Can I remove ads brain wash? This question delves into the complex relationship between advertising, manipulation, and the desire for a cleaner online experience. We explore the psychological underpinnings of persuasive advertising, examining how it might be perceived as manipulative. Beyond the immediate gratification of ad removal, we’ll uncover the potential downsides and explore alternative solutions, including fostering media literacy to navigate the advertising landscape effectively.
The article investigates the methods of removing advertisements, ranging from ad blockers and VPNs to specific tools and platforms. We’ll analyze how the desire to remove ads can stem from a perceived feeling of manipulation. The discussion also encompasses the impact of widespread ad removal on the financial viability of online platforms and the ethical implications of such actions.
Defining “Brainwashing” in the Context of Ads
The term “brainwashing” often evokes images of sinister manipulation, but in the context of advertising, it’s a more nuanced concept. It’s not about outright coercion, but rather the subtle and often unconscious ways ads can shape our desires, beliefs, and ultimately, our purchasing decisions. This exploration delves into the psychological tools used in persuasive advertising, examining the ethical lines crossed, and historical influences on the modern advertising landscape.Persuasive advertising relies on a complex interplay of psychological mechanisms to influence consumer behavior.
These techniques can exploit our cognitive biases, emotional vulnerabilities, and social needs to create a desire for a product or service. For instance, appealing to a consumer’s desire for social acceptance or their need for belonging can be effective. This can be perceived as manipulative when the consumer isn’t fully aware of the techniques being employed. The key distinction is not simply the presence of persuasive tactics, but whether they are used ethically and transparently.
Psychological Mechanisms in Persuasive Advertising
Advertising often leverages several psychological principles. These include the principle of association, where a product is linked to positive emotions or desirable images; the principle of scarcity, where limited availability creates a sense of urgency; and the principle of social proof, where endorsements or testimonials encourage consumers to follow the crowd. Understanding these mechanisms allows consumers to critically evaluate advertisements and make informed decisions.
Ethical Considerations of Manipulative Advertising
The ethical implications of manipulative advertising tactics are significant. Advertising practices that exploit vulnerabilities, manipulate emotions, or misrepresent information can erode consumer trust and lead to negative consequences. For example, advertising aimed at children or vulnerable populations raises serious ethical questions about responsibility and transparency. Furthermore, the potential for harm from targeted advertising and the proliferation of misinformation online are important ethical concerns.
These considerations require a balance between free speech and the protection of consumers from deceptive or harmful practices.
Historical Context of “Brainwashing”
The term “brainwashing” gained prominence in the post-World War II era, primarily stemming from accounts of political indoctrination in China and North Korea. This historical context, while not directly applicable to advertising, provides a framework for understanding how concepts of manipulation and control have evolved. In advertising, the techniques and strategies have evolved over time, mirroring societal shifts and technological advancements.
The original concept of brainwashing has, in effect, morphed into a discourse on the potential for advertising to exert a powerful influence on consumer behavior.
Examples of Potentially “Brainwashing” Advertisements
Identifying advertisements that qualify as “brainwashing” is subjective. However, certain campaigns employ manipulative tactics that warrant consideration. One example is an advertisement that uses fear-mongering tactics to sell a product or service, capitalizing on the consumer’s anxieties. Another example could be an advertisement that targets vulnerable demographics, such as teenagers, with promises of acceptance or belonging. Finally, advertisements that use emotionally manipulative language or imagery, without providing adequate information, can also be categorized as potentially problematic.
Identifying Advertisement Removal Techniques
The constant barrage of advertisements can be overwhelming, disrupting the user experience and potentially leading to feelings of manipulation. Understanding the methods used to remove ads and the tools available is crucial for regaining control over your online experience. This exploration delves into the various techniques for ad removal, examining their effectiveness and limitations.Modern advertising strategies often employ sophisticated methods to capture attention and influence behavior.
This often leads users to seek ways to mitigate these influences, and understanding how these tools work is key to making informed decisions about your online interactions.
