Google Wear OS tiles widgets new feature announced! This exciting update promises a more intuitive and personalized smartwatch experience. Currently, Wear OS tiles and widgets offer a range of functionalities, from quick access to information to controlling apps. This new feature builds on that foundation, introducing innovative ways to interact with your smartwatch and enhance its usefulness.
Expect to see improved organization, efficiency, and personalized experiences. The historical evolution of tiles and widgets on Wear OS devices is fascinating, showcasing how they’ve become essential elements of the smartwatch user interface.
This new feature is a significant step forward in Wear OS functionality. It will provide users with new ways to customize and interact with their devices, potentially changing the way we interact with our smartwatches. By adding these new elements, Google aims to enhance the overall user experience and keep pace with the evolving needs of smartwatch users.
Introduction to Wear OS Tiles and Widgets
Wear OS tiles and widgets are essential components of the user experience on smartwatches. They provide quick access to frequently used apps, information, and settings, enhancing efficiency and usability. These interactive elements allow users to perform actions or view information without opening the full app.The functionality of Wear OS tiles and widgets has evolved significantly since their initial introduction.
Early versions primarily focused on displaying static information like time, weather, and calendar events. Modern iterations leverage the growing processing power of smartwatches, enabling more complex functionalities, dynamic updates, and interactive elements. This evolution reflects a wider trend in mobile operating systems to prioritize user experience and efficiency.
Current Functionalities of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets
Wear OS tiles and widgets are designed to offer a streamlined way to interact with essential services and apps. Typical functionalities include displaying real-time data like the current time, weather updates, upcoming appointments, and step counts. Users can also perform actions such as starting a workout, sending a quick message, or adjusting their device’s settings through these interfaces.
The ability to customize these tiles and widgets allows users to tailor their experience to their specific needs.
Historical Context of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets
The evolution of Wear OS tiles and widgets mirrors the advancement of smartwatch technology. Early devices primarily showcased static information, like the time and date. As processing power and screen real estate increased, more dynamic displays and interactive elements became possible. The integration of third-party apps further enriched the functionalities, enabling users to access essential services directly from their wrist.
Google’s Wear OS just announced some cool new tile widgets, which is exciting! It’s a major update, and I’m already picturing how useful they’ll be. Speaking of smartwatches, Tag Heuer’s 3rd generation connected smartwatch, designed for sports enthusiasts , looks seriously impressive. Hopefully, Google’s new widgets will bring a similar level of innovation to the Wear OS ecosystem.
It’s definitely a step in the right direction for a more engaging user experience.
User Experience with Wear OS Tiles and Widgets
The user experience revolves around simplicity and efficiency. Users can quickly access information and perform actions without navigating through complex menus. The intuitive design and responsiveness of these elements minimize cognitive load and maximize user engagement. A common design pattern involves a visual representation of the data, combined with simple interaction methods like taps and swipes. The intuitive nature of the user interface is crucial for ensuring seamless interaction with the smartwatch.
Types of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets
| Type | Functionality | User Interface Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Time Display | Displays the current time, potentially with date and day. | Digital clock, date display, and potentially a simple icon representing the day of the week. |
| Weather Tile | Displays current weather conditions, forecast, and temperature. | Icon representing weather conditions, temperature, and potentially a brief forecast summary. |
| Calendar Event | Displays upcoming appointments and reminders. | Date, time, and title of the event, potentially an icon representing the event’s nature. |
| Fitness Tracker | Displays fitness data like steps taken, distance covered, or calories burned. | Numerical values for steps, distance, or calories, progress bars, and potentially graphical representations of activity. |
| Messaging | Provides quick access to message threads and notifications. | Icon representing the app, number of unread messages, and possibly a preview of the message. |
The table above illustrates some common tile and widget types found on Wear OS devices. It highlights the variety of information and actions that users can access directly from their watch face. The diversity of tiles and widgets on a device depends on the specific app integrations and the user’s preferences.
New Feature Overview
The recent announcement of enhanced Wear OS tiles and widgets introduces exciting possibilities for users. These improvements aim to provide a more intuitive and engaging experience for interacting with information on smartwatches. The new features are designed to streamline access to critical data and functions, allowing users to quickly glance at important details without needing to navigate through complex menus.The updated framework for tiles and widgets promises a significant advancement in how users interact with their smartwatches.
