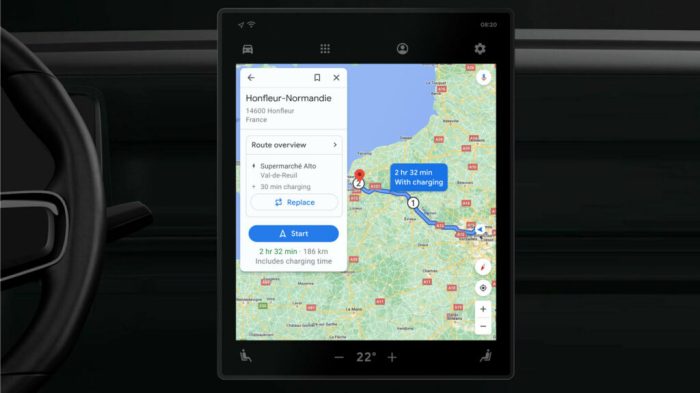
Google Maps might soon show plug and charge EV stations where you pay with your car, revolutionizing the electric vehicle experience. Imagine effortlessly locating charging stations, conveniently paying directly from your car, and seamlessly integrating this into your daily navigation. This groundbreaking integration promises to significantly ease the challenges of EV ownership, making electric driving more convenient and accessible.
Current EV charging infrastructure often involves complicated payment methods and frustrating searches. This new feature, if implemented, could dramatically improve the user experience. It will likely significantly impact charging station operators and car manufacturers as well, potentially changing the entire landscape of electric mobility.
Introduction to the Concept
Google Maps integrating plug-and-charge EV stations represents a significant step forward in the evolution of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure. This integration will allow drivers to locate, access, and pay for charging at compatible stations directly through their car’s onboard system, eliminating the need for credit cards or mobile apps. This streamlined process promises to make EV charging more convenient and accessible, addressing a key pain point for many drivers.The potential benefits for EV drivers are substantial.
This seamless integration will reduce friction in the charging process, saving time and frustration. Drivers can easily identify available stations, plan their routes accordingly, and ensure a convenient charging experience without worrying about the payment process. Furthermore, this integrated system can facilitate the development of a more robust and user-friendly EV charging network.
Current EV Charging Infrastructure and Limitations
Currently, EV charging infrastructure varies widely across regions. Many public charging stations rely on various payment methods, often requiring drivers to download apps, register accounts, and use different payment options for each station. This fragmentation and lack of standardization create a significant barrier to adoption for EV drivers. This often involves a complicated process of finding available charging spots, identifying payment options, and dealing with potential issues or problems related to the particular charging station.
Google Maps might soon show plug-and-charge EV stations where you pay with your car, making EV travel a lot smoother. This is a huge step forward for electric vehicle adoption, but it’s interesting to note that the recent A24 HBO Max Cinemax deal with Warner Bros Discovery a24 hbo max cinemax deal warner bros discovery could potentially impact streaming services in a way that also affects the charging infrastructure for EVs.
Ultimately, though, having a clear map of charging options will make it much easier for anyone to drive an EV.
Potential Improvements in the EV Charging Experience
The proposed integration of plug-and-charge stations into Google Maps promises to revolutionize the EV charging experience. By directly integrating with the car’s onboard system, drivers can eliminate the need for separate payment methods, saving time and effort. This will significantly improve the user experience, encouraging wider adoption of EVs. The integration will also provide real-time information about available charging spots, estimated charging times, and pricing, enabling more efficient route planning and charging strategies.
Comparison of Existing EV Charging Payment Methods, Google maps might soon show plug and charge ev stations where you pay with your car
| Payment Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Card/Debit Card | Traditional payment method | Widely accepted, familiar to most drivers | Requires manual input, potentially exposing sensitive information, can be slower than direct integration |
| Mobile Apps | Specific apps for charging stations | Often provide additional features like station reviews and location tracking | Requires app download, registration, and ongoing maintenance of accounts. Different apps for different stations can lead to fragmentation. |
| Plug-and-Charge | Direct payment through the car’s onboard system | Fast and seamless, reduces friction, enhances user experience | Requires compatibility with the car and charging station; may be less accessible to drivers of older models. |
This table highlights the differences in payment methods and how plug-and-charge technology offers a more streamlined and efficient approach.
