Google passwords chrome fido2 webauthn fingerprint biometrics screen lock – Google passwords, Chrome, FIDO2, WebAuthn, fingerprint biometrics, and screen lock security are all critical elements in today’s digital world. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate workings of these technologies, exploring their individual strengths and how they integrate to create a robust security framework. We’ll cover everything from the basics of password management to the latest advancements in biometric authentication, ultimately showing how these advancements improve security and user experience for accessing Google accounts.
Traditional password systems have significant vulnerabilities, making them easily susceptible to breaches. This guide explores the evolution of security, showcasing how FIDO2 and biometrics provide a much more secure alternative. We’ll examine the practical implementation of these advanced technologies, from setup to troubleshooting, to help you understand and implement them effectively.
Introduction to Password Management and Security
Strong passwords and robust password management are crucial for online safety. Compromised accounts can lead to significant financial and personal losses, including identity theft and unauthorized access to sensitive information. This section delves into the importance of secure passwords, the vulnerabilities of traditional systems, and methods for enhancing online security.Password security is paramount in today’s interconnected world. A well-thought-out password strategy can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Understanding the vulnerabilities of traditional password systems and embracing advanced security measures are key to safeguarding online accounts and personal information.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Password Management
Effective password management is essential for mitigating risks associated with weak passwords. A strong password, combined with a robust password management system, creates a multi-layered defense against cyber threats. Weak passwords are easily cracked by automated tools and sophisticated algorithms, making them a significant vulnerability.
Methods for Creating Secure Passwords
Creating strong passwords is a crucial aspect of online security. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as birthdays, names, or common phrases. Instead, incorporate a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A longer password is generally more secure than a shorter one. A good rule of thumb is to aim for at least 12 characters.
A strong password is a crucial first line of defense against unauthorized access to online accounts.
Vulnerabilities of Traditional Password Systems
Traditional password systems face numerous vulnerabilities. Password reuse across multiple accounts is a significant risk. If one account is compromised, attackers gain access to all accounts using the same password. Password cracking tools and brute-force attacks are effective against weak passwords. Furthermore, phishing attacks and social engineering tactics can exploit human vulnerabilities to gain access to passwords.
Concept of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security beyond a password. It requires users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a code from an authenticator app, a security key, or a biometric scan. This significantly increases the difficulty for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have compromised the password.
Examples of Common Password Security Breaches
Numerous high-profile data breaches have exposed millions of user accounts due to weak passwords and inadequate security practices. These breaches often involve the exploitation of vulnerabilities in websites and applications, resulting in massive data leaks. The consequences can range from financial losses to reputational damage. For example, the Yahoo breach of 2013 exposed over 3 billion user accounts, highlighting the widespread impact of such incidents.
Comparison of Password Storage Methods
| Storage Method | Description | Security | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Passwords stored on the user’s device | Potentially high if the device is secure | Easy access on the device |
| Cloud | Passwords stored on a remote server | High if the service is secure and has robust security measures | Access from various devices with proper authentication |
Password storage methods vary in security and accessibility. Choosing the right method depends on the user’s needs and the level of security required. Local storage offers ease of access but carries risks if the device is compromised. Cloud storage, on the other hand, provides better security and accessibility across multiple devices.
Google Accounts and Password Management: Google Passwords Chrome Fido2 Webauthn Fingerprint Biometrics Screen Lock
Google’s approach to password management is multifaceted, encompassing robust security features, streamlined recovery processes, and a strong emphasis on user control. This comprehensive strategy aims to protect user accounts from unauthorized access while providing a secure and convenient experience. Understanding these elements is crucial for effectively managing your Google accounts and ensuring your data remains protected.Google’s password security features are designed to deter unauthorized access and protect user data.
These features often go beyond basic password requirements, implementing advanced techniques to enhance security. This includes measures like multi-factor authentication and secure password storage, which work in tandem to create a more robust security posture.
Google’s Password Security Features
Google employs a suite of security features to protect user accounts. These include strong password policies, requiring a minimum length and complexity, along with regular password updates. This approach aims to mitigate the risks associated with weak or easily guessed passwords. Furthermore, Google actively monitors user accounts for suspicious activity, alerting users to potential threats and enabling proactive security measures.
Password Recovery for Google Accounts
Google provides multiple avenues for password recovery, offering flexibility and user-friendliness. Users can often recover their passwords through various methods, such as answering security questions, utilizing recovery emails, or employing phone verification. The selection of the appropriate recovery method often depends on the user’s prior account setup and security preferences. This adaptability is a key component in Google’s approach to user security.
