Apple chips Arizona US Europe TSMC: This intricate network of chip production, spanning from the desert landscapes of Arizona to the tech hubs of Europe, and involving the behemoth TSMC, is a fascinating exploration of global supply chains and technological dominance. From the initial design to the final product, we’ll delve into the complexities of Apple’s chip manufacturing strategy, examining its implications for the US chip industry, its partnerships with global giants like TSMC, and the challenges and opportunities presented in the European market.
This in-depth look will unveil the intricate web of factors that shape the future of chip technology.
Apple’s Arizona facility, a state-of-the-art complex, plays a pivotal role in their chip production strategy. This analysis will explore the advantages and disadvantages of establishing such a large-scale operation in the US, considering the economic and political landscape. We’ll also look at the role of the US government in supporting this burgeoning industry, and compare its progress with the established powerhouse of Taiwan.
Apple Chips Production in Arizona: Apple Chips Arizona Us Europe Tsmc
Apple’s commitment to advanced chip manufacturing in Arizona underscores a significant investment in US-based technology. This expansion positions the company to meet growing demand for its innovative chips, while also contributing to the US semiconductor industry’s resurgence. The facilities are a testament to Apple’s long-term vision for technological leadership and strategic partnerships within the American economy.
Facility Details and Capacity
Apple’s Arizona chip manufacturing facilities represent a substantial commitment to domestic production. The scale of these facilities is significant, encompassing cutting-edge technology and a substantial workforce. Specific details on size and capacity are often not publicly disclosed, although the sheer volume of chips produced clearly indicates a considerable production output.
The global race for top-tier tech chips, like those used in Apple products, is heating up, especially in Arizona, the US, and Europe. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is a major player in this game, but securing reliable and secure connections for businesses is crucial for all the players involved. That’s why AT&T is partnering with Palo Alto Networks to develop a new secure connectivity solution for business customers, a move that’s likely to affect the chip manufacturing landscape.
This initiative, as detailed in at t joins forces with palo alto networks to introduce secure connectivity solution for business customers , will likely influence the future of tech manufacturing in the US and Europe, and how they compete with Asian giants like TSMC. This competitive landscape, in turn, could push the demand for these cutting-edge chips in the future.
Technology Employed
Apple’s Arizona facilities leverage the most advanced semiconductor fabrication techniques. This includes sophisticated lithography processes, enabling the production of intricate and highly-performing chips. The specific details of the technology are not publicly disclosed to protect intellectual property, but it is known that continuous advancements are made in the development of new materials and processes to meet future performance demands.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Arizona Location
Choosing Arizona as a location for chip manufacturing presents several advantages, including proximity to a skilled workforce, access to transportation networks, and a supportive government environment for technological advancement. The state’s favorable business climate and resources for attracting skilled talent are also significant factors. However, there are potential disadvantages, including fluctuating costs of materials and labor, as well as potential challenges in maintaining consistent supply chains.
Supply Chain Overview
The supply chain for Apple chips in Arizona is intricate and globally dispersed. It involves procuring raw materials, including specialized chemicals and silicon wafers, from various suppliers worldwide. Manufacturing processes are undertaken in the Arizona facilities, utilizing advanced equipment. The final product is then tested and packaged before distribution to Apple’s various divisions and partners.
Comparison with Other US Facilities
Comparing Apple’s Arizona chip production with similar facilities elsewhere in the US reveals a trend toward increasing domestic manufacturing capacity. While specific data on production volume and technology differences between facilities is not publicly available, the overall trend points to a concerted effort within the US to bolster its semiconductor manufacturing base. The development of specialized infrastructure and talent pools is crucial for sustaining this trend.
Table: Apple Chip Production Facilities
| Location | Capacity (in units per year) | Technology Used | Key Suppliers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | Confidential | Advanced lithography processes, sophisticated chip design | Confidential (various global suppliers) |
| [Other US Facility – Example] | Confidential | Advanced lithography processes, potentially different design focus | Confidential (various global suppliers) |
US Chip Manufacturing Landscape
The US chip industry is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by a confluence of factors including national security concerns, the desire for greater economic self-reliance, and the rising global demand for advanced semiconductors. This shift is pushing the US to invest heavily in domestic chip manufacturing capabilities, creating a dynamic landscape that demands careful analysis of key players, government initiatives, and the industry’s competitiveness on the global stage.
