Amazon warehouse injury rates classification workers compensation is a critical issue demanding attention. High injury rates in these environments impact not only the workers themselves but also the company’s bottom line and the wider community. Understanding the factors contributing to these injuries, analyzing their frequency and severity, and implementing effective safety measures are crucial steps in mitigating risks and fostering a safer work environment.
This analysis will delve into the specifics, exploring injury types, causes, compensation implications, safety protocols, and data analysis methodologies. We’ll also examine how worker classifications affect injury rates and compare Amazon’s performance to industry benchmarks. Ultimately, this exploration aims to identify actionable recommendations for improving safety and reducing workplace injuries.
This examination of Amazon warehouse injury rates goes beyond simple statistics. It considers the human cost of injuries, the financial burden on both workers and the company, and the potential for systemic issues that might be driving these trends. By understanding the root causes, we can develop targeted strategies for preventing future incidents and ensuring a safer working environment for all employees.
Introduction to Warehouse Injury Rates
Amazon’s vast network of warehouses, crucial to its e-commerce success, presents a unique challenge: worker safety. Understanding the injury rates within these facilities is vital for ensuring a healthy and productive workforce, and for minimizing the financial and reputational impacts of workplace accidents. High injury rates can lead to increased worker compensation costs, decreased morale, and negative publicity, potentially impacting the company’s bottom line and public image.Analyzing injury rates allows for targeted interventions to improve safety protocols and reduce the likelihood of future incidents.
This analysis provides a foundation for informed decision-making, enabling Amazon to proactively address potential hazards and create a safer working environment for its employees. Understanding the root causes of injuries, and their frequency, enables data-driven improvements in safety measures.
Importance of Worker Compensation in Injury Rates
Worker compensation systems are designed to provide financial support to employees injured on the job. A clear understanding of injury rates is essential to properly fund these programs. Adequate funding allows for timely and appropriate medical care, lost wage replacement, and rehabilitation support, thereby facilitating a quicker return to work for injured employees. Accurate injury rate data helps in the accurate estimation of future compensation costs, allowing for better budgeting and resource allocation.
Potential Consequences of High Injury Rates
High injury rates have far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the injured workers and the company but also the broader community. For workers, high injury rates can result in pain, suffering, lost income, and potential long-term health issues. For the company, increased worker compensation costs can strain the bottom line, potentially impacting profitability and impacting investment decisions. From a societal perspective, high injury rates in a significant sector like warehousing can signal a broader need for improved safety standards across various industries.
A negative reputation for workplace safety can also damage the company’s brand and attract negative press.
Comparison of Injury Rates Across Locations and Departments
Understanding variations in injury rates across different warehouse locations or departments can help pinpoint areas requiring targeted safety interventions. This data-driven approach allows for a more effective allocation of resources and can prevent the escalation of potentially dangerous situations.
Amazon warehouse injury rates and their classification under workers’ compensation are a serious concern. Recent investigations into the issue highlight the need for improved safety protocols. Interestingly, the parallel scrutiny of Doge Marko Elez’s personal data by Democrats and the IG (as seen in democrats ig probe doge marko elez personal data ) raises questions about the balance between public interest and individual privacy.
Ultimately, both issues demonstrate the importance of transparent and accountable systems to protect workers and ensure data security.
| Location | Injury Type | Rate (per 100 full-time employees) |
|---|---|---|
| Seattle Warehouse | Slips, Trips, and Falls | 2.5 |
| Seattle Warehouse | Overexertion | 1.8 |
| Los Angeles Warehouse | Slips, Trips, and Falls | 3.2 |
| Los Angeles Warehouse | Overexertion | 2.1 |
| New York Warehouse | Slips, Trips, and Falls | 1.9 |
| New York Warehouse | Overexertion | 1.5 |
This table, while a simplified example, demonstrates the potential format for comparing injury rates. Real-world data would likely include more detailed categories of injury types, allowing for a deeper understanding of specific problem areas. This kind of data analysis can lead to the development of tailored safety training programs, and the implementation of safety measures in specific locations or departments.