Comparison of Google’s Password Policies with Other Major Providers
Compared to other major providers, Google’s password policies often incorporate advanced security measures. The focus on multi-factor authentication and robust password storage stands out. While specific details of each provider’s policies may vary, Google often leads in the implementation of these crucial security measures. The specifics of these policies are dynamic and change with evolving threats and technological advancements.
Securing your Google accounts with features like Chrome’s FIDO2, WebAuthn, fingerprint biometrics, and screen lock is crucial. Thinking about how Google Maps might show transit crowding, expansion timelines, and insights into user trips, like on google maps transit crowdedness expansion timeline insights trips , is fascinating. Ultimately, both aspects underscore the importance of robust security measures for online accounts.
Role of Google Chrome in Password Management
Google Chrome plays a critical role in password management by acting as a centralized repository for stored credentials. It facilitates password auto-filling, simplifying login processes and minimizing the risk of forgotten or weak passwords. However, it’s essential to remember that the security of these stored passwords depends on the overall security posture of the user’s device and internet connection.
Google passwords, Chrome’s FIDO2, WebAuthn, fingerprint biometrics, and screen lock security are all important. But, checking out the MSI Raider GE76 gaming laptop, it’s clear that this laptop has the fastest performance in many aspects , which makes it a top choice for users who want smooth transitions between apps and programs. Ultimately, these security features, when combined with a high-performance machine, create a great user experience.
Security Measures Employed by Google in Protecting User Accounts
Google employs various security measures to protect user accounts. These include advanced threat detection systems, which actively monitor user accounts for suspicious activity. These systems identify and respond to potential threats, safeguarding accounts from malicious actors. Google also regularly updates its security protocols to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Setting Up 2-Factor Authentication with Google Accounts
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a critical security measure for protecting Google accounts. It adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification method beyond the password. This process adds a layer of protection that makes it significantly harder for attackers to access accounts, even if they obtain the password.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Navigate to your Google Account settings. |
| 2 | Locate the 2-factor authentication section. |
| 3 | Choose a verification method (e.g., phone, app). |
| 4 | Follow the prompts to complete the setup. |
| 5 | Enable 2FA for enhanced security. |
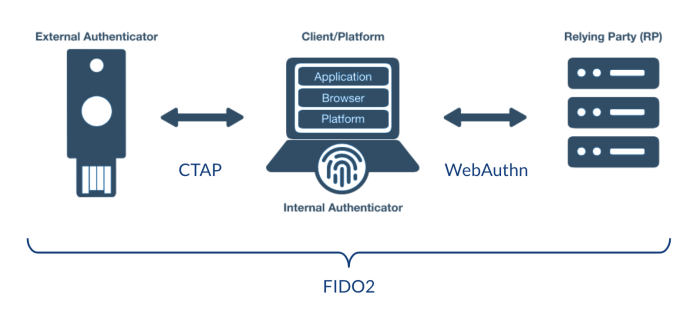
FIDO2 and WebAuthn Authentication
FIDO2 and WebAuthn represent a significant advancement in online security, offering a more secure and convenient way to authenticate compared to traditional password-based systems. These standards provide a strong foundation for passwordless authentication, relying on hardware-based security keys or biometric authentication methods. This approach significantly reduces the risk of password breaches and enhances the overall security posture of online accounts.FIDO2 and WebAuthn are open authentication standards designed to provide a more secure way to access online accounts.
They work by leveraging cryptographic keys stored securely on devices, such as security keys or the user’s own biometric data. This approach bypasses the vulnerability of relying solely on passwords, which can be compromised or guessed. The authentication process is more robust and significantly reduces the risk of phishing attacks.
Principles of FIDO2 and WebAuthn
FIDO2 (Fast Identity Online) and WebAuthn (Web Authentication) are standards that aim to improve security by leveraging cryptographic keys stored on secure hardware, rather than relying solely on passwords. These standards focus on creating a more secure and convenient way to authenticate online, removing the need for storing passwords on websites. The key principle is to create a strong authentication mechanism that doesn’t rely on vulnerable passwords.
Benefits of Using FIDO2 and WebAuthn
Implementing FIDO2 and WebAuthn offers several significant advantages. They improve security by eliminating the need for users to memorize and type passwords, reducing the risk of password breaches and associated issues. This also leads to a more convenient user experience, as authentication is streamlined and more efficient.
