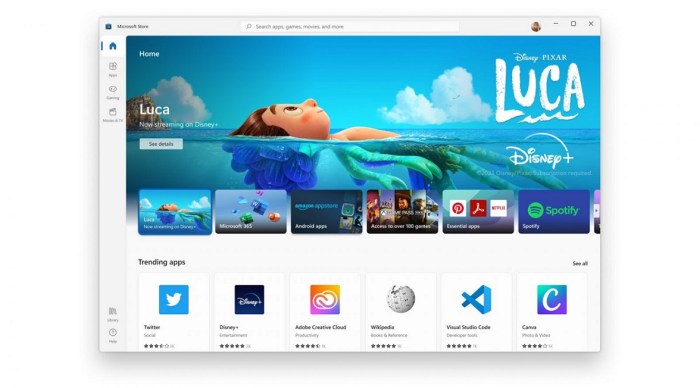
Android apps and windows 11 heres what you should know – Android apps and Windows 11: here’s what you should know. This in-depth look delves into the fascinating world of running Android apps on Windows 11, exploring compatibility, performance, user experience, and the implications for developers and users. We’ll uncover the nuances of this emerging technology, examining its potential benefits and challenges.
From a brief history of Android apps on other platforms to a detailed analysis of compatibility and performance, this article will cover everything you need to understand. We’ll also explore the user experience, development considerations, and even the security and privacy concerns associated with this exciting integration.
Introduction to Android Apps and Windows 11
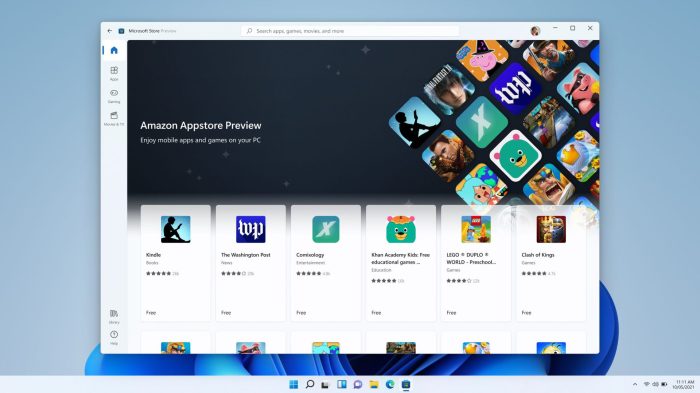
Android app development, a dominant force in the mobile space, is continually evolving. Windows 11, seeking to broaden its appeal, has explored integration with Android apps. This integration, while offering some benefits, presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. This exploration delves into the current state of Android app compatibility with Windows 11, examining their shared and distinct features.
We will also touch on the history of Android apps appearing on other platforms.The current state of Android app compatibility with Windows 11 is a work in progress. Microsoft’s approach involves leveraging the power of the Amazon Appstore, allowing users to access a vast library of Android apps through their Windows 11 device. This method offers a significant advantage for those seeking a wider variety of applications.
However, the experience is not entirely seamless, and the performance of some Android apps may vary on Windows 11 compared to dedicated Android devices.
Key Differences and Similarities Between Android and Windows 11 App Ecosystems
The Android app ecosystem is characterized by its extensive app store, a vibrant developer community, and a focus on mobile-first design. Windows 11, on the other hand, emphasizes a more integrated, desktop-centric experience. While both platforms strive to provide a rich user experience, the underlying architectures and design philosophies differ significantly.Android apps are primarily built using Java or Kotlin, targeting a wide range of devices with varying screen sizes and resolutions.
Windows 11 apps, conversely, are developed using a broader array of technologies, allowing for greater customization and desktop integration. This difference in approach leads to varying user interfaces and app functionalities.
Advantages of Using Android Apps on Windows 11
- Access to a vast library of apps: The Android app ecosystem boasts a massive selection of apps across various categories, unavailable through the Windows Store alone. This diverse range caters to specific needs and interests, offering users more choices.
- Familiarity and ease of use: Many users are already familiar with the Android app interface and design conventions. This familiarity reduces the learning curve for new users of Windows 11 and allows them to seamlessly integrate Android apps into their workflow.