Advertisement Removal Methods Comparison
Various methods exist for mitigating the impact of advertisements. This table compares and contrasts some common techniques.
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ad Blockers | Software that filters and blocks advertisements on websites and apps. | Effective at removing ads, improving browsing speed. Often customizable to specific websites or ads. | May block legitimate content or cause compatibility issues with certain websites. Some websites may use ad revenue for content maintenance. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | A service that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in another location. | Can potentially bypass geo-restrictions on ad-blocking tools or specific ad campaigns. Provides enhanced privacy. | May impact browsing speed, depending on the VPN server location and connection quality. Effectiveness on ad blocking can vary depending on the ad provider’s strategy. |
| Browser Extensions | Specialized extensions for specific browsers that filter or block ads. | Targeted ad blocking, often integrated with the browser’s functionality. | May require browser compatibility and can be affected by updates. Performance can be impacted by the extension’s features. |
| App-Specific Ad Blockers | Ad blocking software integrated into specific apps to prevent ads from appearing within them. | Provides targeted ad blocking within the specific app. | May not work across all app platforms or be subject to app restrictions. May not be available for all apps. |
Potential Ad Removal Tools
A wide range of tools are available to help users mitigate the impact of advertisements. This list explores some options with their respective functionalities and potential limitations.
- AdBlock Plus: A popular ad blocker known for its effectiveness in filtering various types of advertisements. It offers a wide range of customizable options for blocking specific ads or websites. However, it may block legitimate content from some websites.
- uBlock Origin: Another robust ad blocker with a strong reputation for its ability to identify and block a wide variety of ad formats. It’s highly configurable, allowing users to customize filtering rules. Potential limitations include potential conflicts with specific website functionalities.
- Privacy Badger: This extension is designed to protect users’ privacy and mitigate the collection of user data through tracking cookies and advertisements. While not solely focused on ad removal, it indirectly helps to reduce the impact of advertisements.
Using Ad-Blocking Software
A step-by-step guide for using ad-blocking software to remove unwanted advertisements:
- Download and Install: Choose the desired ad blocker and download the appropriate version for your browser.
- Configure Settings: Explore the settings to understand the features and customize the ad blocking rules to suit your preferences. This may include allowing ads from specific websites you frequent.
- Test Functionality: Open different websites and check if ads are successfully blocked.
- Update Regularly: Ensure the software is up-to-date to maintain effectiveness in blocking the latest ad formats.
The Psychological Response to Ads
The desire to remove ads is often a response to feeling manipulated or overwhelmed by advertising strategies. This feeling is driven by the inherent psychological impact of advertisements, which can be designed to create specific responses in the user. Users may find themselves actively seeking tools to control their online environment, and this can be linked to a desire for a more personalized and less intrusive experience.
Finding and Utilizing Ad Removal Tools
Numerous tools are available for removing advertisements from various platforms. Finding the right tool depends on the platform and desired level of control. Researching and comparing available options, considering the specific features of each tool, is essential to achieving the desired results. For example, ad-blocking extensions for web browsers can remove ads from websites, while app-specific blockers are designed to remove ads within specific applications.
This allows for a customized approach to ad removal based on the particular platforms used.
Examining the Connection Between Ad Removal and Perceived Manipulation

The desire to remove ads is more than just a preference; it often stems from a complex interplay of psychological factors and societal perceptions. People’s experiences with advertising, shaped by cultural norms and personal biases, frequently contribute to the feeling that they are being manipulated or influenced. This perception, in turn, can significantly impact their choices, including their decision to remove ads.
Understanding these connections is crucial to comprehending the motivations behind the growing demand for ad-free environments.The act of removing ads often reflects a deeper-seated belief that advertising is a form of manipulation. This belief is not necessarily based on a rational assessment of advertising strategies but rather on an emotional response to the constant barrage of persuasive messages encountered daily.
Individuals might perceive ads as intrusive, deceptive, or simply annoying, leading them to actively seek control over the advertising experience. This control manifests in the desire to eliminate the perceived manipulation inherent in the advertising process.