Security Advantages of FIDO2 over Traditional Passwords
FIDO2 and WebAuthn offer substantial security advantages over traditional password-based systems. Traditional passwords are susceptible to various attacks, including phishing, password cracking, and brute-force attempts. These methods are significantly more resistant to such attacks because the authentication process is tied to a hardware-based security key or biometric factors, making them significantly harder to compromise.
FIDO2-Compatible Devices
A wide range of devices support FIDO2, including security keys from various manufacturers, and many modern smartphones and laptops. The availability of FIDO2-compatible devices is constantly expanding, offering users more options for secure authentication.
Comparison of FIDO2 to Other Authentication Methods
FIDO2 and WebAuthn stand out by offering a strong alternative to traditional password systems and other authentication methods. Compared to SMS-based authentication or one-time passwords, FIDO2 and WebAuthn provide a higher level of security by not relying on easily intercepted communication channels. Additionally, FIDO2 offers a more convenient and less error-prone user experience than multi-factor authentication methods that require users to input multiple codes or tokens.
Securing your Google passwords using Chrome’s FIDO2, WebAuthn, fingerprint, and biometrics screen lock is crucial. Modern security relies heavily on these methods, but sometimes you just need a break from the digital world. That’s where fantastic headphones like the motorizer over-ear headphones come in, offering immersive sound and a welcome escape. Even while enjoying the ultimate listening experience, you can rest assured your digital security remains top-notch thanks to those same robust Google password protections.
Security Strengths Comparison: FIDO2 vs. Traditional Passwords
| Feature | FIDO2/WebAuthn | Traditional Passwords |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High, leveraging hardware-based keys or biometrics | Low, susceptible to various attacks |
| Convenience | High, streamlined authentication process | Low, requires memorization and typing |
| Password Storage | No passwords stored on websites | Passwords stored on websites, increasing vulnerability |
| Vulnerability to Phishing | Lower, relying on device security | High, susceptible to phishing attacks |
Biometrics and Screen Lock Security
Biometric authentication, utilizing unique physical characteristics like fingerprints and facial features, is increasingly prevalent in modern security systems. This approach offers a compelling alternative to traditional password-based methods, promising enhanced security and user convenience. However, the implementation and security of biometric systems require careful consideration of various factors.Implementing biometric authentication systems involves integrating them into various applications, from unlocking smartphones to verifying user identities for online transactions.
The seamless integration of these systems into our daily lives has led to a shift towards a more user-friendly and secure digital landscape.
Fingerprint Authentication
Fingerprint authentication relies on the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual’s fingertips. Scanning devices capture these patterns, converting them into digital templates for comparison with stored data. This process is typically fast and convenient, often integrated into smartphones and laptops for quick access.
Facial Recognition Authentication
Facial recognition authentication uses advanced algorithms to analyze facial features, such as the distance between eyes, nose shape, and jawline. Sophisticated cameras capture facial images, and algorithms extract key features for comparison with pre-existing templates. This method is increasingly used in security applications, including access control and online authentication.
Implementation of Biometrics in Various Applications
Biometric authentication is widely implemented across diverse applications. Smartphones frequently use fingerprint sensors for unlocking devices and authorizing transactions. In corporate settings, biometric systems can control access to buildings and sensitive data. Online banking and e-commerce platforms utilize biometric authentication for enhanced security. Furthermore, biometric identification is used for border control and law enforcement.
Security Considerations of Biometric Authentication
Security considerations for biometric authentication are paramount. The vulnerability of biometric data storage, potential for spoofing, and accuracy issues need careful attention. Data breaches, compromising the security of biometric templates, could have severe implications. Security protocols must be robust to mitigate the risks of spoofing attacks and ensure the accuracy of biometric recognition. The systems must also address the potential for false positives and false negatives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biometric Security
Biometric authentication offers several advantages. It provides a strong layer of security, often more resistant to brute-force attacks compared to passwords. It also enhances user experience by eliminating the need to remember complex passwords. However, biometric systems can be susceptible to spoofing, and the cost of implementation can be substantial. The potential for privacy violations must also be addressed.
Privacy Implications of Using Biometrics
Privacy concerns are significant when implementing biometric systems. The collection, storage, and use of biometric data raise questions about data security and potential misuse. Clear guidelines and regulations are needed to ensure the responsible use of biometric data and to safeguard user privacy. Data minimization, strict access controls, and transparency are critical for mitigating privacy risks.