These updates focus on improving usability and efficiency, making the smartwatch experience more streamlined and personalized. By allowing greater customization and integration with other apps, these enhancements promise a more dynamic and relevant display of information directly on the wrist.
Enhanced Customization Options
Wear OS now allows for more granular control over tile layouts and appearances. Users can arrange tiles in various configurations, including custom rows and columns, offering more flexibility in how information is presented. This personalization feature significantly improves the user experience by enabling a tailored display to individual preferences and needs. Imagine a user who wants to see their workout data, upcoming calendar events, and current weather, all presented on the watch face.
This feature lets them precisely arrange these elements in the preferred format.
Dynamic Data Refresh
The new widgets now offer dynamic data updates, providing real-time information. This is a significant improvement over previous static displays. For example, a weather widget would update every few minutes with the latest conditions, providing users with current and accurate data for making decisions on the go. The refresh rate is customizable to balance data accuracy with battery life, providing users with a level of control over the balance between up-to-date data and battery consumption.
Integration with Third-Party Apps
The expanded API allows for deeper integration with third-party applications. This means users can now have a broader range of data displayed directly on their watch face, such as fitness tracking metrics, financial updates, or news summaries from preferred sources. For instance, a user subscribed to a particular news source could have a dedicated widget displaying headlines and summaries on their watch.
Table of New Features
| Feature Name | Description | Anticipated Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Customization | Allows users to arrange tiles in various configurations (rows, columns, etc.) for a personalized display. | Improved user experience through a tailored and intuitive presentation of information. |
| Dynamic Data Refresh | Widgets update in real-time, providing users with current and accurate data, customizable to balance data accuracy and battery life. | Increased relevance and timeliness of information, enabling users to make informed decisions based on current conditions. |
| Third-Party App Integration | Allows deeper integration with third-party apps, enabling users to display a broader range of data on their watch face. | Greater flexibility in accessing and displaying essential data from various applications, enhancing the overall utility of the smartwatch. |
User Impact and Potential
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets introduce a fresh approach to interacting with smartwatches, promising a more intuitive and efficient user experience. The potential benefits are significant, but challenges remain, particularly in ensuring seamless integration with existing apps and avoiding overwhelming users with too many options. The key is striking a balance between enhanced functionality and user-friendliness.
Anticipated User Impact
The new features are poised to significantly impact user interaction with their Wear OS devices. Users will likely experience a more streamlined and personalized experience, with quick access to essential information and actions. This can lead to greater efficiency in daily tasks, from checking notifications to managing appointments. However, the potential for a negative impact exists if the features are not implemented thoughtfully, leading to a cluttered or confusing interface.
Positive Impacts on Efficiency and Personalization
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets offer a powerful opportunity to enhance user efficiency. By providing quick access to frequently used information and actions, users can save time and effort. Personalization is another key benefit. Users can tailor their watch faces and widgets to display the information most relevant to their needs, creating a truly customized experience. This customization is likely to enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
One potential drawback is the potential for information overload. A proliferation of widgets could lead to a cluttered and distracting watch face. Careful design is crucial to ensure that only the most essential information is presented. Another limitation is the need for app developers to support these new features. If app developers do not embrace this new functionality, the benefits may be limited to specific apps.
Finally, ensuring compatibility across various devices and operating systems is critical to a smooth user experience.
Scenarios for User Benefit
| Scenario | Benefit | Associated Action |
|---|---|---|
| Checking flight status during travel | Quick access to real-time flight updates without opening a full app. | Adding a flight status widget to the watch face. |
| Managing daily tasks and appointments | Easy access to calendar entries, reminders, and to-do lists. | Configuring widgets to display appointments and reminders. |
| Controlling music playback on the go | Conveniently controlling playback without having to pull out a phone. | Using a music playback widget to skip tracks or adjust volume. |
| Monitoring fitness progress | Real-time view of workout data without needing to open the full app. | Adding a fitness tracker widget to the watch face. |
| Accessing and responding to messages | Quick glance at messages and quick responses without opening the phone. | Adding a message widget to the watch face and responding using voice commands or simple text. |
Technical Aspects
The introduction of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets brings significant technical advancements to the platform. This section delves into the core mechanisms powering these new features, outlining the design choices, potential hurdles, and the specifications underpinning the user experience.The implementation of Tiles and Widgets requires a robust architecture capable of handling dynamic updates, diverse widget types, and seamless integration with existing Wear OS components.