Potential Impacts on EV Adoption
The integration of plug-and-charge EV stations directly into navigation systems, allowing payment through the vehicle, promises to significantly reshape the landscape of electric vehicle adoption. This seamless integration, eliminating the need for separate payment apps or physical interactions at charging stations, could drastically reduce friction and encourage wider EV adoption.This innovative approach to charging infrastructure addresses a key barrier to EV adoption: the perceived complexity of charging.
Google Maps might soon show plug-and-charge EV stations, letting you pay with your car. This is a huge step forward for electric vehicle adoption, and it’s a great improvement on the current system. Speaking of advancements, the NYPD’s new body cam rollout for all officers in the New York Police Department could lead to greater transparency and accountability , which is definitely something to watch.
Hopefully, this same level of innovation will soon extend to the integration of EV charging station information on Google Maps, streamlining the whole process of finding and paying for a charge.
By making the process intuitive and automated, the system can foster a more positive user experience, potentially attracting more drivers to the electric vehicle market.
Stimulating EV Adoption and Usage
This seamless payment system will make charging an EV feel as natural as fueling a traditional car. The convenience factor is a key driver in consumer adoption of any technology. Removing the friction of finding a station, connecting the cable, and paying will likely increase the frequency of EV charging. Think of the convenience of simply stopping at a gas station, but with the added benefit of a more sustainable energy source.
Potential Impact on the Overall EV Market
The integration of plug-and-charge stations within navigation systems could significantly increase the market share of EVs. By making the charging process more accessible and intuitive, the system potentially attracts a wider range of consumers who may have previously been hesitant to adopt EVs. This increased adoption can further stimulate the growth of the EV market and incentivize further investment in EV charging infrastructure.
The market reaction to Tesla’s Supercharger network, offering a seamless experience, demonstrates the power of a convenient charging infrastructure.
Potential Implications for the Development and Growth of the Charging Network
The introduction of plug-and-charge technology will likely reduce the need for numerous charging stations at every location, as users will be able to locate stations and pay easily via their car. This could lead to a more focused deployment of charging stations, potentially prioritizing locations with high EV usage or strategic locations for long-distance travel. The shift towards this system could potentially lead to the streamlining of charging station development, making the network more efficient and cost-effective.
Impact on Public Charging Stations
The introduction of this integrated payment system could alter the role of public charging stations. While dedicated public stations may remain crucial for drivers who don’t own EVs or have limited access to home charging, the system may alter the usage patterns of public stations. The decrease in the need for physical interaction at public charging stations could potentially streamline operations and reduce the need for staffing at certain locations.
Potential Market Segments Affected
| Market Segment | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Car Manufacturers | Increased demand for EVs, need to integrate the technology into their vehicles, potentially influencing future vehicle design. |
| Charging Companies | Potential shift from physical station management to a more centralized, automated system, need to adapt and partner with navigation providers. |
| Consumers | Increased EV adoption, improved charging experience, reduced friction in charging processes. |
| Navigation Providers | Integration of EV charging data into their systems, potential for new revenue streams from charging-related services. |
Technical Aspects and Implementation
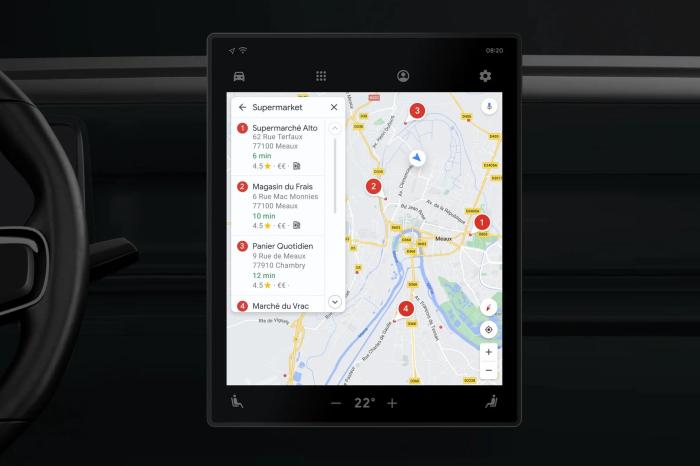
Integrating plug-and-charge EV stations with Google Maps requires a complex interplay of technical components and robust security protocols. Successfully implementing this system hinges on overcoming various challenges, from ensuring secure payment processing to seamless integration with existing charging infrastructure. The potential for widespread EV adoption hinges significantly on the efficiency and reliability of this integration.The seamless integration of EV charging stations into Google Maps necessitates a robust technological infrastructure, capable of handling real-time data updates, secure payment transactions, and user-friendly navigation.