- Potential for innovation: Android’s open-source nature has fostered innovation. The integration of Android apps into Windows 11 may introduce new features and capabilities, expanding the possibilities for software development and application deployment.
Disadvantages of Using Android Apps on Windows 11
- Performance inconsistencies: Android apps may not perform as optimally on Windows 11 as they do on dedicated Android devices. Differences in hardware and operating system architecture can lead to variations in app speed, responsiveness, and overall user experience.
- Potential compatibility issues: Some Android apps might not be fully compatible with the Windows 11 environment. The integration process may introduce compatibility problems or require adjustments for optimal functioning. This can lead to frustration for users.
- Limited customization: The level of customization available for Android apps within the Windows 11 environment might be restricted. The flexibility of Android’s customization options might be reduced when running on a different platform.
History of Android Apps on Other Platforms
While the primary platform for Android apps is mobile, some experimentation with Android app presence on other platforms has occurred. Early efforts focused on limited compatibility with desktop systems, primarily through browser-based implementations. However, the widespread adoption of Android apps on other platforms, such as Windows 11, is a more recent development, focusing on the specific challenges of integrating the Android framework into a different operating system.
Compatibility and Performance
Running Android apps on Windows 11, through the Amazon Appstore or other methods, introduces a unique set of considerations regarding compatibility and performance. This approach leverages emulation, which, while offering broad access, can present some performance challenges compared to native Windows applications. Understanding these technical nuances is crucial for optimal user experience.The core of the Android experience on Windows 11 lies in its virtualization.
Emulation, a key component of this process, creates a virtual environment where Android apps run. This approach allows for a wider range of apps, but it also necessitates a trade-off in performance. The performance of these apps often hinges on the hardware resources available to the emulation layer, and the specific configuration of the system running the apps.
So, you’re diving into Android apps and Windows 11? Great choice! It’s all about finding the right balance between the two platforms, and honestly, it’s a pretty fascinating space. While you’re exploring that, you might also want to check out the Senate’s federal tax credit bill for electric vehicle leases, which could significantly impact your choices. senate federal tax credit bill subsidy electric vehicle lease Ultimately, understanding the features and limitations of each operating system will help you navigate the complexities of the digital landscape.
Knowing which apps work best on which platform is key to a smooth experience.
Technical Aspects of Android App Execution
The Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) uses a virtual machine to run Android apps. This emulated environment allows Android apps to function within the Windows ecosystem. However, the overhead of virtualization can introduce performance differences compared to native Windows apps. The specific implementation of the Android runtime and the underlying operating system components significantly influence the performance of apps.
Performance Bottlenecks and Solutions
Several factors can contribute to performance bottlenecks when running Android apps on Windows 11. Limited system resources, particularly RAM and CPU capacity, can hinder the smooth operation of resource-intensive applications. Similarly, network limitations can also affect the performance of certain apps.To mitigate these bottlenecks, users can consider upgrading their hardware. More powerful processors and increased RAM can enhance the performance of Android apps.
Also, optimizing the apps themselves can help. Developers can potentially create optimized versions of their apps to reduce the demands on system resources.
So, Android apps and Windows 11 – what’s the deal? Well, it’s all pretty interesting, but you also need to know that Twitter’s legacy verification is going away on 420, twitter legacy verification ending on 420. That’s a big change, and it might affect how you use the platform. Regardless, understanding the specifics of compatibility between Android apps and Windows 11 is key to a smooth transition.
Comparison with Native Windows Apps
Native Windows apps are built specifically for the Windows operating system and its APIs. Consequently, they tend to run more efficiently and directly utilize the hardware. In contrast, Android apps on Windows 11 run within a virtual environment, introducing a layer of abstraction that can impact performance. The difference in performance is often noticeable, especially when running demanding graphics-intensive or computationally complex applications.
Methods for Ensuring Compatibility, Android apps and windows 11 heres what you should know
Ensuring compatibility involves several key steps. Using a compatible version of the Android operating system and ensuring the correct hardware configuration are essential factors. Furthermore, app developers should optimize their applications for the Windows Subsystem for Android, taking into account the different requirements of the virtual environment.
