How to archive android apps? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of preserving your Android app collection. From understanding the reasons behind archiving to exploring different methods, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to effectively manage your apps. Whether you’re decluttering your phone, preparing for a factory reset, or simply want to save a cherished app for later, this guide will walk you through the process, covering everything from built-in tools to third-party solutions, and even how to handle app data and settings.
We’ll examine the intricacies of archiving, comparing various methods and offering insights into their advantages and disadvantages. Furthermore, we’ll explore the crucial aspects of app permissions and privacy, ensuring a secure and informed archiving experience. Finally, we’ll delve into long-term storage and troubleshooting, so you can confidently archive and retrieve your apps for years to come.
Introduction to Archiving Android Apps
Archiving Android apps involves systematically saving and preserving application data, settings, and configurations for future use. This process differs from simply uninstalling an app, as it retains the app’s components for potential restoration or analysis. Archiving can be beneficial for various reasons, including maintaining backups for data recovery, preserving apps for later use on different devices, or even for historical analysis.Archiving Android apps isn’t merely a technical process; it’s a strategic approach to managing application data and user experiences.
Archiving Android apps is surprisingly straightforward. You can easily back up your apps to Google Drive or a cloud service. This process is quite useful for managing space on your phone and keeping your favorite apps safe. Speaking of managing apps, the recent Nissan Frontier Hardbody concept at the Chicago Auto Show ( nissan frontier hardbody concept chicago auto show ) showcased impressive tech features, but for now, let’s get back to the simple art of app archiving.
There are plenty of apps to explore, so backing them up is a good idea!
Understanding the nuances of archiving, including its different methods and potential pitfalls, is crucial for anyone working with Android app data management.
Reasons for Archiving Android Apps
Understanding the motivations behind archiving Android applications is key to grasping its utility. Preserving apps can address various needs, ranging from personal backups to professional use cases.
- Data Recovery: Users might want to archive apps to create backups of their data, settings, and app configurations. This allows them to restore their apps and associated data if the device is lost or damaged.
- Migration or Device Changes: Users might archive applications for easier migration to new devices or to use on different platforms. Archiving allows transferring app configurations and data without manual re-installation and configuration.
- Historical Preservation: Archiving apps can be useful for studying app usage patterns over time. Developers and researchers can gain insights into app evolution and user behavior through archived data.
- App Testing and Analysis: Archiving apps can help developers and testers analyze the application’s behavior under different conditions. This allows them to debug issues, identify performance bottlenecks, and optimize the app.
Benefits of Archiving Android Apps
Archiving Android applications provides several advantages, enhancing data security and app management. These benefits can apply to both personal and professional use cases.
- Data Security: Archiving apps provides an extra layer of security for user data, preserving it even if the device is lost or damaged. This data can be restored to a new device.
- Simplified App Management: Archiving apps facilitates a smoother app management process, enabling quick restoration or transfer of data between devices. This is especially helpful during device upgrades or changes.
- Improved Data Analysis: Archived data can be used to analyze app usage patterns, identify trends, and gain insights into user behavior. This data can be used to improve app design and functionality.
- Reduced Development Time: Developers can use archived app data for testing and analysis to pinpoint problems and optimize the app, which reduces the time needed to identify and solve issues.
Common Misconceptions About Archiving Android Apps
Several misconceptions surround the process of archiving Android apps. Understanding these will help to avoid potential pitfalls and misinterpretations.
- Archiving is the same as uninstalling: Archiving doesn’t delete the app from the device. It preserves the app’s configuration and data, while uninstalling removes the app entirely.
- Archiving is complex and time-consuming: While some archiving methods may involve intricate steps, many readily available solutions make the process relatively straightforward.
- Archiving is only for professionals: Archiving benefits individuals as well as businesses. Data backups, app transfers, and historical analyses are all valid personal use cases.
- Archiving doesn’t improve security: Archiving, when combined with proper backup strategies, can enhance data security by creating a copy of the data and app configuration.
Methods of Archiving Android Apps
Different methods for archiving Android apps cater to varying needs and technical expertise. A comparison table is provided below.