This comprehensive approach must address not only the technical challenges but also the user experience to foster widespread adoption.
Potential Technical Challenges
The implementation of plug-and-charge systems presents several technical hurdles. Interoperability issues between different charging standards (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO) and varying payment systems require careful consideration. Ensuring real-time availability and accurate pricing information across a network of charging stations is also a critical challenge. The volume of data generated by a large number of charging stations and users needs a robust data management system to handle the scale.
Necessary Infrastructure and Technological Requirements
The integration requires a sophisticated infrastructure, including robust communication networks to facilitate real-time data exchange between charging stations and Google Maps. A standardized API (Application Programming Interface) is essential to allow for seamless communication between the different systems. This API should be designed to handle high volumes of data efficiently and reliably, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for users.
The system also needs a scalable database to store and manage data related to charging stations, pricing, availability, and user accounts.
Security Measures for Payment Transactions
Secure payment processing is paramount for user trust. Implementing robust encryption protocols is crucial to protect sensitive payment information transmitted between the user’s vehicle and the charging station. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other security measures should be incorporated to further enhance security. The system should comply with relevant data privacy regulations and industry best practices.
Comparison of Payment Methods for Plug-and-Charge
Different payment methods present varying tradeoffs in terms of security, cost, and user experience. Using existing credit card systems might offer convenience, but the added layer of security for direct vehicle-to-station payment could improve user trust. Mobile wallets or dedicated charging apps might offer faster transactions, but the integration process with Google Maps must be streamlined. The choice of payment method should balance security, cost-effectiveness, and user experience.
Procedures for Seamless Integration between Google Maps and Charging Stations
A clear protocol is needed for real-time updates on charging station availability and pricing. This protocol should ensure consistent and accurate information displayed on Google Maps. The system must handle potential disruptions or outages at charging stations, updating the information in Google Maps promptly to minimize user frustration. A detailed procedure for handling payment transactions, including error handling and user notifications, is essential.
Technical Components Involved
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Charging Station Hardware | Includes the charging equipment, communication modules, and payment processing units. |
| Communication Network | Facilitates real-time data exchange between charging stations and Google Maps servers. |
| Google Maps Platform | Provides the mapping interface, user interface, and data management system. |
| Payment Gateway | Processes secure payment transactions between the vehicle and the charging station. |
| Vehicle-to-Grid Communication | Enables communication between the car and the charging station for authentication and payment. |
User Experience and Interface
The seamless integration of plug-and-charge EV stations into Google Maps is crucial for widespread EV adoption. A user-friendly interface is paramount to encourage drivers to utilize these stations. Intuitive navigation and clear information about charging capabilities will determine how readily drivers embrace this technology.
Proposed User Interface for Finding Stations
The Google Maps interface for locating plug-and-charge stations will be highly visual and intuitive. Users will be able to search for stations by location, type of charging (e.g., Level 2, DC Fast Charging), and the specific features they require (e.g., availability of amenities). The map will display charging stations as easily identifiable icons, colored differently to indicate charging type and availability.