Comparison of Biometric Authentication Methods
| Feature | Fingerprint Authentication | Facial Recognition Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Data Captured | Ridge and valley patterns of the fingerprint | Facial features like distance between eyes, nose shape, and jawline |
| Accuracy | Generally high accuracy, but can be affected by smudges or cuts on the finger | High accuracy, but can be affected by lighting conditions, facial expressions, and angle of the face |
| Speed | Fast, typically instantaneous | Speed varies depending on the complexity of the algorithm and the processing power of the device |
| Cost | Relatively low cost for implementation | Cost can be higher due to the need for sophisticated cameras and algorithms |
| Security | Vulnerable to spoofing with fake fingerprints | Vulnerable to spoofing with photos or masks |
Integration of Technologies
Google’s commitment to enhanced security extends beyond traditional password management. This integration seamlessly blends FIDO2 and biometric authentication into the Chrome browser and Google accounts, creating a multi-layered defense against unauthorized access. This approach leverages the strengths of each technology, ultimately improving the user experience and overall security posture.The core principle behind this integration is to provide users with a robust and convenient authentication system.
By combining FIDO2’s strong security with biometric factors like fingerprint or facial recognition, Google aims to reduce the risk of password compromise while also making account access faster and more intuitive.
FIDO2 and Biometric Integration in Chrome
FIDO2, a modern authentication standard, provides a secure key-based authentication method. This key is stored securely on a user’s device, typically on a hardware security module (HSM), and used to verify identity without relying on easily-compromised passwords. Chrome’s integration of FIDO2 enables users to log in to their Google accounts using these secure keys. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, adds an extra layer of security.
This combination offers a strong defense against unauthorized access attempts, as a successful attack would require compromising both the FIDO2 key and the biometric method.
Linking Google Passwords with FIDO2 Authentication
The process of linking Google passwords with FIDO2 authentication is streamlined and user-friendly. Users typically set up FIDO2 keys through the Chrome browser settings. The process often involves creating a key, adding it to their Google account, and then confirming its association. Once configured, the user can opt to use this FIDO2 key for all Google services requiring authentication.
User Experience with FIDO2 and Biometrics
The user experience for accessing Google accounts with FIDO2 and biometrics is intuitive and straightforward. Instead of entering passwords, users simply use their FIDO2 key or biometric method. This often involves a quick scan of a fingerprint or a facial recognition prompt, providing a significantly faster and more convenient login process. This streamlined approach reduces the friction associated with traditional password-based logins.
Setting up and Managing Biometric Screen Locks
Biometric screen locks, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, offer a secure way to protect a user’s device from unauthorized access. Setting up these locks typically involves enrolling the biometric method within the device’s settings. Management includes updating the enrollment information or adding new biometric methods as needed. The user’s device controls how this is managed.
Improving Account Security
By integrating FIDO2 and biometrics, Google accounts become significantly more secure. The combination of strong, key-based authentication with biometric verification greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. The removal of passwords as the primary authentication method significantly decreases the vulnerability to phishing or password-guessing attacks. This also contributes to a more secure overall user experience.
Password Management Integration Table
| Technology | Google Accounts | FIDO2 | Biometrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Management (Traditional) | Requires entering passwords for each service | Not directly integrated | Not directly integrated |
| FIDO2 Integration | Supports authentication via FIDO2 keys | Provides strong, key-based authentication | Complements FIDO2 for a multi-factor approach |
| Biometric Integration | Enhances security with biometric authentication | Complements FIDO2 for a multi-factor approach | Provides secure device access and authentication |
Security Best Practices
Protecting your Google account and passwords is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Robust security practices are crucial to safeguarding sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. This section delves into essential strategies for maintaining the highest levels of online security, focusing on password strength, multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and regular updates.
Password Security Fundamentals
Strong passwords are the cornerstone of online security. Weak passwords are easily cracked, leaving accounts vulnerable to attack. Password complexity is a key factor. Effective passwords combine upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Length also matters; longer passwords are harder to decipher.
Avoid using easily guessed information like birthdays, names, or pet names. A memorable, unique password for each account is vital. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security beyond a password. This involves using multiple verification methods to confirm user identity. If a hacker gains a password, MFA requires additional information (like a code sent to a phone or a verification from a trusted device) before access is granted. By enabling MFA, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized account access.
This crucial security measure is strongly recommended for all Google accounts.
Biometrics and Security
Biometric authentication, like fingerprint or facial recognition, offers a convenient and secure alternative to traditional passwords. Biometric systems leverage unique physical characteristics for identification. These systems enhance security by adding an extra layer of verification, making unauthorized access more challenging. However, it’s essential to understand the limitations and potential risks associated with biometrics. These systems rely on the integrity of the hardware and software, and the possibility of spoofing or compromise exists.
