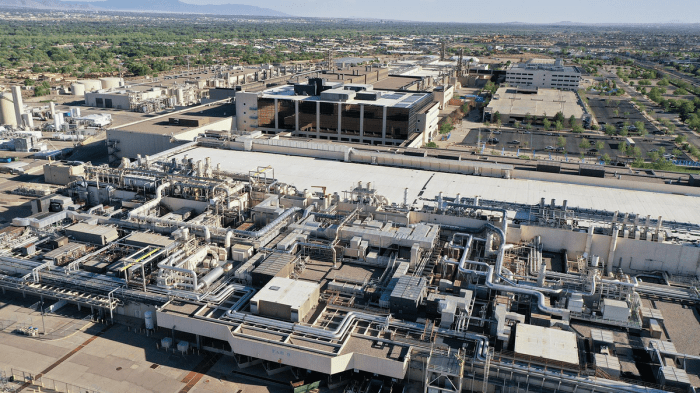
Biden chips act semiconductors subsidies ohio arizona plant china is a game-changer for the US semiconductor industry. This legislation aims to bolster domestic production, reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, and stimulate economic growth in key states like Ohio and Arizona. The Act offers various subsidies to incentivize semiconductor manufacturing, targeting specific companies and projects. This initiative is likely to have a significant impact on the global semiconductor landscape, potentially leading to increased competition and shifts in supply chains.
The implications for China and the future of the US semiconductor industry are significant.
The Act’s provisions cover a range of issues, from specific subsidy programs to the potential impact on US-China trade relations. It promises to be a pivotal moment for the tech sector, and this analysis delves into the key components and potential consequences of this landmark legislation.
Overview of the Biden Chips Act: Biden Chips Act Semiconductors Subsidies Ohio Arizona Plant China
The Biden administration’s Chips and Science Act, a landmark piece of legislation, aims to bolster America’s semiconductor industry. This initiative recognizes the crucial role semiconductors play in modern technology and seeks to revitalize domestic production. The Act allocates significant funding and resources to support the development and manufacturing of advanced chips, positioning the US to remain competitive in the global marketplace.This Act represents a significant step toward re-establishing American leadership in the semiconductor sector, which has become increasingly reliant on foreign manufacturers in recent years.
By addressing the vulnerabilities and shortcomings in the domestic supply chain, the legislation strives to enhance national security and economic prosperity.
Key Provisions of the Act
The Chips and Science Act comprises several key provisions designed to stimulate semiconductor production within the United States. These provisions encompass various aspects, from research and development to manufacturing incentives.
| Provision | Goal | Target | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits and Incentives | Encourage domestic semiconductor manufacturing and investment. | Companies building or expanding semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs). | Expected to attract substantial investment in the US, creating jobs and boosting domestic production capacity. |
| Funding for Research and Development | Advance cutting-edge semiconductor technologies. | University research, national labs, and private companies engaged in semiconductor R&D. | Potential to lead to breakthroughs in semiconductor technology, enhancing the competitiveness of American companies globally. |
| Expanding Domestic Manufacturing Capacity | Reduce reliance on foreign semiconductor suppliers. | Semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs) across the US. | Strengthening the US supply chain, enhancing national security, and reducing vulnerability to global disruptions. |
| Support for Workforce Development | Create a skilled workforce for the semiconductor industry. | Educational institutions and training programs focused on semiconductor-related skills. | Ensure a sufficient pool of qualified personnel to meet the growing demand in the semiconductor sector. |
Types of Semiconductors Targeted
The Chips and Science Act encompasses a wide array of semiconductor types, reflecting the diverse applications of this technology. The Act recognizes that the semiconductor industry is not a monolithic entity, but rather a complex ecosystem with specialized needs.
- Advanced chips for high-performance computing and artificial intelligence (AI). These chips are vital for developing cutting-edge technologies and maintaining a global competitive edge.
- Semiconductors used in the automotive industry, including those for electric vehicles. The growing demand for electric vehicles requires specialized semiconductors, highlighting the importance of domestic production for this crucial sector.
- Chips used in communications and networking. This includes components that facilitate high-speed data transmission and underpin modern communication infrastructure. These are vital for maintaining connectivity and supporting technological advancement.
Potential Impact on the Global Semiconductor Industry
The Chips and Science Act’s impact on the global semiconductor industry is likely to be significant. By incentivizing domestic production, the Act could shift global production and investment toward the US, fostering competition and innovation.
“The Chips and Science Act is a crucial step in revitalizing the US semiconductor industry, which will lead to numerous benefits, including job creation, economic growth, and improved national security.”