A station icon with a green fill will represent an available charging point, while a gray icon indicates a station currently unavailable.
Steps for Locating and Utilizing a Station
Finding and using a plug-and-charge station will be a straightforward process. Users will initiate the search via the Google Maps app or website. The results will display available stations, complete with details about charging speed, payment options, and station amenities. Users can then select the desired station and view detailed information, including estimated charging time, and any associated fees.
The selected station will be marked on the map with clear directions to the location.
Handling Payment Methods and Currencies
The system will handle various payment methods, including those associated with pre-existing user accounts, as well as a new system that integrates with payment gateways. The interface will automatically identify the appropriate payment method and currency based on the user’s location and preferences. This integration ensures a smooth transaction process regardless of the user’s location or preferred payment approach.
For example, if a user is in Europe, the payment system will default to the appropriate currency and payment methods.
User Flow Chart of the Plug-and-Charge Process
 [Image Description: A simple flowchart depicting the user flow for the plug-and-charge process. The steps are initiated with a user searching for a charging station on Google Maps. The search results display available stations with details like charging type, payment options, and amenities. The user selects a station and the application guides them to the station location, displays estimated charging time and fees, and facilitates the payment process. The process concludes with the user completing the payment and parking their vehicle at the station.]
[Image Description: A simple flowchart depicting the user flow for the plug-and-charge process. The steps are initiated with a user searching for a charging station on Google Maps. The search results display available stations with details like charging type, payment options, and amenities. The user selects a station and the application guides them to the station location, displays estimated charging time and fees, and facilitates the payment process. The process concludes with the user completing the payment and parking their vehicle at the station.]
Visual Representations of Charging Station Availability
| Availability Status | Icon Representation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Available | Green Icon | Indicates that the charging station is currently available for use. |
| Unavailable | Gray Icon | Indicates that the charging station is unavailable or undergoing maintenance. |
| Under Maintenance | Orange Icon | Indicates that the charging station is undergoing maintenance. |
| Charging | Blue Icon | Indicates that a vehicle is currently charging at the station. |
The visual representation of charging station availability will use clear and concise icons to provide immediate feedback to users. These icons will be consistently applied throughout the Google Maps interface to ensure user familiarity and ease of use.
Economic Considerations
Integrating plug-and-charge EV stations with car-based payment systems presents significant economic opportunities for both charging station operators and EV drivers. This innovative approach promises a streamlined payment process, potentially boosting EV adoption and efficiency. Understanding the financial implications for all stakeholders is crucial for successful implementation.
Charging Station Operator Revenue Models
The shift to car-based payment systems requires charging station operators to re-evaluate their revenue models. Instead of relying on traditional payment methods like credit cards or mobile apps, operators will likely receive payment directly from the car’s onboard system. This transition necessitates a shift in infrastructure and potentially requires new agreements with car manufacturers. Possible revenue streams include per-kWh pricing, subscription models for frequent users, and potentially partnerships with energy providers.
The key is to ensure a transparent and competitive pricing structure to attract EV drivers and maintain profitability.
Comparison with Existing EV Charging Payment Systems
Existing EV charging payment systems, while functional, often present challenges related to user experience and integration. Card-based payment systems can be cumbersome and require extra steps, while mobile app-based solutions sometimes face compatibility issues or unreliable connectivity. The integration with car-based payment systems promises to streamline the entire process, potentially reducing friction for drivers and increasing overall efficiency for operators.
This simplified experience may lead to increased usage and attract a wider range of drivers.
Cost Savings for EV Drivers and Charging Companies
The potential cost savings for both EV drivers and charging companies are substantial. Drivers save time and effort by eliminating the need for separate payment methods. Charging companies can potentially reduce operational costs associated with maintaining separate payment processing systems. Furthermore, streamlined payments can help charging companies manage their revenue more efficiently. Increased usage due to the simplified process could lead to higher overall revenue.