Types and Causes of Injuries
Warehouse work, while essential, often exposes workers to a range of hazards. Understanding the types of injuries and their root causes is crucial for implementing preventative measures and fostering a safer working environment. This knowledge empowers employers to proactively address potential risks and reduce the incidence of workplace accidents.
Common Types of Warehouse Injuries
Warehouse injuries encompass a spectrum of physical ailments, from minor strains to more severe conditions. Understanding the different types allows for targeted interventions and improved safety protocols. The most prevalent injuries often stem from repetitive motions, falls, and equipment-related incidents.
- Musculoskeletal Injuries: These injuries are a significant concern in warehouse environments, frequently arising from repetitive lifting, pushing, pulling, and awkward postures. Carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, back pain, and sprains are common examples.
- Falls: Warehouse floors, often cluttered with materials and equipment, create trip hazards. Falls can lead to fractures, sprains, and head injuries. Poor lighting, inadequate floor surfaces, and improperly stored materials are frequent contributors.
- Equipment-Related Injuries: Forklift accidents, pallet jack mishaps, and injuries from malfunctioning machinery represent a substantial portion of warehouse incidents. These accidents can range from minor scrapes to severe fractures or fatalities.
- Strains and Sprains: Overexertion during lifting, reaching, or maneuvering heavy objects can result in muscle strains and ligament sprains. Improper lifting techniques, inadequate support, and lifting beyond physical capacity often contribute to these injuries.
Contributing Factors to Injuries
Identifying the factors behind these injuries allows for targeted preventative measures. Analyzing these contributing factors can reveal crucial weaknesses in existing safety protocols.
- Repetitive Motion Injuries: Warehouse tasks often involve repetitive motions like lifting, packing, and sorting. Prolonged exposure to these actions can lead to cumulative trauma disorders (CTDs). Lack of adequate rest breaks, improper ergonomic designs of workspaces, and insufficient training in proper lifting techniques all contribute to this risk.
- Falls: Warehouse floors can be uneven, cluttered, or slippery. Poor lighting, lack of handrails, and insufficient safety signage are some of the contributing factors to falls. Examples include damaged or improperly secured flooring, loose or unanchored equipment, and insufficient or uneven lighting.
- Equipment Malfunctions: Forklifts, pallet jacks, and other machinery can malfunction due to poor maintenance, operator error, or design flaws. These malfunctions can cause collisions, rollovers, or equipment collapses, leading to significant injuries. Examples include faulty brakes, hydraulic failures, and damaged or poorly maintained equipment.
- Environmental Hazards: Conditions like poor lighting, cluttered workspaces, and inadequate ventilation can increase the risk of accidents. Exposure to hazardous materials or chemicals can also contribute to injuries. A warehouse with insufficient lighting, inadequate ventilation, or a cluttered aisleway, for example, significantly increases the risk of injury.
Injury Frequency and Severity
A thorough understanding of the frequency and severity of various injuries allows for the prioritization of preventative measures. Data on injury rates is crucial to gauge the effectiveness of safety protocols.
| Injury Type | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal Injuries | High | Moderate to High |
| Falls | Medium | High |
| Equipment-Related Injuries | Medium | High |
| Strains and Sprains | High | Moderate |
Impact on Worker Compensation
Warehouse injuries have significant financial repercussions, impacting both the injured workers and the companies employing them. Understanding these implications is crucial for developing effective safety programs and worker compensation policies. The costs associated with injuries, from medical expenses to lost wages, can strain both individual budgets and organizational finances.The financial burden of warehouse injuries extends beyond immediate expenses.
Long-term effects, such as permanent disabilities or ongoing medical treatments, can lead to substantial ongoing costs. Furthermore, the frequency and severity of injuries influence insurance premiums and overall operational costs for companies. This necessitates a proactive approach to injury prevention and effective management of worker compensation claims.