Google just dropped some exciting new features for Wear OS tiles and widgets! It’s super cool to see the evolution of these interfaces, especially considering the recent news about the upcoming God of War prequel comic series, detailing Kratos’s journey between God of War III and God of War. This new comic, God of War prequel comic show kratos story between God of War III and God of War , promises to flesh out the mythology around the iconic character.
Ultimately, these new Wear OS features will be a game-changer for users, making it even more convenient to keep up with the latest updates and news.
Efficient data management and display optimization are crucial for a smooth user experience, especially on devices with limited resources.
Underlying Mechanisms
The new features leverage a modular architecture to manage widget display and interactions. Each tile and widget is treated as a separate component, allowing for independent updates and configurations. This modularity facilitates easier development and updates. A dedicated rendering engine is optimized for the low-power environments of Wear OS devices, handling complex layouts and animations efficiently.
Implementation Choices
The implementation of Tiles and Widgets prioritizes performance and power efficiency. A lightweight JSON-based configuration format simplifies the creation and customization of widgets. The use of a layered display approach allows for efficient rendering and avoids redundant calculations. This layered structure also enables the integration of different widget types and sizes.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
One challenge is ensuring compatibility across various Wear OS devices with differing screen sizes and hardware specifications. Solutions include adaptive layouts and rendering strategies that automatically adjust to the device’s capabilities. Another challenge is maintaining a consistent user experience across different widget types. This is addressed through a standardized API for interaction and a set of design guidelines for widget developers.
Technical Specifications
This table Artikels the key technical specifications of the new feature.
| Feature | Specification | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Widget Rendering Engine | Customizable | The engine supports different rendering styles and effects, enabling a wide variety of widget designs. |
| Configuration Format | JSON | JSON facilitates widget customization and configuration through a lightweight and easily parsable format. |
| Data Management | Background Processing | Background processes handle data fetching and updates, ensuring smooth operation without impacting the user interface. |
| Power Consumption | Optimized | Efficient algorithms and power management strategies minimize battery drain during widget operation. |
| Widget Size | Adaptive | Widgets adapt to different screen sizes on various Wear OS devices. |
| API | Standardized | A standardized API allows for consistent interactions and seamless integration between different widget types. |
Competitive Analysis

The introduction of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets marks a significant step in Google’s smartwatch strategy. Understanding how these features stack up against competitors is crucial for evaluating their potential impact on market share. This analysis delves into the competitive landscape, highlighting key differentiators and potential advantages.The new features aim to improve the user experience by providing quick access to essential information and actions directly on the watch face.
This approach contrasts with traditional smartwatch interfaces that often require navigating multiple menus. The ability to customize and personalize these tiles is a critical element, allowing users to tailor their watch experience to their specific needs.
Comparison with Competing Features
The smartwatch market is becoming increasingly competitive, with numerous brands vying for a share of the pie. Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch, and other offerings provide similar features for quick access to information and actions. However, the specific implementation and user experience may vary significantly.
| Feature | Comparison (e.g., Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch) | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Access to Information | Competitors offer similar features, but the degree of customization and integration with other Google services might be different. For example, Apple Watch often emphasizes integration with the broader Apple ecosystem. | Wear OS’s advantage lies in its potential to leverage Google services for a more comprehensive experience. |
| Customization Options | Both Apple Watch and Samsung Galaxy Watch offer a range of customization options, but the specifics and depth of personalization may differ. | Wear OS’s strength is its focus on dynamic customization, offering users greater control over their watch face and information display. |
| Widget Integration | Some competing smartwatches allow widgets, but the level of integration and compatibility with various third-party apps might vary. | The potential of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets is in their ability to provide a more unified and user-friendly experience through a seamless integration of various services and apps. |
Differentiation and Advantages
A key differentiator for Wear OS Tiles and Widgets is their potential to leverage Google’s ecosystem of services. This allows for a more seamless and integrated user experience. For example, quick access to calendar appointments, or notifications from Google apps, can be tailored directly on the watch face.Furthermore, the dynamic nature of the tiles, allowing for updates and changes in real-time, is a distinct advantage.