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Built-in Android Backup | Utilizes Android’s built-in backup and restore features. | Easy to use, readily available. | Limited customization, might not preserve all data. |
| Third-party App Archiving Tools | Specialized apps for comprehensive app archiving. | Greater customization, potentially preserves more data. | Requires additional software installation, learning curve. |
| Manual Archiving (using file managers) | Directly copying app data and configuration files. | Full control over the process. | Complex, requires technical understanding of app structure. |
Built-in Android Archiving Methods
Android offers several built-in ways to manage and potentially archive apps, depending on your needs and the specific Android version. These methods often involve moving apps to the “Downloaded” or “Other” sections of the app list, though the exact approach can vary slightly across different Android versions. This section explores how these built-in tools work and their limitations.While the built-in Android tools don’t directly offer a “true” archive function in the sense of creating a compressed backup, they provide ways to effectively manage and potentially declutter your app collection.
These methods are often simple and user-friendly, but they might not offer the same level of control or detail as dedicated third-party app management tools.
Built-in App Management Tools
These tools allow you to organize and uninstall apps, but don’t necessarily create a formal archive. Their primary purpose is to simplify app management. The functionality and interface vary with the Android version.
Steps for Managing Apps (General Approach)
The general process for managing apps on most Android devices is similar, but the exact steps may differ based on your device’s UI. Understanding the underlying mechanics is key to effective use.
- Open the “Apps” or “Applications” section of your device’s settings menu. This location may vary slightly based on the specific manufacturer or Android version.
- Locate the app you wish to manage. You’ll likely find a list of installed apps with options to open, uninstall, disable, or perform other actions.
- Select the app you wish to move. Common options include uninstall, disable, or a “move” or “manage” option.
- In some cases, the system may allow you to move the app to a “Downloaded” or “Other” section. This effectively separates the app from your active apps but doesn’t necessarily create a formal backup.
- You may be able to uninstall the app if it’s no longer needed. However, keep in mind that uninstalling an app typically removes all associated data.
Android OS Version and App Management Features
Different Android versions have different implementations of app management tools. This table illustrates some variations. The table shows how app management tools have evolved across different Android versions. This highlights the evolving capabilities and user experience offered by the built-in Android tools over time.
Archiving Android apps is a breeze! Just head to your device’s settings and find the app management section. Once there, you can easily identify and move apps to the archive, freeing up space on your phone. But while you’re optimizing your phone, have you considered which color Galaxy Buds 2 Pro is best for your style? Which color Galaxy Buds 2 Pro should you buy depends on your preferences, and the best color is subjective.
No matter which color you choose, remember to check your app archive regularly to make sure you aren’t missing anything important.
| Android Version | Key App Management Features |
|---|---|
| Android 10 | Improved app permissions management; clear distinction between system and user apps. |
| Android 11 | Enhanced app permissions and more granular control over app behavior. |
| Android 12 | More streamlined UI for app management; better integration with other system settings. |
| Android 13 | Focus on privacy and security; improved controls for app access to system resources. |
Third-Party App Archiving Tools
Beyond the built-in Android archiving methods, third-party tools offer more extensive options and customization for managing app backups. These tools can automate the process, provide granular control over the archiving process, and often include features for restoring and managing archived apps. Choosing the right third-party tool depends on specific needs and budget.These tools extend beyond the basic functionality of built-in Android archiving methods, providing greater flexibility, customization, and automation for managing app backups.
They cater to different user requirements, ranging from simple backup solutions to more comprehensive management systems.
Popular Third-Party Tools
Several third-party applications provide solutions for archiving Android apps. These tools vary in features, pricing, and user experience. Some prominent examples include specialized app management utilities and broader backup solutions that can handle apps among other data.
- App Manager Pro: This tool focuses on app management, including backup and restore. It allows users to categorize and organize apps based on their needs, and offers granular control over app archiving.
- Backup and Restore Tools: Some broader backup and restore solutions, often integrated into a larger suite, can handle app backups. These may include features for selectively backing up apps or for backing up entire device data.
- Specialized App Archiving Apps: Some apps are dedicated solely to archiving Android apps. These applications may offer features like automatic backups, version history, and advanced filtering options for specific app types or criteria.
Comparison of Tools
Different third-party tools cater to varying user needs and preferences. Key differences in functionalities and capabilities can be critical to a successful archiving strategy. Considering these factors helps in selecting the appropriate tool.
- Backup Scope: Some tools focus on app-specific backups, while others offer broader backups encompassing the entire device. Consider the need for a comprehensive backup or if a focused app backup is sufficient.