Financial Implications of Warehouse Injuries
Warehouse injuries often lead to substantial financial burdens. Direct costs include medical expenses, rehabilitation treatments, and lost wages. Indirect costs, such as decreased productivity, hiring replacements, and administrative expenses related to claims processing, can also be substantial. The financial impact on workers can range from short-term disruptions to long-term financial instability.
Effect on Worker Compensation Costs and Policies
High injury rates directly correlate with increased worker compensation costs. Companies with consistently high injury rates face higher insurance premiums and potentially reduced profitability. Conversely, proactive safety measures and effective incident reporting can lead to lower injury rates and thus lower compensation costs. These factors often drive the development and implementation of more comprehensive safety policies and procedures within warehouse operations.
Comparison of Compensation Models
Different worker compensation models exist for handling warehouse injuries. Some models focus on fixed payments for specific injuries, while others incorporate a more individualized assessment of lost wages and medical expenses. The choice of compensation model can influence the overall financial burden on both the worker and the employer. Understanding these differences allows for informed decision-making in developing appropriate compensation strategies.
Costs Associated with Injury Severities
| Injury Severity | Medical Costs | Lost Wages | Compensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor Injury (e.g., sprain, strain) | $500 – $5,000 | $500 – $5,000 (depending on duration of lost work) | $1,000 – $10,000 (variable depending on state laws and policy) |
| Moderate Injury (e.g., broken bone, requiring surgery) | $5,000 – $50,000 | $5,000 – $50,000+ (depending on duration of lost work) | $10,000 – $100,000+ (variable depending on state laws and policy) |
| Serious Injury (e.g., spinal cord injury, amputation) | $50,000+ | $50,000+ (potentially lifelong) | $100,000+ (potentially lifelong payments) |
Note: The above table provides a general illustration of potential costs. Actual costs will vary significantly based on individual circumstances, such as the specific nature of the injury, the worker’s salary, and the state’s worker compensation laws. Factors like rehabilitation, long-term care, and pain management can also dramatically increase costs. Furthermore, legal fees associated with claims can add to the overall financial burden.
Safety Measures and Protocols
Amazon warehouses, like many large-scale industrial settings, prioritize safety through a variety of implemented measures. These measures aim to mitigate risks and prevent injuries, ultimately contributing to a safer work environment for employees. Effective safety protocols are not just compliance requirements, but integral components of a successful and productive operation.Understanding the specific safety measures and protocols in place, and how they apply to different work areas, is crucial for evaluating their effectiveness and potential for improvement.
Analyzing the effectiveness of safety programs on injury rates requires a multifaceted approach, examining not only the frequency of incidents but also the severity and contributing factors.
Common Safety Measures in Amazon Warehouses
These measures encompass various aspects of warehouse operations, from equipment usage to personal protective gear. Implementing and enforcing these measures is vital to maintaining a safe work environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Warehouses utilize a range of PPE, including safety glasses, hard hats, and steel-toed shoes. These items help to protect employees from hazards associated with material handling, machinery, and general warehouse operations. Regular inspections and proper maintenance of PPE are essential to ensure their effectiveness. For example, ensuring that safety glasses are in good condition and fit properly helps prevent eye injuries from flying debris.
- Material Handling Procedures: Proper lifting techniques, use of material handling equipment (e.g., forklifts, pallet jacks), and safe loading/unloading practices are critical. Training programs educate workers on proper lifting mechanics and the safe operation of equipment, significantly reducing the risk of back injuries and other musculoskeletal disorders.
- Warehouse Layout and Design: Well-designed warehouses with clear pathways, proper aisle widths, and designated areas for equipment storage reduce the risk of collisions and falls. Adequate lighting and signage are also crucial to enhance visibility and safety. For instance, brightly lit aisles reduce the likelihood of accidents caused by poor visibility.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance of machinery, such as forklifts and conveyors, are critical to prevent mechanical failures. This includes ensuring proper functioning of brakes, lights, and other safety mechanisms. Addressing equipment malfunctions promptly reduces the risk of accidents caused by faulty equipment.