Key Players Beyond Apple
Beyond Apple’s substantial investment in Arizona, several other companies are actively involved in US chip manufacturing. These include Intel, which is expanding its existing facilities and investing in new technologies. GlobalFoundries, a prominent player in the industry, also operates facilities in the US. These companies, along with other smaller players, represent a growing ecosystem of chip manufacturers dedicated to meeting the demands of the domestic market.
Government Support for US Chip Manufacturing
The US government has implemented various initiatives to bolster domestic chip manufacturing. These include substantial financial incentives, tax credits, and targeted investments in research and development. The Chips and Science Act, a landmark piece of legislation, provides substantial funding to support the growth of the US semiconductor industry. These initiatives aim to reduce reliance on foreign chip manufacturers and enhance national security.
US Chip Industry Competitiveness
Compared to Taiwan, which currently dominates global chip manufacturing, the US industry faces a challenge in achieving comparable scale and expertise. Taiwan’s long-standing investment in chip manufacturing, coupled with its robust ecosystem of suppliers and skilled labor, provides a significant advantage. However, the US government’s commitment and substantial investments, combined with the growing domestic demand, are expected to gradually narrow the gap in competitiveness.
Market Share of US Chip Manufacturers
Unfortunately, precise, publicly available data on the exact market share of US chip manufacturers is often limited. Gathering such data would require access to proprietary financial reports from each company. Moreover, industry dynamics and the varying product types produced by different manufacturers further complicate the task of creating a comprehensive market share table.
Factors Influencing Growth and Development
Several factors are shaping the growth and development of the US chip industry. The increasing demand for advanced chips in areas like artificial intelligence, automotive technology, and 5G communication systems is a key driver. Government policies, like the Chips and Science Act, are also playing a pivotal role. Furthermore, the development of a strong domestic supply chain of materials and components is crucial for long-term sustainability.
A skilled workforce is another essential factor.
Apple’s Global Chip Strategy
Apple’s global chip strategy hinges on a multifaceted approach to sourcing components, leveraging strengths in different geographic locations to optimize production costs and technological advancement. This involves intricate partnerships and a carefully considered balance between in-house design and external manufacturing, all tailored to maintain quality and competitive pricing. The company’s strategy is not static, but rather dynamic, adapting to evolving market demands and technological advancements.Apple’s strategy reflects a deep understanding of the global semiconductor landscape.
The company strategically distributes its chip production to leverage cost advantages, access specialized expertise, and manage potential supply chain disruptions. This decentralized approach allows for flexibility and resilience in the face of geopolitical or economic uncertainties.
Apple’s Component Sourcing Strategy
Apple’s strategy for sourcing components involves a complex network of partnerships. They collaborate with leading chip foundries like TSMC, and also have a growing in-house manufacturing presence in Arizona, demonstrating a desire for greater control over the chip production process. This approach is a mix of vertical integration and outsourcing, allowing them to maintain quality standards while optimizing costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing
Outsourcing chip production offers several advantages. It allows Apple to access specialized manufacturing capabilities and cutting-edge technology at foundries like TSMC, which may not be readily available or cost-effective to replicate in-house. This enables Apple to focus its resources on research and development, design, and software integration, leveraging the expertise of external partners. However, outsourcing also presents potential challenges.
Dependencies on external suppliers can create vulnerabilities in the supply chain, and maintaining consistent quality across different manufacturing facilities requires stringent oversight and quality control mechanisms.
Comparison with Competitors, Apple chips arizona us europe tsmc
Apple’s competitors often adopt similar strategies of outsourcing chip production, relying on foundries for the physical manufacturing of their chips. However, the degree of vertical integration and the specific foundry partnerships can vary significantly between companies. Some competitors may favor a more distributed approach, while others may prioritize establishing in-house manufacturing facilities to a greater extent. This variability reflects the differing priorities and resource allocation strategies of each company.
Ever wondered about the global supply chain for those snazzy Apple chips? Arizona, US, Europe, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) all play a role. The intricate network is fascinating, but equally interesting is how those components power something like an Audio Technica vinyl turntable at an LPA2 record player. This meticulous craftsmanship, evident in the audio technica vinyl turntable at lpa2 record player , makes you appreciate the meticulousness of modern electronics, even in seemingly simpler products, and it all circles back to the same global chip network that underpins Apple’s offerings.