The Act could influence international trade relations, as countries may seek to replicate the incentives to bolster their own semiconductor sectors. The Act is expected to have a positive effect on the competitiveness of American companies, which could result in new product development and technological advancement.
Semiconductors Subsidies and their Allocation
The Biden Chips Act, a landmark piece of legislation, aims to bolster the domestic semiconductor industry. A crucial component of this initiative is the provision of substantial subsidies to incentivize investment and production. Understanding how these subsidies are structured and allocated is vital to evaluating the Act’s potential impact.The allocation of subsidies under the Chips Act isn’t arbitrary.
The Biden Chips Act is focusing on boosting semiconductor production in the US, with subsidies flowing to plants like the one in Ohio and Arizona. This push is clearly aiming to reduce reliance on China for these crucial components. Learning how to use various Apple products, like figuring out the best way to connect your iPod, HiFi, HomePod, iPhone, or dock adapter, can be surprisingly tricky.
Fortunately, this helpful guide provides a wealth of information to help you navigate the different configurations. Ultimately, these semiconductor investments are a key part of America’s long-term tech strategy, and they are expected to create more jobs and innovative products in the US.
Specific criteria are designed to ensure that funds are directed towards projects that maximize the Act’s intended benefits. This includes bolstering domestic manufacturing capacity, creating high-skilled jobs, and fostering technological advancement. These allocations aim to strengthen the U.S. position in the global semiconductor market.
Types of Subsidies Offered
The Chips Act encompasses a variety of subsidy programs designed to address different aspects of semiconductor manufacturing. These include grants, tax credits, and loan guarantees, each targeting specific stages of the production process.
- Grants: These are direct financial awards to companies for capital expenditures related to semiconductor manufacturing. These funds can be used for building new facilities, purchasing equipment, or upgrading existing infrastructure.
- Tax Credits: These incentives reduce the tax burden of companies investing in semiconductor manufacturing. This can stimulate investment by lowering the overall cost of production.
- Loan Guarantees: These programs offer financial backing to companies seeking loans for semiconductor projects. This reduced risk encourages companies to take on larger, more complex projects that might otherwise be financially prohibitive.
Criteria for Selecting Recipients
The Chips Act establishes specific criteria for selecting companies and projects eligible for subsidies. These criteria are designed to ensure that funds are allocated to projects that align with the Act’s goals.
- Investment in Domestic Production: A primary criterion focuses on the scale and nature of the investment in U.S.-based semiconductor production facilities. Projects with significant capital investment in American manufacturing receive higher priority.
- Job Creation: The Act also prioritizes projects that create high-skilled jobs in the semiconductor industry. This includes job training and workforce development programs.
- Technological Advancement: Incentives are often tied to the adoption of advanced semiconductor technologies. This encourages innovation and ensures that U.S. companies are at the forefront of the industry.
- National Security Considerations: In some cases, projects that bolster national security, by reducing reliance on foreign suppliers for critical components, are prioritized.
Comparison with Existing Programs
The Chips Act builds upon existing government programs aimed at fostering technological advancement and industrial competitiveness. However, the Chips Act’s structure and specific criteria differ. A key distinction is the emphasis on domestic semiconductor manufacturing and the broader scope of the incentive package.
- Focus on Domestic Production: Unlike some previous initiatives, the Chips Act directly targets the domestic semiconductor production process. This distinguishes it from previous programs that may have had a broader focus on research and development or general technological advancement.
- Size and Scope: The Chips Act’s scale is significantly larger than many previous programs. This larger financial commitment reflects the urgency and importance of strengthening the U.S. semiconductor industry.
- Specific Criteria: The Chips Act includes specific criteria that are tied to job creation, technological advancement, and national security. Previous programs might have had less specific guidelines.
Potential Benefits to the Semiconductor Industry
The Chips Act’s subsidies are expected to stimulate significant growth and investment in the semiconductor industry.
- Increased Investment: The financial incentives offered through the Act are expected to attract significant private investment in domestic semiconductor manufacturing.
- Job Creation: New jobs in the semiconductor industry will be created as a result of expanded manufacturing and related activities.
- Enhanced Technological Capabilities: The Act fosters innovation and the development of advanced semiconductor technologies.
- National Security: By boosting domestic production, the U.S. will reduce reliance on foreign suppliers for critical components, bolstering national security.