Google’s Wear OS just dropped some exciting new tiles and widgets, promising a more personalized and intuitive experience. It’s interesting to see this new functionality emerge, but it’s also worth noting that the creator of the iconic Flappy Bird, Dong Nguyen, isn’t involved in the new game development, as reported on this site. Overall, these Wear OS updates are a welcome addition to the smartwatch ecosystem.
This stands in contrast to static widgets found on some competing smartwatches. This ability to react to real-time updates is crucial for staying informed about relevant information without constantly checking the phone.
Market Position and Competitive Landscape
Wear OS currently holds a relatively smaller market share compared to Apple Watch. The introduction of Tiles and Widgets, however, aims to enhance the platform’s appeal to users seeking a more versatile and customizable smartwatch experience. The market is characterized by strong competition from established brands, making differentiation a key factor in gaining traction.
Impact on Google’s Market Share
The success of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets will depend on several factors, including user adoption, app developer support, and overall user satisfaction. A positive user experience and extensive app integration will drive increased user engagement and contribute to a noticeable increase in Google’s market share within the smartwatch sector. This growth would be incremental, with continued development and expansion of the platform.
Design Considerations and User Interface
The design of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets prioritizes a clean, intuitive, and highly functional user experience. The goal was to create elements that seamlessly integrate with the existing Wear OS aesthetic while providing clear and actionable information at a glance. This approach aims to enhance user engagement and make the platform more valuable for everyday tasks.This new feature set balances the need for information density with the limited screen real estate of a smartwatch.
The design principles focus on maximizing the visual impact without sacrificing clarity or usability. The resulting design choices emphasize accessibility, allowing users with diverse needs to easily interact with the features.
Design Principles, Google wear os tiles widgets new feature announced
The design process adhered to core principles of simplicity, clarity, and accessibility. Prioritizing these factors ensures the widgets are easy to understand and use for a wide range of users. Visual hierarchy was paramount, guiding the user’s eye to the most crucial information.
User Interface Elements
The user interface incorporates several key elements designed for quick comprehension and interaction. These include:
- Interactive Tiles: These tiles are designed to be easily tappable, offering immediate access to actions or information. They are clearly delineated, making them readily identifiable on the watch face.
- Compact Information Displays: Information presented within the widgets is condensed to avoid clutter, yet retains critical data. Essential details are highlighted for quick scanning.
- Dynamic Updates: The widgets dynamically update with fresh data, keeping the information current and relevant. This dynamic nature keeps the user engaged and informed.
- Consistent Branding: The design elements align with existing Wear OS aesthetics, ensuring a cohesive and recognizable experience for users.
Visual Design Examples
Different visual designs were considered for the widgets, keeping in mind the need for clarity and visual appeal.
- Option 1: A weather widget displays current temperature, conditions (sunny, cloudy, rainy), and a simple icon for high/low temperatures. The temperature is presented in a large, bold font, while the conditions are in a slightly smaller, yet legible, font. A small, easily recognizable icon (e.g., sun for sunny) is used for the current conditions.
- Option 2: A fitness widget shows steps taken, distance covered, and current pace. These metrics are visually presented with clear labels and easy-to-read numerical values. Progress bars are used to represent the user’s current fitness levels, allowing for a quick overview.
- Option 3: A calendar widget shows upcoming appointments with a visual cue for the day and time of each appointment. Colors are used to differentiate appointments (e.g., work, personal) for quick identification. A small, simple icon might be included for each event.
Effectiveness and User Adoption
The new design elements are intended to enhance user engagement and interaction with Wear OS. The compact design allows users to access vital information quickly without needing to delve into complex menus. The dynamic updates ensure that the information displayed is always up-to-date, contributing to a sense of immediacy. The intuitive nature of the widgets is expected to lead to high user adoption rates.
Intuitive and Accessible Design
Accessibility was a critical design consideration. The use of clear visual cues, large fonts, and sufficient contrast ensures that the widgets are usable for individuals with visual impairments. The overall design is intended to be intuitive, enabling even novice users to easily understand and utilize the features.
Design Options Table
| Option | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Option 1 (Weather) | Displays current temperature, conditions, and high/low temperatures. | Provides quick, essential weather information in a clear format. |
| Option 2 (Fitness) | Shows steps, distance, and pace with progress bars. | Offers a concise overview of fitness progress. |
| Option 3 (Calendar) | Shows upcoming appointments with visual cues for time and type. | Allows quick access to upcoming events with clear distinctions. |
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Google Wear Os Tiles Widgets New Feature Announced
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets aim to be usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities. This section explores the accessibility features integrated into the new design, focusing on how diverse user needs are addressed, and pinpointing areas for improvement to ensure wider accessibility.The design process for Wear OS Tiles and Widgets considers various user needs and disabilities, ranging from visual impairments to motor skill challenges.
