Forever chemicals PFAS drinking water standards EPA Trump are a critical environmental and public health issue. These “forever chemicals” persist in the environment and can contaminate drinking water sources, leading to potential health risks. The EPA’s evolving regulations, the Trump administration’s stance on the issue, and the public’s concerns all contribute to a complex picture. This exploration delves into the history, current standards, potential impacts, and the ongoing debate surrounding these pervasive pollutants.
This in-depth look examines the different types of PFAS, their potential sources, and how they contaminate water supplies. We’ll analyze the EPA’s historical and current standards, comparing them to international benchmarks. Further, the Trump administration’s approach to PFAS regulation will be assessed, including specific policies and public pronouncements. Understanding the potential health effects of PFAS exposure, and public concerns about contamination, are key elements of this discussion.
Introduction to PFAS in Drinking Water
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals, often referred to as “forever chemicals,” due to their persistence in the environment. They’re used in various industrial applications and consumer products, and their widespread use has led to significant environmental contamination. Their persistence and potential for bioaccumulation mean they can linger in the environment and potentially affect human health.PFAS contamination is a serious concern, particularly in drinking water sources.
The diverse applications of PFAS compounds have resulted in their presence in various locations, with potential health consequences for exposed populations. Understanding the properties, sources, and pathways of PFAS contamination is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
PFAS Types and Sources
PFAS encompasses a large family of compounds with similar chemical structures. Variations in the length and branching of the carbon chain and the presence of other functional groups result in a wide range of PFAS compounds. This diversity contributes to their diverse applications and environmental persistence.
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) are two of the most well-known and studied PFAS, both of which have been widely used in industrial applications.
- Other PFAS, such as perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) and perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), are also prevalent and pose potential environmental concerns. They are present in numerous products and industrial processes, and their widespread use is a significant factor in their environmental contamination.
Potential Sources of PFAS Contamination
The diverse applications of PFAS compounds across various industries and consumer products have led to their presence in diverse environments. These sources contribute to the contamination of drinking water sources.
- Industrial facilities: Manufacturing processes, such as the production of non-stick cookware and firefighting foams, frequently use PFAS. Wastewater discharge from these facilities can introduce PFAS into water bodies.
- Consumer products: PFAS are found in many consumer products, including non-stick cookware, food packaging, and firefighting foam. The improper disposal or leaching of these products can contribute to contamination.
- Agriculture: Agricultural practices, such as the use of PFAS-containing pesticides or herbicides, can contaminate water sources through runoff.
Pathways of PFAS Contamination in Drinking Water
Contamination of drinking water sources can occur through various pathways, depending on the location and the source of PFAS.
- Runoff: Rainfall carries PFAS from contaminated land or surface water into rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
- Groundwater contamination: PFAS can leach into groundwater from landfills, industrial sites, or agricultural areas.
- Surface water contamination: Discharge from industrial facilities, or runoff from agricultural or residential areas, can introduce PFAS into rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
Historical Context of PFAS in the Environment
The widespread use of PFAS in various industries and consumer products, particularly in the 20th century, has led to a notable accumulation of these compounds in the environment.
- Widespread use: The increased production and use of PFAS in the 20th century led to their presence in various environments.
- Environmental concerns: The persistence of PFAS compounds and their potential impact on human health and the environment have spurred significant research and regulatory efforts.