Potential Cost Savings and Revenue Streams
| Stakeholder | Potential Cost Savings | Potential Revenue Streams |
|---|---|---|
| EV Drivers | Time saved in payment process; reduced transaction fees; potential discounts for frequent charging | None (directly) |
| Charging Station Operators | Reduced operational costs associated with payment processing; increased usage potentially leading to higher overall revenue; simplified billing processes. | Per-kWh charging fees; subscriptions for frequent users; potential partnerships with energy providers |
| Car Manufacturers | Potential for increased sales of EVs due to convenience and integration; increased data collection on charging habits. | Potential for revenue share with charging station operators; data analytics opportunities |
| Energy Providers | Potential for increased energy sales; potentially attracting new customers | Revenue share with charging station operators; potential for time-of-use pricing schemes. |
Environmental and Societal Implications
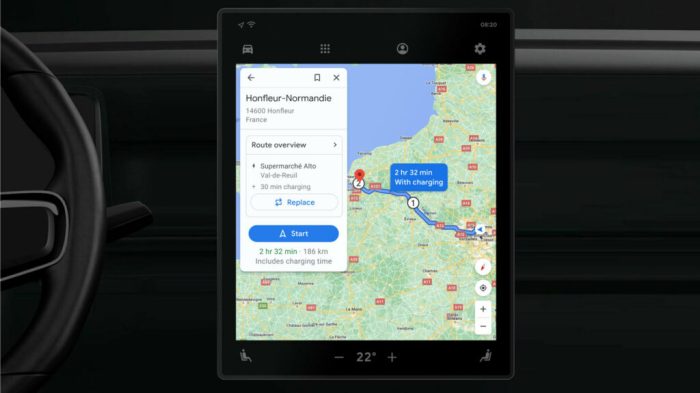
Integrating plug-and-charge EV stations into Google Maps promises a significant shift in how we approach electric vehicle adoption. Beyond the convenience of finding charging stations, this integration has profound environmental and societal implications, influencing everything from carbon emissions to traffic patterns. This section delves into the potential benefits and challenges, examining the broader impact of widespread EV adoption facilitated by this technology.
Potential Environmental Impact of Increased EV Usage
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for mitigating climate change. Increased EV usage, coupled with the convenience of readily available charging stations, can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. This shift is directly linked to reduced greenhouse gas emissions from transportation, a major contributor to global warming. While the environmental impact depends on the source of electricity powering the charging stations, a significant reduction in tailpipe emissions is undeniable.
The shift to renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, is a key factor in maximizing the environmental benefits of EV adoption.
Societal Benefits of Increased EV Adoption
Beyond the environmental benefits, widespread EV adoption presents considerable societal advantages. Reduced air pollution leads to improved public health, particularly in urban areas. Cleaner air translates into fewer respiratory illnesses and a healthier population. The transition to EVs also opens up opportunities for job creation in the manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors related to EVs and charging infrastructure.
Google Maps is reportedly getting a cool new feature: showing EV charging stations where you pay directly with your car. This is a huge step forward for electric vehicle adoption, but how do you actually use those charging stations? Figuring out how to watch YouTube videos on your Lenovo Smart Display is a helpful skill, too, and learning that could be a useful step in the process, so check out this guide: how watch youtube videos lenovo smart display.
Knowing how to easily access those charging stations, especially with the payment integration, will be key to widespread EV adoption.
The ease of access to EVs can also make transportation more accessible for individuals with mobility challenges, promoting inclusivity.
Impact on Reducing Carbon Emissions
A critical aspect of this integration is its potential to accelerate the reduction of carbon emissions. When EVs are charged using renewable energy sources, their carbon footprint becomes negligible compared to gasoline-powered vehicles. The widespread availability of plug-and-charge stations empowers EV drivers to easily find charging points, encouraging more people to adopt electric vehicles. This positive feedback loop further reduces carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
For example, in areas with a high penetration of solar energy, charging EVs with solar power would dramatically reduce the overall carbon footprint of transportation.