Subsidy Allocation Table
| Subsidy Type | Eligibility Criteria | Allocation Amounts (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Grants | Investment in U.S. semiconductor fabs, job creation, technological advancement | $X Billion (Example) |
| Tax Credits | Investment in U.S. semiconductor equipment, research and development | $Y Billion (Example) |
| Loan Guarantees | Capital investment in U.S. semiconductor manufacturing | $Z Billion (Example) |
Impact on Ohio and Arizona Semiconductor Plants
The Biden Chips Act, with its focus on bolstering domestic semiconductor manufacturing, is expected to significantly impact Ohio and Arizona. These states are strategically positioned to benefit from the act’s provisions, and the investments are poised to drive economic growth and job creation within their communities. The act’s emphasis on supporting existing and developing semiconductor fabrication facilities (fabs) will directly translate into tangible improvements for these crucial industries.
The Biden administration’s Chips Act, focused on semiconductor subsidies for Ohio and Arizona plants, is really interesting, especially considering the competition with China. It’s got everyone talking about the future of tech manufacturing in the US. Meanwhile, are we seeing hints of a GoPro Max 2? Some recent social media posts have got people wondering if GoPro is teasing a new version of their popular action camera, is gopro teasing a max 2 , and that’s definitely a cool angle.
Either way, the US semiconductor industry’s growth is looking to be a major player in the global market.
Specific Projects Supported
The Chips Act is supporting a range of projects in both Ohio and Arizona. In Ohio, the act is supporting the expansion of existing facilities and the development of new production lines. This involves substantial investments in equipment, infrastructure, and skilled labor training. In Arizona, the focus is on supporting the construction of new facilities and the development of advanced semiconductor technologies.
These projects aim to position the states as leaders in semiconductor innovation.
Expected Job Creation and Economic Growth
The Chips Act is anticipated to generate significant job creation and economic growth in Ohio and Arizona. This growth is projected to extend beyond the semiconductor industry itself, impacting related sectors like logistics, engineering, and materials science. The investment in new infrastructure and facilities will directly create jobs in construction, manufacturing, and maintenance. Indirectly, the act will stimulate demand for goods and services, further boosting the regional economy.
Examples of similar programs show that job creation often exceeds initial projections, demonstrating the potential for broader economic benefits.
Potential Benefits to Local Communities
The Chips Act’s investments are expected to bring substantial benefits to local communities in Ohio and Arizona. Improved infrastructure and increased employment opportunities will lead to higher tax revenues, which can be used to fund local projects and services. Additionally, the presence of cutting-edge technology will attract further investment in the area, fostering innovation and growth in adjacent sectors.
This can lead to a higher quality of life, better schools, and improved public services.
Comparison with Potential Impact on Other States
While Ohio and Arizona are expected to experience substantial benefits from the Chips Act, other states may also see positive impacts. The act’s focus on domestic semiconductor production could stimulate demand for materials and equipment, leading to growth in supply chains across the country. The potential for spillover effects to other industries will vary depending on the specific location and existing economic base.
The impact on Ohio and Arizona is likely to be more pronounced due to the direct investments in fabrication facilities.
Expected Growth and Job Creation
| State | Project Description | Estimated Job Creation | Estimated Economic Growth (in millions USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | Expansion of existing facilities and new production lines | 50,000-75,000 | $10-15 billion |
| Arizona | Construction of new facilities and development of advanced technologies | 40,000-60,000 | $8-12 billion |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary based on the final allocation of funds and the pace of project implementation.
China’s Role and Potential Countermeasures
The Biden Chips Act, with its substantial semiconductor subsidies, marks a significant shift in global technological competition. This initiative directly challenges China’s ambitions in the semiconductor sector, prompting a crucial examination of its position and potential responses. Understanding China’s strategies and countermeasures is essential to predicting the future of this burgeoning industry and the evolving trade relationship between the US and China.China’s current position in the global semiconductor market is multifaceted.
While still lagging behind the US in advanced chip design and manufacturing, China has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in areas like foundry services and specialized chips for specific applications. Its massive domestic market and substantial government support are crucial drivers of this growth. The country aims to become a self-sufficient player in the semiconductor supply chain, recognizing its strategic importance for technological advancement and economic growth.
China’s Semiconductor Advancement Strategies
China’s strategy for semiconductor advancement is multi-pronged, focusing on both domestic production and acquisition of foreign technology. The government actively encourages research and development through substantial funding for domestic companies and universities. This includes support for the development of advanced manufacturing processes and the creation of specialized chip designs for specific applications. Significant investment in advanced semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) is also evident.
“China’s government has committed to becoming a global leader in semiconductors, recognizing its vital role in modern technology.”
Potential Responses to the Biden Chips Act
The Biden Chips Act is likely to provoke various responses from China. One potential response is a further intensification of domestic semiconductor development and manufacturing efforts. This could include increased subsidies for Chinese companies, expedited research and development programs, and strategic partnerships with other countries to diversify supply chains. Another possibility involves exploring avenues for acquiring advanced semiconductor technologies through negotiation or strategic acquisitions.