- Hardware Optimization: A more powerful processor, higher RAM capacity, and a robust storage system will enhance the performance of Android apps running on Windows 11.
- App Optimization: Developers can tailor their apps for the virtualized environment by reducing resource usage and optimizing code for efficiency.
- System Configuration: Ensuring sufficient system resources and appropriate configuration settings for the Windows Subsystem for Android will also help improve the user experience.
User Experience and Interface
The transition of Android apps to Windows 11 presents a unique opportunity to bridge the gap between mobile and desktop experiences. This necessitates careful consideration of user interface design to ensure a smooth and intuitive experience for users accustomed to both platforms. The differences in design philosophies and operating principles must be addressed to maximize compatibility and usability.The user experience of running Android apps on Windows 11 is significantly different from running them on a native Android device.
The key difference lies in the underlying operating systems and their inherent design philosophies. Windows 11, with its desktop-centric approach, provides a different context for Android apps, potentially impacting how users interact with them. Careful design considerations are crucial to mitigate these differences and create a positive user experience.
Design Considerations for Seamless Transition
To ensure a seamless transition, developers must consider several key design elements. These considerations aim to leverage the strengths of both platforms while mitigating the drawbacks of porting Android apps to a Windows 11 environment.
- Maintaining Familiarity with Android Design Principles: A crucial aspect is preserving the core design principles of Android. This includes maintaining familiar navigation patterns, visual cues, and overall aesthetic consistency. This ensures that users accustomed to the Android interface feel comfortable navigating the application. A good example is maintaining consistent button layouts, color schemes, and text styles, reducing the cognitive load on users.
- Adapting to Windows 11 UI Standards: At the same time, the application needs to respect and adhere to Windows 11’s visual language. This means adopting Windows 11’s typography, iconography, and overall visual hierarchy. This integration creates a cohesive visual experience, blending Android app aesthetics with the broader Windows 11 context. This is essential for maintaining consistency with other Windows 11 applications and minimizing visual dissonance.
- Providing Clear Contextual Feedback: Crucially, Android apps running on Windows 11 must provide clear and consistent feedback to user actions. This includes visual cues, auditory signals, and textual confirmations to let users know their input is registered and understood. This is especially important for actions that differ between the two platforms. For example, an Android “tap” gesture on a button might need a different visual confirmation on Windows 11, perhaps a subtle animation or a visual highlight.
User Interface Differences Between Android and Windows 11
The fundamental differences between the two platforms significantly impact the user interface. Android, by nature, is designed for touch-based interaction, while Windows 11 relies heavily on a mouse and keyboard.
- Input Methods: Android apps primarily rely on touch input, whereas Windows 11 applications are designed to accommodate mouse and keyboard interaction. Android apps running on Windows 11 must seamlessly integrate support for both methods, providing an intuitive and consistent user experience regardless of the input device used.
- Window Management: Android’s window management system differs from Windows 11. Android generally presents a single, full-screen application, while Windows 11 allows for multiple windows and tasks. Android apps on Windows 11 need to adapt to this multi-tasking environment and display their interface appropriately within the Windows 11 window framework.
- Visual Cues and Feedback: Android often utilizes subtle animations and visual cues to indicate actions. Windows 11, while incorporating animations, emphasizes visual feedback through different UI elements, which Android apps should mirror or adapt to for better integration.
Making the UI Intuitive for Both Ecosystems
The goal is to create a unified experience for users, regardless of their primary interaction method.
- Universal Accessibility: The user interface must be accessible to users regardless of whether they primarily use touch, a mouse, or a keyboard. This necessitates the use of clear visual cues, consistent feedback, and adequate support for various input methods.
- Contextual Design: The user interface elements must clearly communicate the context of the current interaction. This is crucial to avoid confusion and maintain a consistent user experience.
- Learnability: The UI should be easy to learn and navigate for both touch and mouse users. This means utilizing familiar design patterns and providing clear visual cues to guide users.
Development Considerations for Android Apps on Windows 11: Android Apps And Windows 11 Heres What You Should Know
Building Android apps for Windows 11 presents a unique set of considerations for developers. This approach leverages the power of the Windows ecosystem, enabling a wider reach for Android applications. Crucially, developers must understand the nuances of compatibility and performance optimization to ensure a seamless user experience.This exploration delves into the essential framework, tools, and potential challenges associated with Android app development on Windows 11.
