. This section delves into these alternative options, highlighting their security implications and practical applications.
Overview of Alternative Access Methods
Trusted devices on iOS 11 offer a variety of secondary authentication methods beyond passcodes and biometrics. These methods enhance security and accessibility, allowing users to regain control in unforeseen circumstances. They provide a crucial safeguard against lockouts and ensure continued device functionality.
Activation and Utilization of Alternative Access Methods
Different alternative access methods have distinct activation procedures. Each method is designed with security in mind, requiring specific steps to ensure legitimate access. Understanding these procedures is vital for effective utilization.
- Recovery Key: This method involves generating a unique recovery key, which is a string of characters. Users can store this key in a secure location, separate from their device. In case of a forgotten or compromised passcode, the recovery key can be used to reset the passcode and regain access to the device. This method prioritizes security by requiring a separate, secure method of storage.
- Emergency Contact: Designating an emergency contact allows a trusted individual to remotely assist in resetting the passcode. This is a helpful option for situations where the user needs immediate assistance, but the recovery key isn’t immediately accessible. The security relies on establishing a trusted relationship with a designated contact.
- Trusted Third-Party Applications: Certain applications might integrate with trusted device passcode systems. These applications might provide alternative access mechanisms, potentially relying on their own authentication methods for verification. This integration requires a high level of trust in the third-party app and its security protocols.
Security Implications of Using Alternative Methods
Alternative access methods introduce various security considerations. Security relies on the appropriate implementation of each method. Compromise of these secondary access mechanisms could potentially jeopardize the security of the device.
- Recovery Key Security: Protecting the recovery key is paramount. Losing or exposing this key grants unauthorized access to the device. The recovery key’s security hinges on the user’s commitment to keeping it confidential and inaccessible to others.
- Emergency Contact Trust: Choosing a reliable emergency contact is crucial. Misplacing trust in an unreliable contact could lead to unauthorized access. The security of this method hinges on the user’s discretion in selecting a trustworthy contact.
- Third-Party Application Security: The security of third-party applications plays a vital role. A compromised application could potentially lead to unauthorized access through the alternative access method. Users must be cautious in selecting and utilizing such third-party integrations.
Procedures for Enabling and Disabling Alternative Access Methods
The activation and deactivation processes for each method vary. Following the correct procedures ensures proper functionality and security. Users must carefully review the steps for enabling and disabling each method to ensure proper configuration.
| Access Method | Enabling Procedure | Disabling Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Key | Generate the key, store securely, and note the key in a separate location. | The recovery key is typically not disabled; it’s meant for emergency situations. |
| Emergency Contact | Add a trusted contact and configure the necessary permissions. | Remove the emergency contact from the device’s settings. |
| Trusted Third-Party Applications | Install and configure the application, enabling the alternative access functionality. | Uninstall the application or disable the alternative access feature within the application settings. |
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks of Using Alternative Access Methods
Alternative methods are not without limitations. Their effectiveness hinges on careful planning and implementation. The user should consider the implications of each method.
- Recovery Key Management: Remembering and securely storing the recovery key is crucial. A lost or forgotten key can render the alternative method ineffective.
- Emergency Contact Reliance: Relying on an emergency contact assumes their availability and willingness to assist. The method’s success depends on the cooperation of the designated contact.
- Third-Party Application Dependence: Alternative access via third-party applications can be susceptible to issues related to the application’s security or functionality. The effectiveness of this method hinges on the reliability of the third-party app.
Passcode Change Implications for Other Features
Changing a trusted device passcode on iOS 11 isn’t just a simple security adjustment; it ripples through various interconnected features. Understanding these implications is crucial to avoid unexpected disruptions and ensure smooth functionality. This section details the potential effects on app access, security settings, backup options, and other critical areas.
Impact on App Access and Permissions
The trusted device passcode is a crucial component in controlling app access. When you change this passcode, apps that rely on the previously established credentials may encounter issues. These apps might require re-authentication or verification steps. For example, if a banking app was previously authorized on the trusted device, a new authentication process, potentially involving a one-time code, may be required after the passcode change.
Effect on Other Security Settings
Several security settings on iOS 11 are intrinsically linked to the trusted device passcode. A change in this passcode might affect features like two-factor authentication for accounts or the device’s general security posture. For example, if a two-factor authentication app utilizes the trusted device passcode for verification, the app will likely require re-registration after the change.