Cost Comparison of Chip Production
| Location | Estimated Cost per Chip (USD) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona, US | $X | Reduced transportation costs, proximity to design teams, potential for greater control over quality | Potentially higher labor costs compared to Taiwan, limited volume production capacity |
| Europe | $Y | Closer to European markets, potential for reduced geopolitical risks, support for European manufacturing ecosystem | Potentially higher labor costs and stricter regulations compared to Taiwan, distance from TSMC’s advanced facilities |
| Taiwan (TSMC) | $Z | Access to advanced chip technologies, large-scale production capabilities, highly specialized workforce | Higher transportation costs, reliance on a single supplier, potential geopolitical risks associated with Taiwan |
Note: The cost figures (X, Y, Z) are estimates and are subject to change based on various factors.
Apple Chip Technologies
Apple utilizes a range of advanced chip technologies across its product lines. These include custom-designed ARM-based processors, optimized for specific functionalities, like the A-series chips used in iPhones and iPads. The company also incorporates specialized components, like GPUs, for enhanced graphical performance, and memory controllers for efficient data handling. These technologies are meticulously integrated to deliver optimal performance and power efficiency across their diverse product portfolio.
TSMC’s Role in the Global Chip Industry
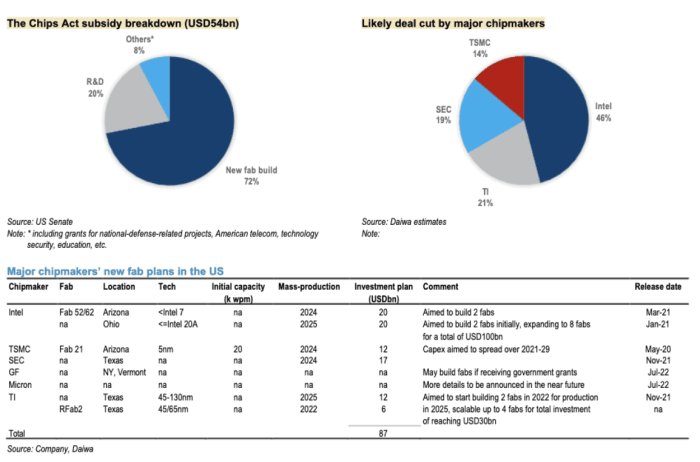
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) stands as a titan in the global semiconductor industry, playing a crucial role in manufacturing the advanced chips powering modern technology. Its expertise in producing cutting-edge integrated circuits (ICs) has cemented its position as the world’s leading contract chip manufacturer, influencing the design and availability of crucial components in countless devices.TSMC’s dominance stems from its unparalleled ability to produce complex and sophisticated chips, setting the standard for technological advancement in chip manufacturing.
This prowess extends beyond simply assembling components; it involves sophisticated process engineering, advanced materials science, and the mastery of intricate fabrication techniques. This makes TSMC a vital partner for companies like Apple, allowing them to focus on design while TSMC handles the intricate production process.
TSMC’s Technological Advancements in Chip Production
TSMC consistently pushes the boundaries of chip manufacturing technology. Their relentless pursuit of innovation has led to the development of advanced processes like FinFET and 3D stacking, which significantly enhance the performance, power efficiency, and density of integrated circuits. These advancements enable the creation of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient chips, driving progress across various sectors.
Comparison of TSMC’s Capabilities with Other Leading Foundries
TSMC’s technological leadership is evident when compared to other prominent foundries like Samsung and Intel. While Samsung and Intel possess substantial capabilities, TSMC generally holds a competitive edge in terms of process node advancements and production scale. This competitive advantage is further reinforced by TSMC’s global network of facilities and dedicated workforce, providing unparalleled manufacturing capacity and flexibility.
TSMC’s Market Share and Influence on Global Chip Supply Chains
TSMC’s market share is substantial, dominating a significant portion of the global chip manufacturing market. This dominance translates into considerable influence over global chip supply chains. The reliance on TSMC for production creates interdependencies and vulnerabilities, impacting the availability and cost of chips worldwide. This influence is particularly notable in the production of advanced chips, where TSMC’s expertise is highly sought after.