By understanding these aspects, developers can navigate the complexities and create compelling applications tailored for the Windows 11 environment.
Framework for Android App Development on Windows 11
A robust framework is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance. This framework should encompass cross-platform considerations, enabling developers to maintain code consistency across various operating systems. Furthermore, the framework must prioritize performance optimization, especially concerning resource management and memory usage. This is critical for a smooth user experience.
So, Android apps and Windows 11, what’s the deal? It’s all about compatibility and performance these days, which can be a bit tricky. Meanwhile, did you hear about the Taylor Swift “Midnights” exclusive track, “You’re Losing Me?” The fandom is going wild, and it’s fascinating to see how much impact music can have! This article dives deep into the reaction, and honestly, it reminds me of the challenges with app compatibility on Windows 11.
Hopefully, both music and apps will be seamlessly integrated soon, making our lives a little easier. Overall, navigating these digital landscapes is quite the journey, isn’t it?
Essential Tools and Techniques
Developing Android apps for Windows 11 requires a set of specialized tools. These tools must seamlessly integrate with the Windows development environment. This ensures a smooth workflow and efficient debugging capabilities.
- Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA): This is a key component for running Android apps on Windows. It allows developers to use familiar Android development tools and techniques. It provides a virtualized Android environment within Windows, mimicking the Android operating system.
- Android Studio: This popular Integrated Development Environment (IDE) remains the standard for Android app development. Developers can utilize its comprehensive features to build, debug, and test applications. It supports the tools and libraries necessary for developing for the WSA.
- Java/Kotlin: The dominant programming languages for Android development are Java and Kotlin. Developers need proficiency in one or both to create applications. These languages are designed to interface effectively with the Android framework.
- Emulators/Simulators: Emulators provide a virtual environment for testing and debugging applications. They allow developers to simulate various Android device configurations. Simulators can be used in conjunction with emulators, or instead of them, depending on the developer’s needs.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Several challenges might arise during Android app development on Windows 11. Careful planning and a comprehensive understanding of the Windows ecosystem can mitigate these challenges.
- Compatibility Issues: Differences between the Windows and Android environments can lead to compatibility problems. Careful testing and debugging, along with employing cross-platform solutions, can address compatibility issues. Comprehensive testing across various Android device configurations within the WSA is crucial.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Optimizing for resource usage and efficient code execution is essential for smooth performance. Using profiling tools to identify performance bottlenecks and implementing efficient algorithms are essential.
- Integration with Windows Features: Seamless integration with Windows 11 features like the system UI, storage access, and other services can be a challenge. A clear understanding of the Windows API and appropriate handling of these features is essential.
Future Trends and Developments
The field of Android app development on Windows 11 is continuously evolving. New trends and developments can significantly impact the way developers create and deploy applications.
- Increased Use of Cross-Platform Frameworks: Frameworks like Flutter or React Native might become more prevalent for developing Android apps targeting Windows 11. This reduces development time and effort, as the same codebase can be used for different platforms.
- Advancements in WSA: Future enhancements to the Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) could improve performance, compatibility, and support for more advanced Android features. This will likely reduce the complexity for developers.
- Integration with Windows Services: Enhanced integration with Windows 11 services like the Microsoft Store and other Windows APIs could open new opportunities for Android apps. This integration will provide broader access to features and capabilities.
Use Cases and Examples
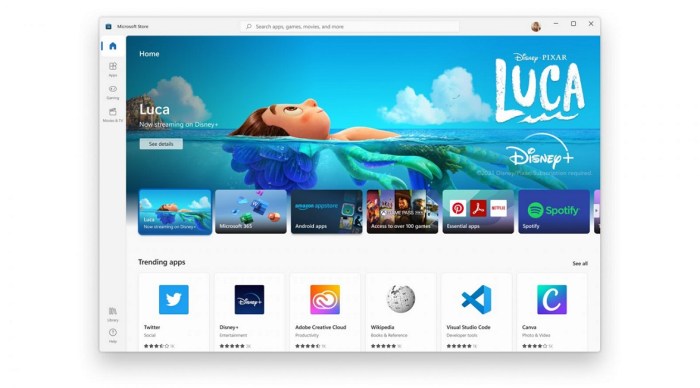
The ability to run Android apps on Windows 11 opens up a world of possibilities, bridging the gap between two dominant operating systems. This allows users to leverage the vast Android app ecosystem within a Windows environment, providing a more comprehensive and versatile computing experience. From productivity tools to entertainment options, this cross-platform compatibility significantly enhances user choice and flexibility.This section explores real-world examples of Android app integration on Windows 11, comparing their functionality to native Windows applications, and analyzing the features and limitations of different app categories.