Implementing accessibility features is crucial to creating a more inclusive and user-friendly experience for all Wear OS users.
Accessibility Considerations for Diverse Needs
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets incorporate several features designed to enhance accessibility for users with varying needs. These features aim to make the information presented through tiles and widgets more readily available and usable for a wider range of users.
- Visual Contrast and Font Sizes: The new design emphasizes high contrast between text and backgrounds, and allows users to adjust font sizes for better readability. This feature is particularly important for users with low vision or visual impairments. This adaptability ensures that text is easily discernible across different display conditions.
- Haptic Feedback: Appropriate haptic feedback is provided for tile interactions. This ensures that users can perceive actions and changes even without visual cues, enhancing the usability for users with visual impairments. For example, a subtle vibration can confirm a selection, while a more pronounced vibration could signify an error.
- Voice Control and Text-to-Speech: Integration with voice control allows users to interact with tiles and widgets using voice commands. Text-to-speech capabilities allow users to hear the content of the tiles, facilitating access for users with visual impairments. This functionality enables users to control devices and access information without needing to use their hands. Furthermore, a user can quickly navigate the widgets using their voice.
- Customizable Layout and Order: The ability to customize the layout and order of tiles allows users to tailor their experience. This is especially helpful for users with cognitive differences who may find a particular arrangement more manageable.
Specific Examples of Accessibility in Action
Imagine a user with a visual impairment. They can use voice control to activate a specific widget to check the weather. The widget will verbally announce the current temperature, conditions, and forecast, eliminating the need for visual recognition. Alternatively, a user with limited mobility can easily interact with tiles using voice commands or a single-button press. Haptic feedback provides crucial confirmation of their actions, further improving their experience.
Areas for Further Improvement
While the initial features are a significant step forward, further improvements can enhance accessibility for a wider range of users. These include the following:
- Improved Voice Recognition Accuracy: Enhanced voice recognition accuracy can minimize misinterpretations, especially in noisy environments.
- Wider Range of Customization Options: Providing a broader range of customization options for font sizes, colors, and layouts can cater to diverse visual preferences and needs.
- Support for Assistive Technology: Incorporating support for assistive technologies like screen readers and screen magnifiers will further improve accessibility for users with visual impairments.
Table Demonstrating Accessibility Solutions
| Feature | Accessibility Consideration | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Voice Control | Limited Mobility | Users can interact with tiles and widgets using voice commands. |
| Haptic Feedback | Visual Impairment | Confirmation of actions and changes through vibrations. |
| Customizable Layout | Cognitive Differences | Users can tailor the arrangement of tiles to their preferences. |
| Text-to-Speech | Visual Impairment | Read aloud the content of tiles. |
Future Trends and Predictions
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets are poised to evolve significantly, mirroring the broader trend of increasing smartwatch sophistication and user expectations. The potential for personalization and contextual awareness is immense, leading to a more seamless and intuitive interaction with these devices. This section delves into predicted developments, enhancements, and future applications.The increasing integration of Wear OS with other Google services, such as Google Assistant and Google Calendar, will likely shape the future of tiles and widgets.
This integration will facilitate a more holistic and proactive user experience. We can expect greater functionality and more dynamic interactions between these components.
Potential Enhancements and Improvements
Wear OS Tiles and Widgets can be further enhanced through improved responsiveness and dynamic updating. Users will appreciate features that provide real-time information updates, reducing the need for constant manual checks. For example, a fitness tile could display not only current metrics but also projected progress towards daily goals. This dynamic element would elevate the experience beyond static displays.
Predicting the Evolution of Tiles and Widgets in the Smartwatch Market
The evolution of tiles and widgets in the smartwatch market will likely focus on enhanced interactivity and contextual awareness. Imagine a weather tile that not only displays the current forecast but also dynamically adjusts its presentation based on the user’s current location and upcoming activities. Personalized recommendations, based on user activity, will be increasingly integrated into the design. Such improvements will create a more relevant and intuitive user interface.