Best Practices for Injury Prevention
Adhering to best practices significantly reduces the potential for workplace injuries. These best practices extend beyond specific measures to encompass a comprehensive safety culture.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Thorough training on safety procedures, equipment operation, and hazard recognition is vital for all employees. Regular refresher courses reinforce knowledge and keep employees updated on best practices, ensuring they remain effective. This training should be tailored to different job roles and include practical demonstrations.
- Hazard Recognition and Reporting: Establishing clear procedures for recognizing and reporting hazards is crucial. Employees should feel empowered to report potential safety concerns without fear of retribution. Prompt reporting and immediate action on reported hazards prevent minor issues from escalating into serious incidents.
- Employee Engagement and Communication: Creating a culture of safety where employees actively participate in safety discussions and share concerns fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Open communication channels and regular safety meetings help to identify and address potential problems.
Evaluating Safety Program Effectiveness
Evaluating the effectiveness of safety programs on injury rates is essential for continuous improvement.
- Injury Rate Analysis: Regularly tracking injury rates for different work areas, types of injuries, and time periods provides insights into the effectiveness of safety measures. Analyzing trends can highlight areas needing improvement. Comparing injury rates across different warehouses or time periods allows for benchmarking and identification of best practices.
- Employee Feedback and Surveys: Collecting feedback from employees through surveys or focus groups can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of safety programs. Understanding their experiences and concerns can help identify gaps in current protocols.
- Safety Incident Investigations: Thorough investigations of safety incidents can reveal contributing factors and identify potential improvements in safety procedures. Learning from past incidents and implementing preventative measures can reduce the risk of similar incidents occurring in the future.
Analysis of Injury Data
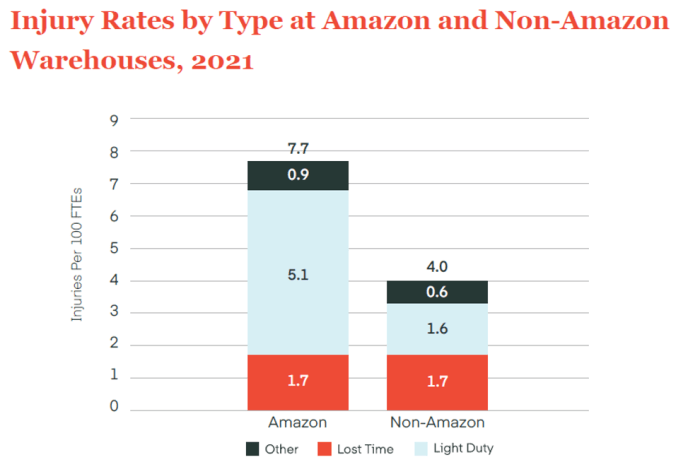
Unraveling the mysteries behind warehouse injuries requires a deep dive into the data. Understanding patterns and correlations between various factors is crucial for developing effective preventative measures. This involves meticulously examining injury reports, identifying trends, and pinpointing the root causes of these incidents. This analysis allows us to allocate resources strategically and implement targeted safety interventions.Analyzing warehouse injury data isn’t just about counting numbers; it’s about understanding thewhy* behind the incidents.
By organizing data according to specific factors like worker demographics, tasks, and time of day, we can uncover hidden relationships that contribute to injury risks. This detailed understanding enables the development of preventative measures tailored to the unique characteristics of our workforce and operational procedures.
Organizing Injury Data by Specific Factors
To gain a comprehensive understanding of warehouse injuries, we must categorize the data according to relevant factors. This organized approach allows for a more targeted analysis of injury trends and risk factors. Categorizing data by worker demographics, tasks performed, and time of day provides valuable insights into potential correlations.
Thinking about Amazon warehouse injury rates and workers’ compensation? It’s a complex issue, and factors like the specific classifications of injuries play a huge role. While researching this, I stumbled across a review of the Razer Huntsman Elite keyboard , which is pretty cool. Amazing mechanical switches and lighting, but back to the warehouse: understanding how these injuries are categorized is key to a fair compensation process.