TSMC’s Role in the Supply Chain for Apple Chips
Apple heavily relies on TSMC for the manufacturing of its cutting-edge chips, particularly its A-series processors. This partnership demonstrates TSMC’s vital role in Apple’s supply chain. TSMC’s ability to meet Apple’s demanding specifications for high-performance and low-power chips is critical to the success of Apple products. This strategic alliance ensures a steady supply of chips for Apple devices, and underscores the significance of TSMC in the global technology landscape.
Apple Chips in Europe
Apple’s global ambitions extend beyond the US and Asia, and Europe is a key strategic area for the company’s chip operations. This presence is driven by a combination of factors, including the desire to reduce reliance on single-source manufacturing and bolstering relationships with European partners. The EU’s regulations play a significant role in shaping Apple’s chip manufacturing and sourcing strategies within the continent.
Apple’s European Chip Presence and Activities
Apple has established a presence in Europe, not just for product sales but also for chip-related activities. This includes research and development facilities, potentially strategic partnerships with European chip design companies, and collaborations with European manufacturers. These activities are not limited to a single country but are spread across the continent. Their aim is multifaceted, from improving efficiency to building a stronger supply chain and minimizing dependence on specific regions.
Motivations Behind Apple’s Investments in Europe
Several factors motivate Apple’s investments in Europe’s chip market. Proximity to key European markets allows for faster response times and reduced shipping costs, crucial in today’s fast-paced technology landscape. Additionally, diversifying manufacturing locations reduces reliance on single-source supply chains, enhancing resilience against potential disruptions. The EU’s emphasis on technological self-reliance is another catalyst for Apple’s strategic decisions in Europe.
Impact of EU Regulations on Apple’s Chip Manufacturing and Sourcing Strategies
EU regulations, such as those focused on data protection and digital markets, influence Apple’s chip manufacturing and sourcing strategies. Compliance with these regulations is paramount, and Apple must navigate these requirements to ensure smooth operations and maintain its strong reputation within the European market.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Apple in the European Chip Market
Apple faces challenges in the European chip market, such as navigating complex EU regulations and potential trade disputes. However, opportunities also exist, such as tapping into the skilled workforce and establishing closer ties with European chip design companies. The ability to effectively address these challenges and leverage the opportunities will be pivotal to Apple’s success in Europe.
Apple chips production in Arizona, the US, Europe, and reliance on TSMC is fascinating. It’s a global supply chain, but navigating the complex production process is tricky. For those new to the game, checking out some ghost tsushima tips and tricks beginners can help with similar challenges of mastering complex systems. Ultimately, the interplay of these factors shapes the global chip market, and the future of the industry.
Apple’s Product Lines and Chip Specifications
| Product Line | Chip Specifications |
|---|---|
| iPhone | A-series chips (e.g., A16 Bionic, A15 Bionic), incorporating custom designs and optimized for specific functionalities |
| iPad | A-series chips (e.g., A14 Bionic, A12 Bionic), tailored for the tablet form factor, focusing on processing power and graphics capabilities |
| Mac | M-series chips (e.g., M1 Pro, M2 Max), designed specifically for MacBooks and desktops, emphasizing high-performance computing and energy efficiency |
| Apple Watch | S-series chips (e.g., S8, S7), focused on integration with health and fitness features, including processing power and sensor communication |
| AirPods | H1 and subsequent chips, optimizing audio quality, connectivity, and battery life for the wireless earbuds |
Impact of Geopolitical Factors
The global semiconductor industry, a vital component of modern economies, is increasingly intertwined with geopolitical realities. Trade disputes, political instability, and strategic rivalries significantly impact the production, supply, and pricing of chips, impacting everything from consumer electronics to critical infrastructure. Understanding these influences is crucial for businesses and policymakers navigating the complex landscape of the 21st-century chip economy.The intricate web of global chip manufacturing and supply chains is vulnerable to disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions.
Trade wars, sanctions, and export controls can severely restrict the flow of materials, components, and finished products, leading to shortages and price hikes. These disruptions can have ripple effects throughout the global economy, affecting industries that rely on semiconductors for their operations.
Trade Tensions and Global Chip Production
Trade tensions between nations often lead to tariffs and quotas on semiconductor exports and imports. These measures can disrupt supply chains, increase production costs, and limit access to critical components, ultimately hindering innovation and economic growth. For instance, the trade war between the US and China in recent years has led to uncertainty and volatility in the global chip market, with companies facing challenges in sourcing materials and components.