Potential Use Cases and Applications
The future use cases for Wear OS Tiles and Widgets are extensive. A dedicated tile for managing travel plans, displaying real-time updates for flights and trains, is a prime example. Furthermore, a dedicated health and fitness tile could display personalized recommendations based on user activity and health data, guiding users towards healthier choices. These scenarios represent just a few of the many potential applications of Wear OS tiles and widgets.
Integration with Other Wearable Technologies
The seamless integration of Wear OS Tiles and Widgets with other wearable technologies, like fitness trackers and smart home systems, is highly probable. This integration will create a unified ecosystem, where information flows effortlessly between devices, providing a holistic view of the user’s life. For instance, a tile for managing smart home appliances could be linked to the user’s calendar, automatically adjusting settings based on scheduled events.
Personalized Recommendations and Dynamic Displays
Personalized recommendations and dynamic displays will play a significant role in the future of Wear OS tiles and widgets. A tile showcasing restaurant suggestions, customized based on the user’s dietary preferences and location, is a clear example. These dynamically updated widgets will provide more relevant and valuable information, enhancing user engagement.
Closing Summary
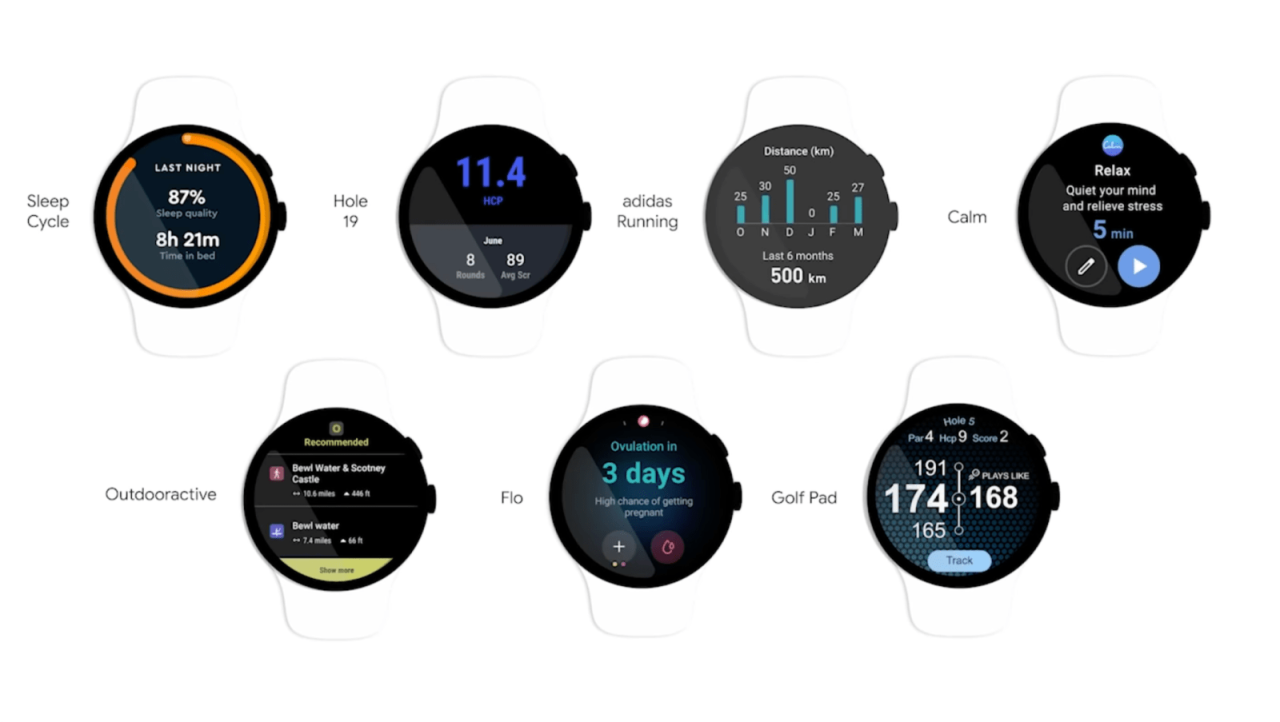
In conclusion, Google’s new Wear OS tiles and widgets features offer a compelling vision for the future of smartwatch interaction. The new features hold great potential to enhance user experience and make smartwatches even more useful in our daily lives. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are substantial, offering a glimpse into the future of smartwatch technology.