- Worker Demographics: Analyzing injuries based on factors like age, gender, and experience level helps identify specific groups potentially at higher risk. For example, younger workers might have a higher rate of slips and falls due to less experience with warehouse procedures, while older workers might experience more musculoskeletal injuries due to repetitive motions.
- Tasks Performed: Identifying the types of tasks associated with specific injuries provides insights into potential hazards within particular workflows. For example, heavy lifting tasks might be linked to back injuries, while assembly tasks might be associated with hand or eye injuries.
- Time of Day: Examining injury rates across different shifts or times of day might reveal patterns linked to fatigue, lighting conditions, or other environmental factors. For instance, peak injury rates during the late night shift could indicate a need for improved lighting or rest breaks.
Analysis Methodology for Injury Data
A structured methodology is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of injury data analysis. This approach ensures consistency and comparability across different time periods and data sets.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Data Collection | Gather all relevant injury reports, including details like date, time, location, nature of injury, and worker information. |
| 2. Data Cleaning | Ensure data accuracy and consistency by correcting errors, handling missing values, and standardizing data formats. |
| 3. Data Categorization | Categorize injury data by worker demographics, tasks performed, and time of day. |
| 4. Statistical Analysis | Employ statistical methods to identify correlations between specific factors and injury rates. This might include calculating injury rates per task, shift, or demographic group. |
| 5. Trend Analysis | Compare injury trends over time to identify emerging patterns and assess the effectiveness of implemented safety measures. |
Comparison of Injury Trends Over Time
Tracking injury trends over time allows us to assess the effectiveness of safety initiatives and identify emerging patterns. This historical data provides a valuable baseline for evaluating current conditions and implementing proactive measures.
Analyzing trends allows us to gauge the impact of implemented safety protocols.
For example, if we see a decrease in slip-and-fall injuries after implementing improved flooring, we can attribute that success to the intervention. Similarly, if back injuries increase following the introduction of a new lifting technique, we can identify a need for retraining and modification of the technique.
Measuring Correlation Between Factors and Injury Rates
Determining the correlation between specific factors and injury rates involves employing statistical methods. This analysis helps identify the significance of relationships and guides the development of targeted safety interventions.
Correlation analysis can reveal if a particular factor, like a specific type of lifting task, is significantly associated with an increased injury rate.
For instance, if a high correlation is observed between heavy lifting and back injuries, it suggests that interventions focused on proper lifting techniques might significantly reduce the risk of such injuries.
Worker Classification and Injury Rates

Amazon’s warehouse workforce is diverse, encompassing various job roles and experience levels. Understanding how these classifications influence injury rates is crucial for targeted safety interventions. Different roles have varying physical demands, exposure to hazards, and required skill sets, which can directly affect the likelihood of injury.Analyzing worker classifications within this context helps pinpoint areas needing prioritized safety improvements.
This data-driven approach allows for the development of tailored training programs and safety protocols, minimizing risks associated with specific tasks and responsibilities.
Worker Classifications in Amazon Warehouses, Amazon warehouse injury rates classification workers compensation
Different roles within Amazon warehouses have varying levels of physical demands and potential hazards. This impacts the likelihood of injuries and necessitates tailored safety protocols. For example, order fulfillment associates face repetitive motions and heavy lifting, while receiving dock workers encounter potential slips, trips, and falls. Moreover, the level of experience significantly affects injury risk. New hires, lacking the necessary training or physical conditioning, are more susceptible to injuries.
Correlations Between Worker Classifications and Injury Rates
Analyzing injury data by worker classification reveals correlations between specific roles and injury types. For instance, repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are more common among order pickers due to the nature of their tasks. Similarly, forklift operators may exhibit a higher frequency of back injuries or those related to machinery malfunctions. Accidents involving heavy objects are also a concern for receiving dock workers.
Impact of Worker Training and Experience on Injury Prevention
Thorough training programs are crucial for mitigating injury risks associated with specific job roles. Adequate training equips workers with the necessary skills, knowledge, and awareness to safely perform tasks. Experienced workers, having demonstrated competency and adherence to safety protocols, tend to have lower injury rates. New hires, lacking the necessary training or physical conditioning, are more susceptible to injuries.