Psychological Factors Driving Ad Removal
The desire for an ad-free experience can be rooted in several psychological factors. The feeling of being bombarded with persuasive messages can induce a sense of stress and overwhelm. This perceived pressure can manifest as a desire to control the information environment and limit the exposure to potentially manipulative advertising techniques. Individuals might experience discomfort from the perceived intrusion of advertisements into their personal space and the feeling of being targeted by commercial interests.
This discomfort can motivate them to remove ads, seeking a more curated and less intrusive online experience. The perceived intrusiveness of advertising, particularly when it’s perceived as irrelevant or unwelcome, can contribute to this desire for control.
Perceived Link Between Ads and Manipulation
People often associate advertising with manipulation due to the persuasive techniques employed. These techniques, such as emotional appeals, celebrity endorsements, and the creation of aspirational lifestyles, are frequently used to influence consumer behavior. This perceived manipulation can be exacerbated by the sheer volume of advertising encountered daily. The constant bombardment of ads can lead to feelings of being overwhelmed, targeted, and even manipulated.
This feeling of being influenced can drive a desire to remove ads as a means of reclaiming control over one’s own choices.
Ever wondered if you can remove those pesky ads from your brain? It’s a bit like trying to change the paint color on a Porsche, a totally different beast. Fortunately, you can find out more about Porsche paint to sample PTS colors for Taycan, Panamera, 718 Boxster at this resource. But when it comes to those ads, well, it’s a more complex process than choosing a shade of metallic green.
You might have to dig deeper into ad blockers and privacy settings.
Potential Biases Contributing to Manipulation Perception
Various biases can contribute to the perception of advertising as manipulative. Cognitive biases, such as confirmation bias, can lead individuals to selectively interpret information that confirms their pre-existing negative beliefs about advertising. For example, someone already distrustful of commercial messages may readily interpret ads as manipulative, even if the ads are presented fairly and transparently. Similarly, cultural factors play a role in shaping perceptions.
Different cultures have varying levels of trust in advertising, and these cultural norms can influence individual responses to persuasive marketing messages. A culture that values transparency and skepticism might perceive advertising as more manipulative than a culture that places more emphasis on the freedom of commercial expression.
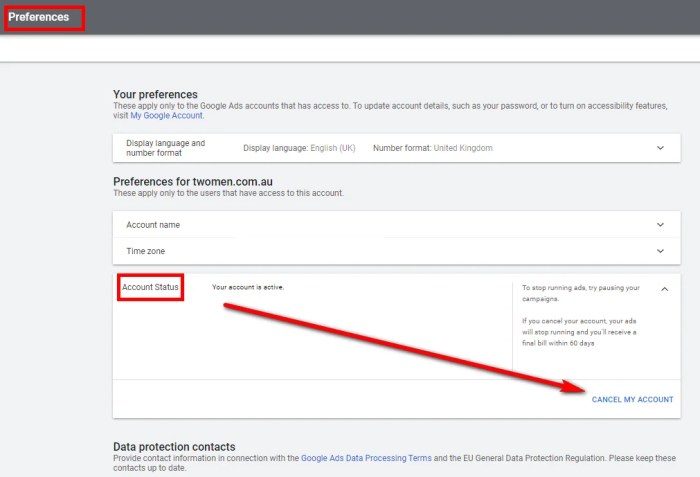
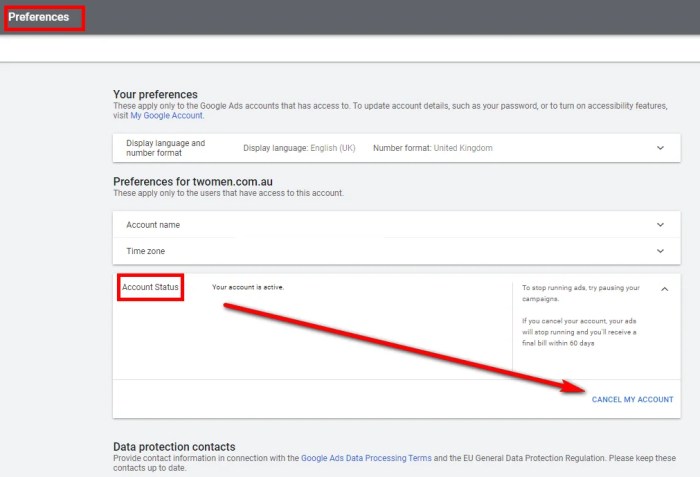
Ad Removal as a Response to Perceived Manipulation
The act of removing ads can be viewed as a direct response to perceived manipulative advertising tactics. By eliminating ads, individuals seek to limit their exposure to persuasive messages and regain control over their own decision-making processes. This response can be seen as a form of self-protection, a way to shield oneself from the perceived influence of advertising.