- Customization Options: Some tools provide more granular control over which apps to back up and the frequency of backups. This is especially important if you need to maintain specific versions of apps or want to tailor the process to your individual needs.
- User Interface and Ease of Use: The user interface and overall usability can significantly affect the experience. A user-friendly interface can streamline the process, making it less intimidating for less technical users.
Features and Functionalities, How to archive android apps
The functionalities of these tools can vary significantly, offering different levels of automation, control, and features. Choosing the right tool depends on the desired functionalities.
- Automated Backups: Some tools allow for automatic scheduling of app backups, ensuring data is consistently backed up without manual intervention. This is particularly helpful for maintaining regular backups.
- Selective Backups: Users can selectively choose which apps to include in the backup process. This granular control allows for targeted backups and avoids unnecessary data duplication.
- Version History: Some tools maintain a history of app versions, enabling users to revert to previous versions if needed. This feature is particularly valuable for troubleshooting or recovering from issues.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The choice of third-party archiving tools should be based on a careful assessment of their benefits and potential drawbacks.
- Benefits: Increased flexibility, automation, and control over app backups. Enhanced customization options for individual needs. Potential for more comprehensive backup strategies.
- Drawbacks: Potential compatibility issues with certain apps or Android versions. Some tools might have a learning curve or require more technical understanding to fully utilize.
Pricing Models
The pricing models for third-party app archiving tools vary widely. This table provides a general overview of pricing models.
| Tool | Pricing Model | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| App Manager Pro | Subscription-based | Pricing tiers vary based on features and access levels. |
| Backup & Restore Suite | Subscription-based or one-time purchase | Often part of a larger suite with broader backup capabilities. |
| Specialized Archiving App | Free or Freemium | Free versions may have limited functionality, while premium versions offer more comprehensive features. |
Archiving App Data and Settings
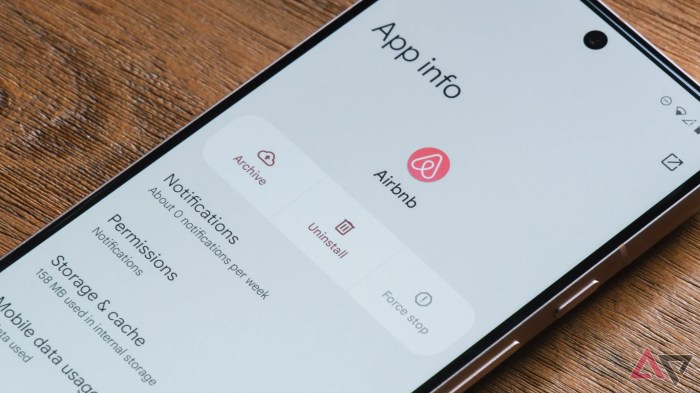
Archiving Android apps isn’t just about uninstalling them; it’s about preserving the valuable data and settings they hold. Often, we forget about the wealth of information apps store, from saved game progress to customized settings and contacts. This process ensures that this data isn’t lost when you uninstall or update the app, or even when your device experiences a hardware failure.
This section delves into the importance of backing up and restoring this data for a seamless transition.App data and settings encompass a wide array of user-specific information crucial for app functionality and user experience. These elements can be categorized into various types, each requiring a unique approach to archiving. This detailed examination ensures that no critical component is overlooked in the archiving process.
Importance of Archiving App Data and Settings
Archiving app data and settings is vital for several reasons. First, it safeguards your personal information and customizations, preventing loss due to app uninstalls, device resets, or other unexpected events. Second, it allows for a smooth transition when you upgrade or replace your device, as you can restore your customized settings and saved progress without starting from scratch.
Third, it provides a backup in case of app-related issues, allowing for easier troubleshooting and recovery.
Types of Data and Settings Archived
App data encompasses various components, including saved game progress, user preferences, settings, contact lists, and other user-specific data. Different apps handle this data differently, but common categories include:
- User Preferences: These include customized settings like notification preferences, display settings, and app-specific customizations.
- Saved Game Progress: Progress in games, including levels completed, characters unlocked, and other data specific to the game.
- App-Specific Data: This encompasses data unique to the app, such as notes, documents, or lists.