Real-World Examples of Android App Usage on Windows 11
This section showcases how Android apps are used on Windows 11, providing a tangible understanding of their integration into the Windows ecosystem. Many Android apps are readily available for use on Windows 11, offering functionalities similar to their native Windows counterparts.
- Productivity: Tasks such as note-taking, to-do list management, and project organization can be handled through Android apps like Google Keep or Todoist. These apps offer similar functionalities to native Windows apps like OneNote or To Do, though their integration with Windows ecosystem features may differ.
- Entertainment: Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify, available through Android apps, seamlessly integrate with Windows 11. Users can access their preferred content directly within the Windows environment.
- Communication: Instant messaging apps like WhatsApp and Telegram offer a consistent user experience across platforms. This allows users to manage their communication channels from within their Windows environment.
Comparison of Android Apps and Native Windows Counterparts
A direct comparison of functionalities reveals some nuances. While many Android apps replicate core functions, differences exist in the integration with Windows-specific features.
| Android App | Windows Equivalent | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Google Keep | OneNote | Google Keep excels in quick note-taking and sharing, while OneNote offers more robust formatting and collaborative features. OneNote is integrated more deeply into the Windows ecosystem. |
| Spotify | Windows Music | Spotify offers a broader music library and more comprehensive features, while Windows Music is simpler. Spotify integrates more deeply with the Android ecosystem. |
| Microsoft Teams/Skype | WhatsApp prioritizes simplicity and instant communication, while Microsoft Teams/Skype are geared toward business communication and features like video conferencing. |
Features and Limitations of Android Apps on Windows 11
This table details the strengths and weaknesses of Android apps running on Windows 11.
| App Category | Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity | Access to a vast range of productivity tools; often with similar functionality to native Windows apps; user-friendly interfaces; integration with cloud services. | May lack deep integration with Windows-specific features; performance can vary depending on the app and device configuration. |
| Entertainment | Access to a diverse range of streaming services and games; often offers a wider selection than native Windows options; compatibility with mobile controls. | Potential for slower loading times or performance issues depending on the app and device; limited access to advanced Windows features. |
| Communication | Seamless communication across platforms; user-friendly interface for instant messaging and calls. | May have limited integration with other Windows communication tools. |
Security and Privacy Concerns
Bridging the gap between Android and Windows 11 for app usage introduces a unique set of security considerations. Users must understand the potential vulnerabilities and the measures taken to mitigate them, while developers must adhere to stringent security protocols. This section delves into the security implications of running Android apps on Windows 11, addressing privacy concerns, and outlining security best practices for both users and developers.The compatibility of Android apps on Windows 11, while offering convenience, necessitates a careful examination of security protocols.
This approach ensures a secure environment for both app users and the data they handle.
Security Implications of Android Apps on Windows 11
The execution of Android apps within the Windows 11 environment introduces a layer of complexity in terms of security. The differing operating systems, security models, and potential for malicious code necessitate careful consideration. Android apps, when running on Windows 11, may not have the same level of protection against attacks as native Windows apps, due to the translation layer involved.
This translation layer, while necessary for compatibility, could potentially expose vulnerabilities.
Privacy Concerns and Mitigation Measures
Data privacy is paramount. Users should be aware of how their data is handled when interacting with Android apps on Windows 11. It is important to examine app permissions and understand how data is collected, used, and potentially shared. Users should be vigilant about the data they share with Android apps running on Windows 11, and choose apps carefully, considering the permissions they request.