This desire to control the information environment and reduce exposure to potentially manipulative tactics is a crucial element in understanding the motivations behind ad removal.
Manifestation of “Brainwashing” Perception in Different Cultures
The perception of being “brainwashed” through advertising can manifest in diverse ways across different cultures. In some cultures, there might be a stronger emphasis on skepticism towards advertising, leading to a heightened perception of manipulation. Conversely, in cultures where advertising is more integrated into daily life, the perception of being influenced might be less pronounced, or even viewed as a normal part of the economic landscape.
These cultural variations highlight the influence of societal norms on individual perceptions of advertising and the associated feeling of being manipulated.
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Ad Removal
The desire to remove ads often stems from a feeling of manipulation. However, simply blocking ads doesn’t address the underlying issue of how advertising works and its potential influence on our choices. Instead of resorting to removal, we can cultivate a more informed and critical relationship with advertising. This approach empowers us to navigate the persuasive strategies employed by advertisers while minimizing the feeling of being manipulated.By developing critical thinking skills around advertising, we can become more discerning consumers, recognizing the motivations and techniques used to shape our preferences and ultimately, make more conscious purchasing decisions.
This approach allows us to appreciate the complexity of advertising without feeling victimized by it.
Alternative Approaches to Navigating Advertising
Understanding the persuasive techniques used in advertising is crucial to navigating its influence effectively. This involves recognizing common tactics, such as emotional appeals, celebrity endorsements, and social proof, and developing an awareness of how these tactics might be employed to influence our decisions.
Figuring out if you can remove those pesky ads from your brainwashing (metaphorically speaking, of course!) is a tough one. But, if you’re looking for the best wireless chargers for your Galaxy S20, check out this helpful guide on best wireless chargers galaxy s20. Ultimately, removing unwanted brainwashing influences, whether from ads or other sources, takes a conscious effort and critical thinking, not just a new phone accessory.
Strategies for Critical Media Consumption
A critical approach to media consumption requires conscious effort and awareness. Developing critical thinking skills empowers us to analyze the messages presented in advertisements, evaluating the validity of the claims made and the potential motivations behind them. This includes considering the source of the advertisement, the target audience, and the context in which the advertisement appears.
- Identifying the underlying message: Advertisements often try to evoke emotions or desires rather than explicitly stating their purpose. By understanding the emotional or aspirational aspects of an ad, we can analyze the true intent behind the marketing message. For example, an ad showing a family enjoying a meal together might be trying to associate the product with positive feelings and family values, rather than simply showcasing the product’s features.
- Recognizing persuasive techniques: Ads frequently utilize techniques to influence our perceptions. Understanding these techniques, such as bandwagon effect, fear-mongering, or testimonials, can help us recognize potential manipulation and make more objective judgments. For instance, an ad that highlights the popularity of a product might use the bandwagon effect to persuade potential customers.
- Considering the source and context: The credibility of an ad is dependent on the source. A product endorsed by a credible expert or an organization with a strong reputation carries more weight than an endorsement from an unknown individual. The context in which an ad appears also plays a role in its effectiveness. An ad for a luxury car in a high-end magazine might be perceived differently than the same ad appearing in a local newspaper.