Careful consideration and ongoing security updates are crucial to mitigate risks.
Importance of Regular Updates
Regular security updates are vital for maintaining the security of your devices and software. Updates often patch vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. Software maintenance addresses critical security flaws and ensures that your systems are running on the most secure versions. Regularly updating your operating system, browser, and other applications is an active defense against emerging threats. Staying up-to-date helps prevent security breaches and keeps your accounts protected.
Secure Password Management in Chrome
Chrome offers several built-in features for managing passwords securely. These include automatic filling and suggestions for strong passwords. However, it’s important to use a password manager like a dedicated application or browser extension for comprehensive password security. Using a password manager is recommended for securely storing and managing all your passwords across different accounts. This centralized approach helps maintain strong passwords and prevents potential breaches.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Biometrics
Biometric authentication, while convenient, has potential risks. Compromised devices, vulnerabilities in the software, or even spoofing attempts can lead to unauthorized access. Regular security audits, and careful review of security settings, can help minimize these risks. Choosing strong passwords for your device, enabling MFA, and being cautious about suspicious apps and websites, are all critical steps to protect your biometric security.
Summary of Google Account and Password Security Best Practices
| Security Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Use unique, complex passwords for each account. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Enable MFA for all Google accounts. |
| Regular Updates | Keep all software and operating systems updated. |
| Secure Password Management | Utilize a password manager for strong and secure passwords. |
| Biometric Security | Understand the limitations and mitigate risks associated with biometrics. |
Illustrative Examples
Understanding how FIDO2, biometrics, and password managers work together is crucial for robust security. This section provides practical scenarios and troubleshooting steps to illustrate the effectiveness of these integrated security measures. From logging in with your fingerprint to recovering your account, we’ll break down the process in a clear and concise manner.
Accessing a Google Account with FIDO2 and Fingerprint Authentication
This scenario details the smooth login process using FIDO2 security keys and fingerprint authentication. Upon opening the Google Chrome browser, the user is presented with the login page. Instead of entering a password, the user is prompted to use their registered FIDO2 security key. Successfully inserting the key triggers a secure connection. Then, the browser requests biometric authentication, in this case, a fingerprint scan.
Upon successful scan, the user is granted access to their Google account.
Recovering a Google Account Using FIDO2 and Backup Codes
Recovering a compromised account is essential. If a user loses access to their Google account, they can utilize their registered FIDO2 security key and backup codes. First, the user navigates to the account recovery page. They enter the relevant information, and the system will then guide them through the process. If they possess a FIDO2 security key, they will be prompted to use it for verification.
Subsequently, they’ll be asked to input a backup code from their recovery options. Verification of both the key and code confirms the user’s identity, and access is restored.
Troubleshooting Authentication Issues Related to Biometrics
Biometric authentication can occasionally face challenges. If a user encounters difficulties with fingerprint login, several steps can be taken to resolve the problem. First, ensure the fingerprint sensor is clean. If the issue persists, try restarting the device. If the problem persists, check for updates to the operating system and applications.
Furthermore, review the device’s settings for biometric authentication to ensure correct configuration. Lastly, consider contacting Google support for further assistance.
Security Benefits of Using a Secure Browser like Google Chrome, Google passwords chrome fido2 webauthn fingerprint biometrics screen lock
Google Chrome, with its integrated security features, enhances the protection of user accounts. Chrome employs advanced security measures to mitigate risks. This includes encryption of communications between the browser and websites, preventing man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, Chrome’s built-in protection against phishing and malware significantly reduces the likelihood of account compromise. Furthermore, Chrome’s regular updates address emerging security vulnerabilities.
These proactive measures safeguard sensitive information and maintain a secure online environment.
User Interface for a Password Manager Integrating FIDO2 and Biometrics
The password manager interface integrates FIDO2 and biometrics seamlessly. The main screen displays a list of accounts. Each account is represented by an icon. Tapping an icon reveals the account details, including the website address, username, and password. For secure access, users can employ FIDO2 keys.
Moreover, for quick access, biometric authentication (fingerprint) is an option. When adding a new account, the password manager prompts the user to create a strong password and then store it securely. The interface incorporates a clear and intuitive design, making account management simple and secure.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, integrating Google passwords, Chrome, FIDO2, WebAuthn, fingerprint biometrics, and screen lock security creates a formidable defense against cyber threats. By understanding the intricacies of each technology and their combined potential, you can significantly bolster your online security. This guide provides a detailed overview, enabling you to confidently navigate the evolving digital landscape with enhanced protection for your sensitive information.