Influence on Data Backup and Recovery Options
Data backup and recovery procedures on iOS 11 often utilize the trusted device passcode for verification. Changing the passcode could necessitate re-authorization of backup services or the need for a new recovery key. This is especially true for iCloud backups, where the passcode plays a role in the security of the backup process. If you change your trusted device passcode, you may need to re-authenticate with iCloud to ensure continued access and the integrity of your backups.
Figuring out how to change your iOS 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint can be a bit tricky. Sometimes, the best way to troubleshoot is to record your Mac screen, especially if you’re struggling with the steps. Check out this guide on record your mac screen the easy way heres how to do it for a helpful walkthrough.
Hopefully, watching a screen recording will make the process of changing your iOS 11 trusted device passcode fingerprint much clearer.
Examples of Features Affected by the Passcode Change
A change in the trusted device passcode can affect several features, including:
- iCloud Drive: Access to files stored on iCloud Drive might be temporarily restricted or require re-authentication.
- FaceTime: If FaceTime was previously set up on the trusted device, a re-authentication step might be necessary.
- App Store Purchases: For apps that previously used the trusted device for purchase authentication, you may need to verify your identity again.
- Business Applications: Company-issued apps that rely on the trusted device passcode may need a new login sequence.
Summary Table: Passcode Change Impacts
| Feature | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| App Access | Re-authentication or verification required for some apps. |
| Security Settings | Potential disruption of two-factor authentication or other security procedures. |
| Data Backup/Recovery | Possible need for re-authorization or a new recovery key. |
| iCloud Drive | Temporary restriction or re-authentication for access. |
| FaceTime | Potential need for re-authentication. |
| App Store Purchases | Potential need for re-verification. |
| Business Applications | New login sequence might be required. |
Impact of iOS 11 Updates on Trusted Device Passcodes
iOS 11 introduced significant changes to how trusted device passcodes function on Apple devices. These updates aimed to enhance security and streamline the user experience, but also brought about some adjustments and considerations for users accustomed to previous versions. Understanding these changes is crucial for maintaining the security of your trusted devices.The iOS 11 updates to trusted device passcodes reflect Apple’s ongoing commitment to improving security protocols.
This evolution in security features is a continuous process, designed to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities in mobile operating systems.
Impact on Security Features and Procedures
The introduction of iOS 11 brought enhancements to the way trusted device passcodes were managed and enforced. These changes included more robust authentication methods, increased complexity for unauthorized access, and a refined user interface for passcode management. This resulted in a more secure environment for sensitive data on devices designated as trusted.
Compatibility Issues with Older Versions
Compatibility issues with older versions of iOS can arise when dealing with trusted device passcodes in iOS 11. Users relying on older devices running iOS versions prior to 11 might encounter challenges in accessing or managing trusted devices. This is because the new features and security protocols are tailored for the iOS 11 platform and later.
Impact on Existing Passcodes
Existing trusted device passcodes in iOS 10 or earlier might not be directly compatible with the iOS 11 system. Users need to ensure that they understand the changes and adapt their existing passcode management strategies to maintain security and functionality in the new environment. In many cases, an update to iOS 11 prompts users to set up a new trusted device passcode or re-authenticate existing ones to take advantage of the enhanced security measures.
Overall Management of Trusted Devices
The iOS 11 updates significantly improved the overall management of trusted devices. By integrating more robust authentication and streamlining the passcode process, Apple aimed to balance user convenience with enhanced security. This improvement extends to a more user-friendly approach to managing trusted devices.
Comparison of Passcode Management Features Across iOS 11 Versions
| iOS Version | Passcode Management Features |
|---|---|
| iOS 11.0 | Introduced enhanced passcode security, requiring a new passcode for existing trusted devices. |
| iOS 11.1 | Further refined passcode management, potentially including bug fixes and minor usability improvements. |
| iOS 11.2 – 11.x | Continued improvements in passcode management based on feedback and security vulnerabilities addressed. |
This table provides a concise overview of the evolving passcode management features across different iOS 11 versions. The table highlights the initial introduction of enhanced features in iOS 11.0 and the continuous improvements in subsequent versions. Understanding these changes is important to maintain a secure and efficient system for trusted device access.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, changing your iOS 11 trusted device fingerprint passcode is a manageable process when approached systematically. This guide provided a comprehensive overview of the steps, troubleshooting techniques, and security considerations. Understanding the potential impact on other features and alternative access methods is essential. By following the Artikeld procedures and best practices, you can maintain the highest level of security for your iOS 11 device.