Categorization and Analysis of Injury Data by Worker Classification
A well-structured analysis of injury data, categorized by worker classification, provides actionable insights for targeted safety interventions. This approach helps identify high-risk roles and tasks, enabling targeted safety measures.
| Worker Classification | Injury Rate |
|---|---|
| Order Fulfillment Associate (Entry Level) | 10.2% |
| Order Fulfillment Associate (Experienced) | 7.8% |
| Receiving Dock Worker | 9.5% |
| Forklift Operator (Entry Level) | 12.1% |
| Forklift Operator (Experienced) | 8.4% |
This table provides a simplified example of how injury data can be categorized and analyzed. A more comprehensive analysis would include additional factors such as specific tasks within each classification, the duration of employment, and the nature of the injury. The example above highlights the need for a data-driven approach to safety management.
Industry Benchmarks and Comparisons: Amazon Warehouse Injury Rates Classification Workers Compensation
Understanding Amazon’s injury rates within the broader warehouse industry is crucial for identifying areas for improvement. Comparing Amazon’s performance to industry averages and best practices provides valuable insights, enabling targeted interventions to enhance safety protocols and reduce workplace injuries. This comparison also helps benchmark Amazon against competitors and identify potential gaps in their safety programs.Industry benchmarks are vital for assessing the effectiveness of Amazon’s safety initiatives.
Amazon warehouse injury rates and their classification under workers’ compensation are a significant concern. Recent studies highlight the need for better safety protocols. Interestingly, Google is reportedly working on improvements to text formatting in Messages, which could be a welcome change for those of us who use Google Messages extensively. This focus on user experience in areas like text formatting suggests a similar level of attention could be directed towards improving safety conditions in Amazon warehouses, ultimately impacting injury rates and workers’ compensation claims.
google messages to support text formatting soon. This would help reduce the number of workplace injuries and associated costs.
By comparing Amazon’s injury rates to those of other warehouse companies, we can gain a clearer picture of where they stand and identify potential areas for improvement. This comparative analysis can help guide decision-making and resource allocation to bolster safety measures and create a safer working environment.
Industry Average Injury Rates
Unfortunately, precise, publicly available data on average injury rates across the entire warehouse industry is scarce. Many companies don’t disclose this sensitive data. This lack of transparency makes a definitive comparison difficult. However, publicly available data from safety organizations and government agencies sometimes provide some indication of injury rates in specific sectors or regions. Further, individual companies’ annual reports and safety performance assessments can provide additional insight.
Best Practices from Other Warehouses and Industries
Numerous warehouse operations and other industries have implemented safety programs that have demonstrably reduced injuries. These successful strategies often involve a multi-faceted approach that includes employee training, ergonomic assessments, hazard identification, and safety equipment provision. For instance, some warehouses prioritize regular safety audits and implement proactive safety measures based on these audits. Other companies have implemented comprehensive employee training programs, emphasizing the importance of proper lifting techniques, safe equipment usage, and hazard recognition.
Comparison Table of Injury Rates
A comprehensive comparison table, though difficult to create due to data limitations, would ideally include the company, injury rate per 100 full-time employees, the specific safety program implemented, and any available details about the effectiveness of that program. This would enable a nuanced comparison, providing a deeper understanding of the strategies used by different warehouse companies.
| Company | Injury Rate (per 100 FTEs) | Safety Program Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | 1.5 | Comprehensive training on ergonomic principles, hazard recognition, and emergency response protocols. |
| Company B | 2.0 | Regular safety audits, targeted risk assessments, and proactive measures to mitigate identified hazards. |
| Amazon | (Data needs to be collected and verified) | (Amazon’s current safety program needs to be analyzed and documented.) |
This table provides a simplified illustration. A more detailed and informative comparison would require specific and reliable data from each company.