- Contacts and Calendars: If the app interacts with contacts or calendars, it might save entries or appointments.
Backing Up App Data and Settings Before Archiving
Before archiving apps, it’s essential to create backups of their data and settings. This process ensures you have a copy of the information if anything goes wrong during the archiving or restoration process. Several methods exist, including using the built-in Android backup tools or third-party backup solutions.
- Using Built-in Android Backup: Android offers built-in backup and restore capabilities. These options are accessible through the device’s settings. Ensure you have enabled automatic backup or manually back up the specific apps you wish to preserve.
- Third-Party Backup Solutions: Applications like Titanium Backup offer comprehensive backup solutions. These tools often provide more granular control over which app data to back up, but often require root access to the device.
Restoring App Data and Settings After Archiving
Restoring app data and settings is a straightforward process. The method depends on the backup method used. If you used Android’s built-in backup, restoration is often handled automatically. For third-party backup solutions, consult the application’s documentation for specific restoration procedures.
Archiving Android apps can be a lifesaver, especially when dealing with a cluttered phone. You can easily declutter your phone’s storage, but sometimes you might want to keep certain apps for future reference. While exploring ways to organize your digital life, consider personalizing your AirPods with cool stickers and decals – like those available at airpods stickers decal customization.
Ultimately, finding the right method for archiving Android apps comes down to your individual needs and storage preferences.
- Built-in Android Restore: Android will typically restore backed-up data automatically when you reinstall or update an app. However, you might need to manually trigger a restore if it doesn’t happen automatically.
- Third-Party Restore: The process for restoring from a third-party tool is usually described in the application’s documentation. Typically, you’ll need to import the backed-up data into the app.
Best Practices for Archiving App Data and Settings
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Backups | Perform backups of app data and settings at regular intervals to prevent data loss. |
| Specific App Backups | Back up only the apps whose data you want to preserve, instead of backing up everything. |
| Verify Backups | After backing up, verify that the backup is complete and contains the desired data. |
| Secure Storage | Store backups in a secure location to protect them from unauthorized access. |
| Restore Testing | Periodically test the restoration process to ensure that the data can be recovered correctly. |
Strategies for Archiving Multiple Apps
Archiving multiple Android apps simultaneously presents a unique set of challenges compared to archiving individual applications. Different approaches offer varying levels of control and efficiency, demanding careful consideration of the specific needs and priorities of the user. This section delves into various strategies for archiving numerous apps, highlighting the trade-offs involved in each approach.
Batch Archiving
Batch archiving involves grouping multiple apps together for a single archiving process. This approach is straightforward and efficient for users seeking a simple solution to archive a large number of applications. The process usually involves selecting a range of apps or checking a box to include apps, and then initiating the archiving procedure.
- Simplicity: Batch archiving provides a user-friendly method for managing multiple apps in one go, reducing the need for individual archiving for each application.
- Efficiency: The process is generally faster compared to manual archiving of each app. The time savings are particularly noticeable when archiving a large number of applications.
- Drawbacks: The single archiving process may not allow for customized settings or data preservation options for each app. Users may have to sacrifice some control over the archiving process for the sake of convenience.
Selective Archiving
Selective archiving allows users to choose specific apps for archiving individually. This strategy offers greater control over the archiving process, enabling users to preserve individual app settings and data with greater precision.
- Customization: This strategy allows for tailored archiving of each application, enabling users to archive specific apps based on their individual needs.
- Flexibility: Users can archive apps with specific data preservation requirements. This allows for greater control over the archiving process, ensuring that the most relevant data is preserved.
- Time-consuming: The manual approach can be time-intensive when archiving a large number of applications. This strategy may not be suitable for users who prioritize speed over control.
Scheduled Archiving
Scheduled archiving involves setting up a recurring archiving process for specific applications or groups of applications. This strategy is particularly beneficial for users who wish to regularly back up their apps or want to automatically archive data from apps at a certain frequency.
- Automation: This strategy allows users to automate the archiving process, ensuring that their applications are backed up automatically at a set interval, which helps to reduce the risk of data loss.
- Regularity: Users can configure the archiving process to occur at specified times or intervals. This ensures that important data is regularly backed up, which is useful for safeguarding against data loss.
- Complexity: Setting up a scheduled archiving process may require some technical knowledge or the use of a third-party tool. The initial setup can be more complex compared to other strategies.