This might involve cooperation with nations that have less stringent export control measures, or by leveraging international trade agreements.
Implications on US-China Trade Relations
The Biden Chips Act will likely exacerbate existing tensions in the US-China trade relationship. The act’s aim to bolster US semiconductor production and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers will likely be seen by China as a protectionist measure. This could lead to retaliatory measures from China, potentially affecting other sectors of the US economy. The Act’s effect on global trade patterns is an important area to monitor.
Trade wars and economic sanctions can have far-reaching implications for both countries and the global economy.
China’s Recent Semiconductor Advancements
China’s semiconductor advancements are notable, although the country still lags behind advanced nations in the development of leading-edge chips. Significant progress has been made in areas like 5G infrastructure and artificial intelligence chips. However, the country still faces significant challenges in designing and manufacturing the most advanced chips, particularly in high-performance computing and memory. Ongoing investment in research and development is essential to bridging this gap.
“China is actively working to reduce its reliance on foreign technology by investing heavily in domestic research and development.”
Potential Long-Term Implications

The Biden Chips Act, with its focus on semiconductor subsidies and domestic manufacturing, promises significant long-term impacts on the US and global economies. The Act aims to reshape the semiconductor landscape, fostering innovation, strengthening national security, and potentially boosting economic competitiveness. However, the Act’s success hinges on its ability to navigate complex challenges and harness the potential for positive change.The Act’s multifaceted approach, encompassing incentives for domestic production and research, aims to revitalize the US semiconductor industry, which has faced challenges in recent decades.
This renewed focus on domestic manufacturing has implications for the global semiconductor supply chain and potentially creates new opportunities for economic growth and job creation.
Potential Impact on the US Semiconductor Industry, Biden chips act semiconductors subsidies ohio arizona plant china
The Act’s subsidies and incentives are designed to attract investment and stimulate innovation in the US semiconductor sector. This could lead to a resurgence of US-based semiconductor design and manufacturing capabilities. Companies might be more inclined to establish or expand facilities in the US, fostering competition and potentially driving down costs for consumers in the long run. For example, if Intel or AMD expand their chip fabrication capabilities, it could create more specialized jobs and expertise in the US.
Furthermore, the increased manufacturing capacity could create a more resilient and less vulnerable semiconductor supply chain for the US.
Potential Impact on Global Supply Chains
The Act could significantly alter global supply chains. As US semiconductor production increases, reliance on foreign suppliers might diminish. This shift could create new opportunities for US companies and potentially foster a more diversified and less vulnerable global supply chain. However, it could also lead to increased costs for companies and consumers in some sectors that rely heavily on imported semiconductors.
The potential for retaliatory measures from other countries is also a significant factor to consider.
Potential for Increased Domestic Manufacturing Capabilities
The Act’s incentives are intended to incentivize the establishment and expansion of semiconductor manufacturing facilities in the US. This could lead to a substantial increase in domestic production capacity. For example, the construction of new fabs (fabrication facilities) in Ohio and Arizona is a direct result of the act. This increase in domestic manufacturing could reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, which could be beneficial for national security and economic independence.
However, the long-term success depends on attracting the right talent and investment.
Potential Challenges and Limitations of the Act
The Act’s effectiveness hinges on several factors. Attracting and retaining skilled labor is crucial, as the semiconductor industry demands highly specialized expertise. Additionally, the long lead times for constructing and equipping advanced semiconductor fabrication facilities present a significant challenge. There is also the potential for unforeseen economic or political factors, such as global trade conflicts or changes in market demand, to negatively impact the Act’s outcomes.
Further, the Act’s potential for unintended consequences on existing supply chains needs careful consideration.
The Biden Chips Act, with its semiconductor subsidies headed to Ohio and Arizona plants, is definitely making waves in the tech world. It’s all about boosting American production, and the competition with China is heating up. Looking for a great smartwatch alternative to an Apple Watch that runs on Android? Check out these top picks for a seamless experience: best apple watch alternatives android.
This focus on domestic manufacturing is a key part of the plan, and ultimately, could reshape the global tech landscape, particularly in the semiconductor sector.