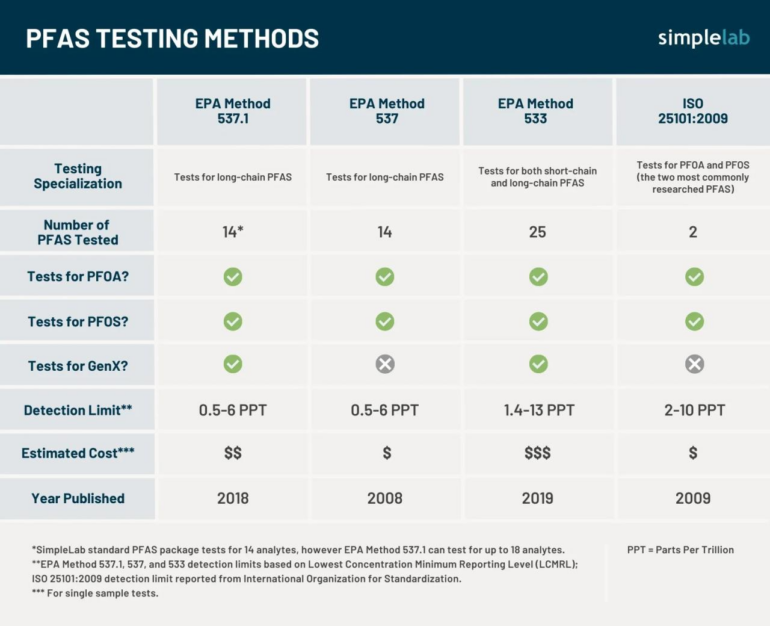
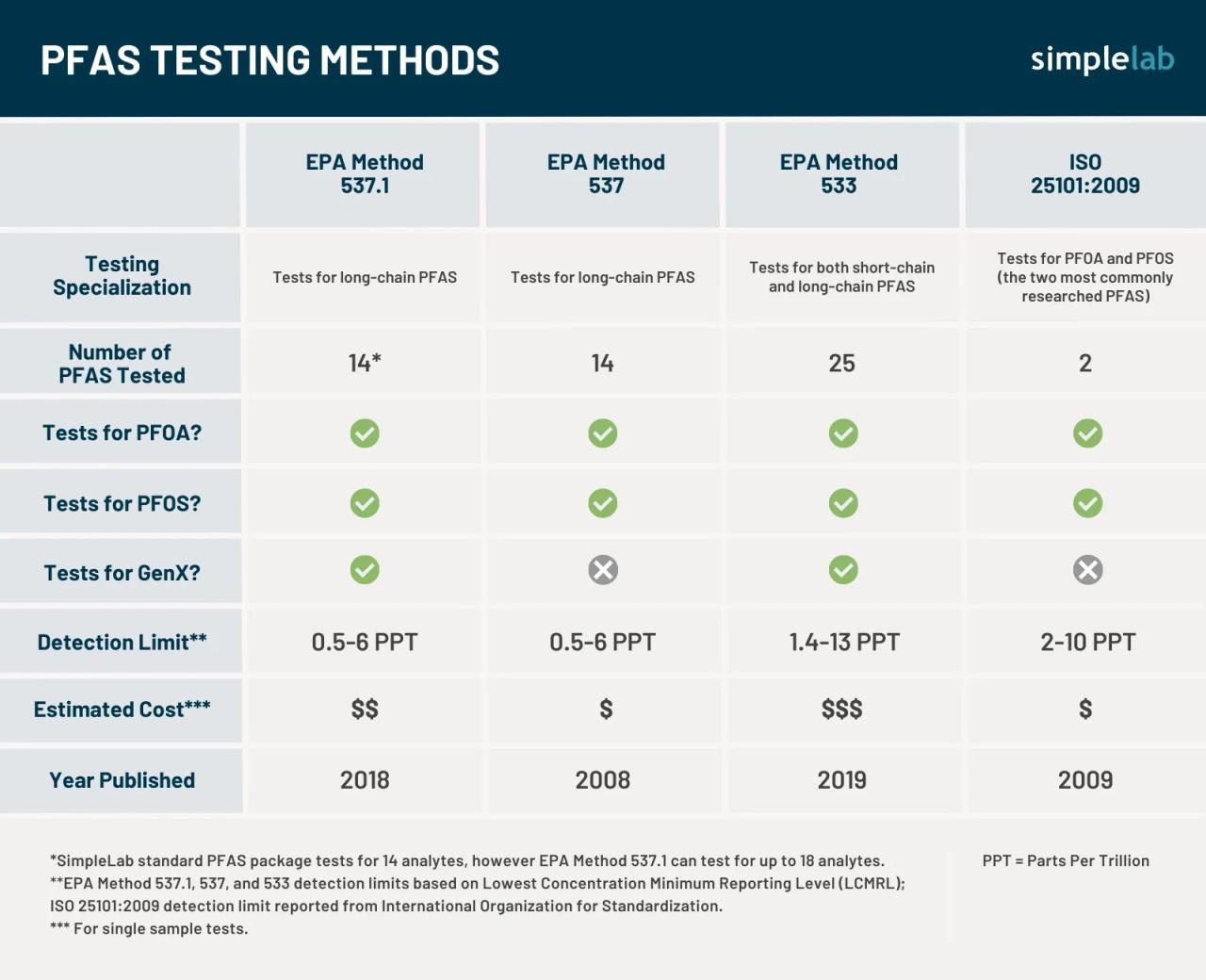
PFAS Properties Comparison
A table outlining the key properties of different PFAS types can illustrate the diverse nature of these compounds. Understanding these properties is crucial for evaluating their potential environmental impacts and for developing effective remediation strategies.