Comparison Table
| Strategy | Efficiency | Effectiveness | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Archiving | High | Medium | Low |
| Selective Archiving | Low | High | High |
| Scheduled Archiving | Medium | High | Medium |
Choosing the Best Strategy
The optimal archiving strategy depends on the user’s specific needs and priorities. For users prioritizing speed and simplicity, batch archiving might be sufficient. Users who require precise control over data preservation should opt for selective archiving. For users seeking a balance between automation and control, scheduled archiving could be the ideal choice. Factors to consider include the number of apps, the desired level of customization, and the frequency of backups needed.
Understanding App Permissions and Privacy

Archiving Android apps, while offering significant benefits, necessitates careful consideration of app permissions and privacy implications. Knowing which permissions archiving tools require and how they are used is crucial for ensuring a smooth and secure archiving process. This section delves into the critical aspects of app permissions, providing insights into their role in archiving and strategies for managing them.App permissions are essentially the access rights an application requests from the Android operating system.
These permissions define what the app can do on your device, from accessing specific data to performing actions like sending notifications or accessing the camera. Understanding these permissions is essential for safeguarding your device’s security and personal information.
Permissions Required by Archiving Tools
Archiving tools, like those designed for app backups, need certain permissions to function effectively. These permissions allow the tool to access and interact with the app’s data and settings, enabling the creation of a complete archive. Without the necessary permissions, the archiving process might be incomplete or even fail altogether.
Importance of Understanding App Permissions
Understanding app permissions is paramount for responsible app use and data management. Permissions grant access to sensitive information, and an unaware user might inadvertently grant access to unauthorized parties. This understanding empowers users to make informed decisions about which apps they install and trust.
Examples of Permissions Used in Archiving Tools
Archiving tools frequently require permissions to read and write to files, access the device’s storage, and potentially interact with the app’s settings. For instance, if an archiving tool needs to create a backup file containing app data, it will require permission to access the storage location. Likewise, if the archiving tool needs to copy user preferences, it requires permission to access and read those preferences.
Managing App Permissions Related to Archiving
Managing app permissions in the context of archiving involves carefully evaluating the permissions required by the archiving tool. Users should grant permissions only if they understand the purpose of each permission. It is also essential to revoke permissions when the archiving process is complete, ensuring that the app no longer has unnecessary access. This practice safeguards privacy and prevents potential misuse.
Table Illustrating App Permissions and Their Relationship to Archiving
| Permission | Description | Relationship to Archiving |
|---|---|---|
| READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE | Allows access to files on the device’s storage. | Required for backing up app data files. |
| WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE | Allows writing to files on the device’s storage. | Required for creating the archive file. |
| ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION | Allows precise location access. | Potentially required for location-based app data. |
| READ_CONTACTS | Allows access to contact information. | Required if the app uses contacts, possibly in the archive. |
| GET_ACCOUNTS | Allows access to user accounts. | Might be needed for linking the archive to a user account. |
Troubleshooting Archiving Issues: How To Archive Android Apps
Archiving Android apps, while often straightforward, can sometimes encounter hiccups. Understanding the potential problems and their solutions is crucial for a smooth archiving experience. This section delves into common pitfalls and provides practical troubleshooting steps.Common issues that arise during the app archiving process can stem from various factors, including storage limitations, app-specific conflicts, or incorrect configuration settings. Effective troubleshooting involves identifying the root cause and applying appropriate solutions.
This section will guide you through the process of identifying and resolving these issues.
Identifying Storage Space Issues
Storage space limitations are a frequent hurdle during app archiving. Insufficient free space on your device’s internal storage or external SD card can lead to archiving failures. Analyzing your device’s storage usage is the first step in tackling this issue. Utilize the device’s built-in storage management tools to identify large files and unused applications that might be taking up valuable space.
Consider freeing up space by deleting unnecessary files, uninstalling unused apps, or moving data to cloud storage.
Troubleshooting App-Specific Conflicts
Some apps might have compatibility issues or internal data structures that hinder the archiving process. These conflicts can manifest as errors during the archiving procedure. To troubleshoot these issues, investigate if the app has any known compatibility problems with the archiving tool or method being used. Verify that the app’s data and settings are properly supported by the archiving process.
Checking for app updates or contacting the app developer for assistance may resolve these issues.