Security Protocols and Best Practices for Users
Users can significantly enhance the security of their Android apps on Windows 11 by following best practices. These practices include:
- Vetting Apps Carefully: Thoroughly researching apps before installation is crucial. Read reviews, check permissions, and look for evidence of a strong security record from the developer.
- Managing Permissions Cautiously: Understand the permissions requested by each app. Grant only the permissions necessary for the app to function. Limit unnecessary access to sensitive data.
- Using Strong Passwords and Multi-factor Authentication: Securely protect accounts associated with the Android apps on Windows 11. Enabling multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security.
- Regularly Updating Apps and Windows: Updates often contain critical security patches. Keeping apps and the Windows operating system up-to-date minimizes vulnerabilities.
- Avoiding Suspicious Links and Downloads: Be wary of suspicious emails, messages, or websites that may try to trick you into installing malicious apps.
Security Protocols and Best Practices for Developers
Developers should implement robust security measures when building Android apps for Windows 11. This involves a proactive approach to security at every stage of development.
- Secure Data Handling: Implement encryption techniques to protect sensitive user data both in transit and at rest. Developers should prioritize secure data storage methods.
- Least Privilege Principle: Limit the permissions of the app to only what is absolutely necessary. This minimizes the potential damage if the app is compromised.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the app. This is an ongoing process, not a one-time event.
- Adherence to Security Standards: Comply with relevant security standards and regulations when designing and implementing the app. This could include standards like OWASP guidelines.
- Input Validation: Validate all user inputs to prevent malicious code injection or other attacks. This is crucial to prevent exploits and data breaches.
Comparison of Security Features
| Feature | Android Apps | Native Windows Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Generally possible, but varies by app | Often built-in and standardized |
| Sandboxing | Present, but may have limitations in cross-platform environments | Robust sandboxing mechanisms |
| Update Management | Often handled by the app itself | Usually integrated with the operating system update process |
| Security Audits | Varies greatly based on developer practices | Often part of the development process and platform guidelines |
This table highlights the differences in security features between Android apps and native Windows apps. While Android apps can offer security measures, the inherent security architecture of native Windows apps often provides a more robust foundation.
Future Outlook
The future of Android apps on Windows 11 holds significant potential, driven by ongoing technological advancements and evolving user expectations. This dynamic environment promises exciting developments, shaping the user experience and impacting the app market in profound ways. The interplay between the strengths of Android’s ecosystem and the expanding capabilities of Windows 11 will be a key factor in this evolution.
Potential Developments in App Functionality
The integration of Android apps into the Windows 11 ecosystem will likely lead to expanded functionality and versatility. Expect to see a greater range of apps tailored to specific Windows 11 features, such as seamless integration with other Windows applications and improved accessibility options. The potential for cross-platform collaboration between Android and Windows apps will open up new possibilities for creative endeavors and productivity tools.
This enhanced functionality is anticipated to lead to a more unified and comprehensive digital experience for users.
Evolution of User Experience and Features
User experience will undoubtedly improve as the platform matures. Expect smoother transitions between Android apps and Windows 11 applications, alongside enhanced performance and optimized resource management. Improved compatibility will lead to a more intuitive and user-friendly environment, streamlining the overall app experience. This evolution will likely involve features that provide a more integrated user experience across different application categories.
Role of the Platform in Future Developments
Windows 11, with its focus on multitasking, productivity, and accessibility, will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of Android apps. The platform’s emphasis on efficiency and a user-friendly interface will encourage developers to create apps that are both robust and seamlessly integrated within the Windows ecosystem. This will drive innovation in app design, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible within the hybrid platform.
Impact on the Market
The integration of Android apps on Windows 11 will undoubtedly impact the app market. A wider user base will gain access to a larger pool of apps, leading to a potentially increased market share for Android developers. This broader reach, coupled with the potential for enhanced app functionality, will likely drive increased competition and innovation within the app development industry.
New revenue streams and growth opportunities for developers will likely emerge.
Summary
In conclusion, the integration of Android apps on Windows 11 presents a compelling blend of convenience and challenge. While compatibility and performance issues may persist, the potential for enhanced functionality and a broader app ecosystem is undeniable. The future of this integration is promising, and ongoing developments will likely shape the landscape of both platforms in the coming years.