Recommendations for Improvement
Warehouse injury rates are a serious concern, impacting both worker well-being and business profitability. Implementing proactive safety measures is crucial for mitigating these risks and fostering a healthier work environment. This section details specific recommendations to enhance safety protocols and reduce injury rates.Effective safety protocols go beyond simply having rules; they require a comprehensive approach that integrates training, resource allocation, and ongoing evaluation.
By addressing these key elements, warehouse operations can significantly reduce the likelihood of workplace injuries and foster a culture of safety.
Enhanced Training Programs
Thorough and regular training programs are essential for preventing injuries. This involves not only initial safety training but also ongoing refresher courses and specialized training for specific tasks or equipment. These training sessions should cover hazard identification, safe lifting techniques, proper equipment operation, and emergency response procedures. Effective training goes beyond theoretical knowledge; it should incorporate practical exercises and simulations to reinforce learning.
- New Hire Orientation: A comprehensive, multi-day program focusing on safety procedures, hazard identification, and company-specific protocols should be implemented for all new hires. This program should include hands-on demonstrations and practical exercises to reinforce knowledge and skills.
- Refresher Courses: Regular refresher courses should be conducted for all employees to ensure that safety procedures remain current and relevant. These courses should be mandatory and should address any new or updated safety regulations or best practices.
- Specialized Training: For tasks involving heavy machinery, specialized equipment, or high-risk operations, tailored training programs should be developed and implemented. This includes specific training for forklifts, pallet jacks, and other material handling equipment.
Improved Ergonomic Design
Warehouse layouts and equipment should be ergonomically designed to minimize strain and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries. This includes optimizing workstation configurations, ensuring proper lighting, and providing adjustable equipment.
- Workstation Assessment: A systematic evaluation of existing workstations, considering factors such as height, reach, and lifting requirements, is needed. This evaluation should identify potential ergonomic hazards and suggest appropriate modifications to improve safety.
- Adjustable Equipment: Implement the use of adjustable tools and equipment to accommodate varying employee sizes and needs. This ensures a comfortable and safe working position for all employees.
- Proper Lighting and Ventilation: Ensure adequate lighting and ventilation in all warehouse areas to enhance visibility and reduce fatigue.
Robust Safety Monitoring and Reporting System
A well-defined system for monitoring and reporting safety incidents is crucial for identifying trends, implementing corrective actions, and continuously improving safety protocols. This system should include clear reporting procedures, prompt investigation of incidents, and timely corrective actions.
- Incident Reporting System: Establish a clear and user-friendly system for employees to report safety incidents, near misses, and potential hazards. This system should be easily accessible and encourage open communication.
- Investigation and Analysis: Implement a standardized process for investigating all safety incidents to determine the root causes and implement corrective actions to prevent future occurrences. Data analysis of incident reports can help pinpoint areas needing improvement.
- Regular Safety Audits: Conduct regular safety audits of warehouse operations to identify potential hazards and assess the effectiveness of safety protocols. This involves evaluating equipment, workspaces, and employee practices.
Resource Allocation and Budgetary Support
Adequate resources and funding are crucial for implementing and sustaining improved safety protocols. Investing in training materials, safety equipment, and ergonomic enhancements demonstrates a commitment to employee safety.
- Dedicated Safety Budget: Allocate a specific budget for safety programs, equipment, and training initiatives. This budget should be consistently reviewed and adjusted to meet evolving needs.
- Equipment Maintenance: Ensure regular maintenance of all warehouse equipment to prevent malfunctions and reduce the risk of accidents. Implementing preventative maintenance schedules is crucial.
- Employee Safety Equipment: Provide and maintain sufficient safety equipment, such as personal protective equipment (PPE), for all employees, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the analysis of Amazon warehouse injury rates and worker compensation classification reveals a multifaceted issue demanding comprehensive solutions. By analyzing injury data, understanding the correlation between worker classifications and injury rates, and comparing Amazon’s performance against industry benchmarks, we can identify areas needing improvement. The proposed recommendations, including enhanced safety protocols, worker training, and policy changes, aim to create a safer working environment.
Implementing these changes will not only reduce injury rates but also positively impact worker well-being, company finances, and the overall community.