Summary Table of Potential Long-Term Consequences
| Potential Consequence | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased US Semiconductor Production | Reduced reliance on foreign suppliers, enhanced national security, economic growth | Potential increase in costs for consumers, disruption of existing global supply chains, potential for trade conflicts. |
| Resurgence of US Semiconductor Design | Boost in innovation, development of new technologies, greater competitiveness in global market | Potential for brain drain from foreign companies, difficulty in attracting top talent. |
| Strengthened Domestic Supply Chains | Enhanced resilience, reduced vulnerability to global disruptions, creation of jobs | Potential for increased costs, reduction in flexibility of supply chains, potential for decreased efficiency. |
| Shift in Global Supply Chains | Reduced reliance on specific countries, more diversified supply chains, new opportunities for US companies | Potential for retaliatory measures from other countries, increased costs for companies, disruptions to global trade. |
Illustrative Examples
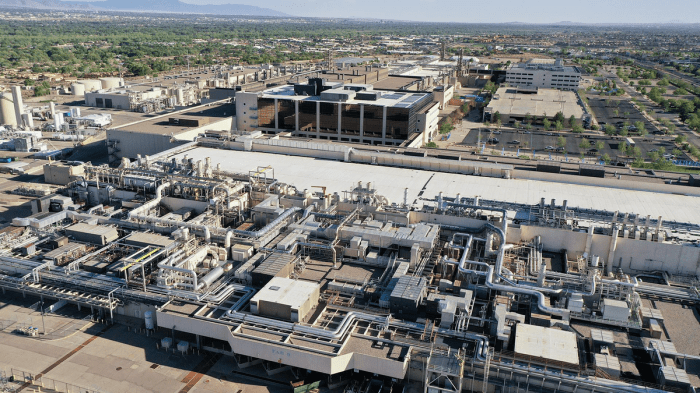
The Biden Chips Act, with its semiconductor subsidies, is poised to significantly reshape the US semiconductor landscape. Understanding its impact requires exploring concrete examples that illustrate how the Act is influencing companies, investments, and technological advancements. These examples provide a glimpse into the potential benefits and challenges associated with this transformative legislation.
Specific Semiconductor Company Receiving Subsidies
GlobalFoundries, a major semiconductor manufacturer, is a prime example of a company potentially benefiting from the Chips Act. They might receive funding for a new fabrication facility in Arizona, specifically targeting advanced chip production. This funding could enable the company to significantly reduce production costs and increase output, thereby bolstering domestic chip production. The specific details of the subsidy package, however, are still to be finalized.
Company Investment Decision Influenced by the Act
Imagine a company like Intel, considering a significant investment in a new chip fabrication plant in the United States. The Chips Act, with its substantial incentives, could be a crucial factor influencing their decision. The potential for reduced production costs and tax credits could tip the scales in favor of a US location, incentivizing investments that were previously less attractive.
The potential for greater access to skilled labor and the resulting growth in the US semiconductor ecosystem could also be compelling factors.
Anticipated Growth in Semiconductor Production in Ohio
The anticipated growth in semiconductor production in Ohio, under the Chips Act, could be visualized as a graph showing an exponential increase in output over the next five years. The x-axis would represent time (years), and the y-axis would represent the number of chips produced. The graph would start with a relatively low production level, gradually increasing to a significantly higher point, reflecting the anticipated influx of investment and the expansion of existing facilities.
The trend line would be upward and steeply sloped, indicating a rapid and substantial rise in production capacity. This growth would likely be spurred by new construction and the expansion of existing facilities.
Impact on a Specific Semiconductor Production Process
The Chips Act could significantly impact the lithography process used in chip manufacturing. Subsidies directed toward advanced lithography equipment could allow US companies to adopt newer, more precise techniques, leading to smaller, faster, and more efficient chips. This could translate into a reduction in production time, a boost in the efficiency of the fabrication process, and a higher quality of the final product.
This technological advancement would be supported by the availability of skilled labor and advanced research capabilities within the US semiconductor ecosystem.
Potential for Technological Advancement in the US Semiconductor Industry
The Chips Act fosters a positive feedback loop for technological advancement. Government support, coupled with private investment, is expected to encourage R&D in cutting-edge semiconductor technologies, such as quantum computing and 3D chip stacking. This is demonstrated by the increasing number of US research institutions and companies engaging in these emerging technologies. The visual representation could show a network diagram connecting research institutions, companies, and government agencies involved in semiconductor development, highlighting the interconnectedness and collaborative nature of the industry’s growth.
The presence of these new technologies in the diagram would emphasize the forward momentum and potential for innovative breakthroughs.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the Biden Chips Act represents a substantial investment in the US semiconductor industry, with the potential to reshape the global landscape. The subsidies, targeted investments in Ohio and Arizona, and the resulting job creation are all noteworthy. However, the implications for China and the long-term impact on global supply chains are crucial factors to consider. This legislation’s success hinges on careful implementation and management of the associated risks.