Impact on Traffic Patterns
The integration of EV charging stations into navigation systems could potentially influence traffic patterns. Strategically placed charging stations could help drivers optimize their routes to minimize charging time, reduce congestion at peak hours, and improve overall traffic flow. This could potentially lead to more efficient use of existing infrastructure. Intelligent routing algorithms, integrating real-time charging station availability and charging times, are crucial for maximizing this benefit.
Potential Environmental Benefits of this Integration
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Switching from gasoline-powered vehicles to EVs significantly lowers emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. |
| Improved Air Quality | Lower tailpipe emissions lead to cleaner air, reducing respiratory illnesses and improving public health. |
| Increased Renewable Energy Use | Charging EVs with renewable energy sources like solar and wind power maximizes the environmental benefits. |
| Optimized Traffic Flow | Smart routing based on charging station availability and times can reduce congestion and improve overall traffic efficiency. |
| Reduced Noise Pollution | Electric vehicles produce less noise than gasoline-powered vehicles, contributing to a quieter environment. |
Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Integrating plug-and-charge EV stations into Google Maps presents exciting opportunities but also significant challenges. Successfully deploying this technology requires careful consideration of potential pitfalls, from security concerns to scalability issues. This section explores these hurdles and proposes strategies to overcome them.
Security Concerns
The system needs robust security measures to prevent fraud, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Malicious actors could potentially manipulate charging sessions, leading to financial losses and compromised user trust.
- Data Encryption and Authentication: Implementing strong encryption protocols for all data exchanges, including payment information and charging session details, is crucial. Multi-factor authentication systems, combined with secure payment gateways, can add another layer of protection. Examples like two-factor authentication used in online banking demonstrate the effectiveness of such measures.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Fraud Detection: Continuous monitoring of charging sessions for suspicious activities can help detect and prevent fraudulent transactions. Algorithms that identify unusual charging patterns or inconsistencies in payment data can flag potential threats. This proactive approach is similar to the fraud detection systems used by credit card companies to identify and block potentially fraudulent transactions.
- Physical Security Measures: Protecting physical infrastructure, such as charging stations, is essential. Implementing robust access controls, surveillance systems, and physical barriers can deter vandalism and theft. Similar measures are used in high-value retail settings and other locations to safeguard assets.
Scalability Issues
The rapid adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the subsequent demand for charging stations might strain the system’s capacity to handle a large influx of users.
- Network Infrastructure: Expanding the network of compatible charging stations to support the projected growth of EVs is essential. Investing in high-capacity power grids and robust communication networks can ensure smooth operations during peak demand periods. This is similar to how telecommunication companies must upgrade their infrastructure to handle increasing data traffic.
- Data Processing Capacity: The volume of data generated by numerous charging sessions could overwhelm the system’s data processing capabilities. Cloud-based solutions and distributed computing architectures can help manage the load and ensure efficient data processing. Large-scale online retailers like Amazon use similar approaches to handle enormous volumes of customer data.
- Deployment Strategy: A phased rollout of charging stations, prioritizing high-traffic areas and strategic locations, can help manage the demand. Data-driven insights into charging patterns can optimize the placement of stations for maximum efficiency. This method is akin to the phased release of new products to the market.
Summary of Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
| Potential Challenges | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Security Concerns (fraud, unauthorized access, data breaches) | Data encryption, multi-factor authentication, real-time monitoring, physical security measures |
| Scalability Issues (network infrastructure, data processing capacity, deployment strategy) | Expanding network capacity, distributed computing, phased deployment, data-driven insights |
Closing Notes: Google Maps Might Soon Show Plug And Charge Ev Stations Where You Pay With Your Car
The potential integration of plug-and-charge EV stations into Google Maps presents a compelling vision for the future of electric vehicles. This change promises to simplify the charging process, boost EV adoption, and reshape the entire ecosystem surrounding electric mobility. However, challenges remain, from the technical implementation to the economic considerations. Ultimately, this innovation could unlock the full potential of electric vehicles and pave the way for a greener future.