A Framework for Critical Engagement with Ads, Can i remove ads brain wash
Developing a structured approach to analyzing advertisements can significantly enhance our ability to discern persuasive techniques. By systematically evaluating various aspects of an advertisement, we can make informed choices that align with our values and needs.
| Aspect | Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|
| Product/Service | Is the product/service presented accurately? Are its features and benefits highlighted honestly? Are there any hidden costs or limitations? |
| Target Audience | Who is the intended audience? How does the ad appeal to their values and desires? Are there any stereotypes or biases presented? |
| Persuasive Techniques | What emotional appeals or persuasive techniques are used? How effective are these techniques in influencing the target audience? Are there any logical fallacies or misleading statements? |
| Source/Credibility | Who is the source of the advertisement? Is the source credible and trustworthy? Are there any conflicts of interest? |
| Context/Environment | Where and when does the ad appear? What is the overall message conveyed by the surrounding content? |
Illustrating the Impact of Ad Removal on User Experience
The allure of a clean, ad-free browsing experience is undeniable. However, the potential ramifications for users, creators, and the entire digital ecosystem extend far beyond the simple removal of visual clutter. This section explores the complex interplay between ad removal, user experience, and the sustainability of online content.The impact of ad removal on user experience is multifaceted, affecting not just the aesthetic but also the functionality and overall satisfaction of the online journey.
Different methods of ad removal can lead to vastly different outcomes, impacting website usability, performance, and user engagement.
Ever wondered if you can remove those pesky ads from your brainwashing? While there’s no magic bullet, the recent downturn in the US PC market, with supply issues and the Windows 11 launch potentially playing a role, as discussed here , might offer some indirect clues. Ultimately, though, getting rid of ad-based brainwashing still requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on critical thinking and media literacy.
Impact on Website Usability
The absence of ads can subtly alter website navigation. Sites optimized for a specific ad layout might experience unexpected behavior or display inconsistencies. A significant portion of website designs incorporate ads for structural elements. Removing them might require substantial redesign efforts to maintain a seamless user experience. For instance, a website relying on banner ads to create space for content might find its layout compressed, leading to less navigable and less appealing content.
Similarly, pop-up ads might serve a crucial purpose for user interaction, such as showcasing promotions or crucial updates. Their removal might hinder user access to vital information.
Impact on Website Performance
Ad removal can potentially enhance website performance by reducing the number of requests for external resources. However, this is often oversimplified. Instead of merely removing the ads, the entire architecture of the website must be reconsidered. Removing ads often leads to an increased load time. Many ads are strategically placed to optimize loading speed by caching assets, and removing them can lead to a slower page load time.
Furthermore, some ads utilize efficient code that can contribute to improved performance. Removal of these ads could lead to an increased load time, making the site less responsive. This could result in a noticeable negative impact on user experience.
Impact on User Engagement
While some users might initially appreciate the ad-free browsing experience, the lack of advertisements could also negatively affect user engagement. Ad revenue often underwrites free content. Without it, platforms might struggle to maintain their services. Consider a website that offers free content, such as news articles or educational resources. The removal of ads could lead to a decrease in readership or engagement as the financial viability of the platform is compromised.
Conversely, users might feel less incentivized to interact with the platform, ultimately decreasing overall engagement.
Negative Consequences for Content Creators and Businesses
The removal of ads directly impacts the financial viability of online content creators and businesses. A large portion of online content creators and businesses rely on advertising revenue for their operations. Without this revenue, content creation and business operations could be compromised. Content creators might have to shift to alternative revenue models, such as paid subscriptions or merchandise sales.
This could lead to a decrease in the diversity and quantity of content available online. Moreover, businesses might be forced to reduce staff or scale back operations, potentially leading to job losses.
Impact on Financial Viability of Online Platforms and Free Content
Widespread ad removal significantly threatens the financial viability of online platforms. Many platforms, such as social media sites and news websites, heavily rely on advertising revenue to sustain operations and provide free content. If ad revenue disappears, platforms might need to implement paid subscriptions or premium features to offset the loss, potentially making free content less accessible. Free content, a fundamental aspect of the digital ecosystem, might be at risk.