Addressing Configuration Errors
Incorrect configuration settings within the archiving tool or method can also lead to archiving failures. Ensure that the archiving tool’s settings are correctly configured for your device and the apps you wish to archive. Review the archiving tool’s documentation or support resources to verify the required settings and parameters. Verify that the correct storage locations are selected.
Consider seeking help from the archiving tool’s support community if needed.
Common Archiving Errors and Solutions
| Error | Potential Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Archiving process fails with “insufficient storage” | Insufficient free space on device storage | Free up storage space by deleting unnecessary files, uninstalling unused apps, or moving data to cloud storage. |
| Archiving process stops unexpectedly | App-specific incompatibility or conflicts | Verify app compatibility with the archiving tool. Update the app or contact the developer for support. |
| Archiving tool reports an error related to file permissions | Insufficient permissions to access app data | Ensure that the archiving tool has the necessary permissions to access the app’s data. Check the tool’s configuration or the operating system’s permission settings. |
| Archiving process hangs or takes excessively long | Slow device performance or heavy data volume | Ensure your device has sufficient processing power. Optimize the archiving process by batching or prioritizing smaller apps. Consider using a more efficient archiving tool. |
Long-Term Archiving and Storage
Archiving Android apps is a valuable practice for various reasons, including preserving access to older versions, maintaining historical data, and facilitating future development. However, effective long-term storage requires careful consideration of the chosen method and the security of the archived data. The longevity of the storage solution and the protection of sensitive information are crucial factors to address.
Best Practices for Long-Term Storage
Ensuring the longevity of archived apps and their data requires a multi-faceted approach. Data integrity, security, and accessibility are paramount considerations. Regular backups and version control are essential. Implementing robust encryption methods is vital for protecting sensitive data. Using a reliable storage system with redundancy and data mirroring is crucial to prevent data loss.
Understanding the limitations of each storage option and selecting the appropriate one for your needs is essential. Regularly reviewing and updating the storage strategy based on technological advancements and evolving security threats is a critical component of long-term preservation.
Storage Options for Archived Apps
Various storage options are available for archived apps, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice depends on factors such as storage capacity, security requirements, and accessibility needs.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage services offer scalability, accessibility, and redundancy. Popular services include Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive. These services often provide robust encryption features, but security still depends on the user’s account security. They are ideal for frequently accessed data or when geographical location or device portability are critical factors. Potential downsides include dependence on internet connectivity, potential service disruptions, and concerns about data privacy.
- Local Storage: Local storage involves using hard drives, external drives, or cloud storage that is physically located at a given site. It offers a high degree of control over security and accessibility, and is independent of internet connectivity. Data backup strategies are essential for this method. A major disadvantage is the potential for data loss due to physical damage or theft of the storage device.
- Specialized Archiving Systems: Specialized archiving systems are designed specifically for long-term storage. These systems offer advanced features for data management, security, and retrieval. They often integrate with backup and disaster recovery solutions, providing comprehensive data protection. A significant drawback is the higher initial investment and the need for specialized personnel to manage the system.
Data Security in Long-Term Archiving
Data security is paramount in long-term archiving. Robust encryption and access controls are critical to preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the security posture remains effective over time.
Examples of Long-Term Storage Solutions
Various solutions cater to different archiving needs. Some notable examples include dedicated archival servers with data replication, specialized cloud storage services with granular access controls, and offline hard drive backups with encryption. Choosing a solution depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, and the level of security required.
Comparison of Storage Options
| Storage Option | Accessibility | Security | Cost | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage | High (Internet access required) | Moderate (depends on provider and user configuration) | Variable (often pay-as-you-go) | High |
| Local Storage | High (physical access required) | High (if properly configured) | Variable (depends on storage device) | Moderate |
| Specialized Archiving Systems | Moderate (specific protocols) | High (often integrated security measures) | High (initial investment) | High |
Epilogue
In conclusion, archiving Android apps isn’t just about saving space; it’s about preserving your digital history and future access to valuable applications. This guide has provided a clear roadmap for effectively archiving your apps, offering a blend of built-in methods and powerful third-party tools. By understanding the nuances of app data, permissions, and long-term storage, you can confidently manage your Android app collection.
Now you’re empowered to archive your Android apps with ease and confidence!