This underscores the importance of diversification and resilience in global supply chains.
Impact of Political Instability on Material Availability
Political instability in regions crucial to semiconductor production can significantly affect the availability of raw materials. For example, disruptions in the mining and refining of materials like silicon, gallium, and germanium, essential for chip manufacturing, can lead to shortages and price spikes, impacting production schedules and ultimately affecting consumer products. Furthermore, instability can impede the movement of workers and equipment, disrupting the entire manufacturing process.
Geopolitical Influences on Chip Manufacturing Locations
Geopolitical factors play a crucial role in the choice of locations for chip manufacturing facilities. Countries often seek to attract investment in chip production to enhance their technological capabilities and economic competitiveness. However, concerns about national security, trade policies, and access to resources can influence the decision-making process. Governments may incentivize domestic chip production to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers and safeguard strategic assets.
Strategies for Mitigating Geopolitical Risks
Diversification of supply chains across multiple regions is a crucial strategy to mitigate the risks associated with geopolitical instability. Companies can spread their production and sourcing activities across different countries, reducing reliance on any single region or supplier. This approach can enhance resilience and help maintain uninterrupted production despite unforeseen disruptions. Furthermore, strengthening relationships with reliable partners and investing in domestic chip production capacity can also help to reduce vulnerability.
Building strategic partnerships with other countries to ensure access to raw materials and components is also a key strategy. Companies must adapt their strategies to the ever-changing geopolitical landscape.
Future Trends in Chip Manufacturing

The semiconductor industry is constantly evolving, driven by the insatiable demand for faster, more powerful, and energy-efficient chips. This dynamic landscape necessitates a keen understanding of emerging trends, from innovative manufacturing techniques to the role of automation. Predicting the future of chip manufacturing is challenging, but examining current advancements provides valuable insight into potential trajectories.The race to miniaturize chips and increase processing power is intensifying.
New materials and fabrication methods are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. The impact on Apple’s chip strategy, and the global chip industry as a whole, is significant and multifaceted.
Emerging Trends in Chip Manufacturing Technology
Advancements in chip manufacturing technology are crucial for maintaining competitive edge in the semiconductor industry. These advancements are focused on creating smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient chips. New materials like gallium nitride and advanced packaging techniques are being explored to overcome limitations in traditional silicon-based chips. This will lead to more complex and powerful integrated circuits.
Future Demand for Advanced Chip Technologies
The demand for advanced chip technologies is soaring across various sectors. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the internet of things (IoT) are driving the need for ever-increasing processing power and memory capacity. Autonomous vehicles, for example, rely heavily on sophisticated chips for real-time data processing. This demand is projected to continue growing, fueled by the increasing integration of technology into everyday life.
Potential for Automation and AI in Chip Production
Automation and artificial intelligence are poised to revolutionize chip production. Automated systems can streamline processes, reduce human error, and increase production efficiency. AI can optimize manufacturing processes in real-time, leading to higher yields and reduced costs. This increased automation will be critical for manufacturers to keep pace with demand.
Impact on Apple’s Chip Manufacturing Strategy
Apple’s chip manufacturing strategy will need to adapt to these trends. The company will likely invest in research and development of advanced manufacturing techniques. They may explore partnerships with innovative startups and companies in this field. Integration of automation and AI in their production lines is crucial for maintaining their competitive edge and meeting demand.
Impact on the Global Chip Industry
These trends will reshape the global chip industry, with significant implications for global supply chains. The shift towards automation and AI will necessitate workforce retraining and adaptation. Increased competition among chip manufacturers will drive innovation and efficiency. The need for skilled labor in advanced semiconductor fabrication will also become critical. This will necessitate international cooperation in research and training.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the global chip industry, as exemplified by Apple’s diverse strategies across Arizona, the US, Europe, and TSMC, is a complex interplay of technological advancement, geopolitical factors, and economic realities. From the intricate details of production to the impact of trade tensions, the future of chip manufacturing presents both challenges and opportunities. This exploration has highlighted the intricate web of supply chains, emphasizing the critical role of partnerships like Apple and TSMC in shaping the technological landscape.