The absence of ad revenue could necessitate substantial changes in business models and pricing structures, affecting the overall experience for users.
Potential Long-Term Effects on the Digital Ecosystem
The long-term effects of widespread ad removal are complex and uncertain. A significant portion of the digital ecosystem relies on the advertising revenue model. The removal of ads could lead to a shift in the balance of power within the online world. The sustainability of free content might be jeopardized, leading to a potential decrease in the quantity and diversity of online content.
This, in turn, could impact the quality of information available to users. Moreover, the shift in the financial structure could create a new digital landscape, with new players and business models emerging. The long-term consequences remain to be seen, but the potential for significant disruption is undeniable.
Analyzing the Role of Media Literacy in Understanding Advertising: Can I Remove Ads Brain Wash
Navigating the modern media landscape requires a discerning eye, especially when it comes to advertising. Advertisements are meticulously crafted to influence our choices, often employing subtle techniques that can be difficult to detect without a critical understanding of their underlying mechanisms. This is where media literacy plays a crucial role.Media literacy equips individuals with the tools and knowledge necessary to critically analyze and interpret advertising messages, moving beyond surface-level perceptions and recognizing the persuasive strategies employed.
It’s not about rejecting advertising entirely, but about understanding its purpose and impact on our thoughts and actions.
The Importance of Media Literacy in Interpreting Advertising Messages
Media literacy empowers individuals to decode the often-hidden meanings embedded within advertisements. It encourages questioning the motives behind a campaign and recognizing the intended audience. By understanding the techniques used, consumers can avoid being manipulated by persuasive tactics. This critical evaluation is essential for forming informed opinions and making thoughtful decisions, especially in areas like consumerism, politics, and health.
Examples of Media Literacy Skills in Evaluating Advertisements
Developing media literacy skills allows individuals to dissect various elements of an advertisement. This involves recognizing the use of persuasive techniques such as emotional appeals, celebrity endorsements, and bandwagon effect. For example, a commercial highlighting a celebrity using a particular product often implies that using the product will enhance the viewer’s social standing. By understanding these implied connections, viewers can approach the message with greater objectivity.
Further, understanding the target audience and how the advertisement caters to their needs and desires helps to assess the effectiveness of the campaign.
The Relationship Between Media Literacy and Perception of Ads as Manipulative
A strong foundation in media literacy significantly impacts how individuals perceive advertising messages. With improved media literacy, consumers are better equipped to identify manipulative tactics like creating false needs, exploiting emotional vulnerabilities, and using misleading statistics. They are able to differentiate between genuine product benefits and cleverly crafted illusions. This enhanced understanding can significantly reduce the likelihood of feeling manipulated by advertising.
Strategies for Fostering Media Literacy to Navigate Advertising
Developing media literacy requires continuous effort and engagement with media content. Educational programs in schools and communities can provide valuable insights into advertising techniques and the impact of persuasive messaging. Furthermore, encouraging critical thinking through discussions and analysis of advertisements can empower individuals to become more discerning consumers. Engaging with diverse media platforms and actively seeking out multiple perspectives can also foster a more comprehensive understanding of advertising practices.
How Media Literacy Empowers Individuals to Recognize and Resist Manipulative Advertising Techniques
By understanding the underlying techniques employed in advertising, individuals can better resist manipulative strategies. This involves recognizing the potential for emotional appeals, misleading statistics, and the use of stereotypes to influence purchasing decisions. Recognizing these patterns allows consumers to approach advertising with a more critical and discerning mindset. This empowered awareness enables individuals to make more informed choices, ultimately leading to a more conscious and responsible relationship with advertising.
Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the desire to remove ads, often rooted in the perception of manipulative advertising, highlights the need for a nuanced understanding of the advertising ecosystem. This exploration suggests that fostering media literacy is crucial to navigating advertising’s influence without resorting to ad removal as the sole solution. The discussion also emphasizes the impact on both users and businesses, urging a more balanced approach that considers the needs of all stakeholders.