| PFAS Type | Chemical Formula | Potential Sources | Persistence | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA | C8F17COOH | Non-stick cookware, firefighting foam | High | Potentially harmful |
| PFOS | C8F17SO3H | Firefighting foam, industrial processes | High | Potentially harmful |
| PFHxS | C6F13SO3H | Various industrial applications | Moderate | Potentially harmful |
| PFNA | C9F19COOH | Various industrial applications | High | Potentially harmful |
EPA Drinking Water Standards for PFAS
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a crucial role in safeguarding public health by setting and enforcing drinking water standards. These standards aim to protect people from harmful contaminants, including emerging pollutants like PFAS. The development and evolution of these standards are a complex process, often involving scientific research, public input, and political considerations.The EPA’s journey in regulating PFAS in drinking water has been a dynamic one, marked by scientific advancements, public pressure, and evolving understanding of the risks associated with these chemicals.
Initially, the absence of comprehensive data and regulations created a significant challenge. The EPA’s response to this situation involved a careful balancing act of prioritizing public health while addressing the practical implications of regulating these substances.
Evolution of EPA Regulations
The EPA’s approach to regulating PFAS in drinking water has evolved over time, driven by increasing scientific evidence of the chemicals’ potential harm. Early stages focused on identifying the prevalence and potential risks of PFAS. As research progressed and the health concerns solidified, the EPA transitioned to developing more stringent regulations to mitigate the potential risks to human health.
The EPA’s stance on forever chemicals (PFAS) in drinking water standards under the Trump administration is a hot topic. While the debate rages on, it’s fascinating to see how social media platforms like Twitter handle interactions. For instance, on iOS, you can now quote, retweet, and even add comments to tweets, enhancing the discussion surrounding these important issues.
This feature, as detailed in this article on twitter ios quote tweets retweets with comments , is a valuable tool for engaging with the complex issue of PFAS in drinking water and could influence the outcome of ongoing EPA regulations. Ultimately, these tools can aid in the transparency and public discussion surrounding forever chemicals and their impacts.
This process reflects a shift from a reactive to a proactive approach to environmental protection.
Current EPA Drinking Water Standards
The EPA’s current approach to regulating PFAS in drinking water incorporates a multi-pronged strategy. Currently, there isn’t a single, unified standard for all PFAS; instead, the EPA uses a “group-level” approach, targeting a specific group of PFAS and establishing a maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG). This approach is aimed at addressing the diverse nature of PFAS chemicals and ensuring that the standards effectively target the most concerning types.
Rationale Behind the EPA’s Standards
The EPA’s standards for PFAS in drinking water are underpinned by a comprehensive assessment of the scientific evidence. This includes the potential health effects of various PFAS, the exposure pathways, and the concentrations found in drinking water sources. The standards are intended to minimize the risks associated with exposure to these chemicals, aligning with the principle of precaution.
The specific rationale for each standard is based on an extensive risk assessment process, involving scientists and experts from diverse fields.
Comparison with Other Countries’ Standards
Different countries have adopted varying approaches to regulating PFAS in drinking water. Some countries have established more stringent standards than the EPA, reflecting their own priorities and risk assessments. Other countries might have less stringent regulations, reflecting different societal values, resource availability, and scientific understanding. The disparity in standards underscores the global challenge in regulating emerging contaminants like PFAS.
Comparing standards is vital for understanding the international consensus on managing PFAS and informs the development of consistent approaches.
Table of EPA’s PFAS Standards Over Time
The table below illustrates the evolving approach of the EPA’s PFAS standards over time. Each entry represents a specific time frame and the relevant action or regulation implemented. The table highlights the progression of regulations and the evolving scientific understanding of PFAS. Note that this is not an exhaustive list and only shows a selection of major developments.
| Time Period | Action/Regulation | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-2020 | Initial identification of PFAS as a concern | Limited understanding of PFAS prevalence and health effects |
| 2022-Present | Establishment of MCLGs for specific PFAS groups | Increasing scientific evidence; evolving understanding of risk; establishment of a framework |
Trump Administration’s Role and Actions
The Trump administration’s approach to PFAS regulations in drinking water presented a significant departure from the Obama administration’s trajectory. While the EPA had been working towards establishing stricter standards, the Trump administration’s stance, influenced by various factors, resulted in a notable shift in the regulatory landscape. This shift, often criticized for its potential impact on public health, prompted considerable debate and discussion among environmental advocates, policymakers, and the public.The Trump administration’s policies concerning PFAS in drinking water were deeply intertwined with broader economic and political considerations.
The administration’s emphasis on deregulation and industry concerns played a significant role in shaping its approach to PFAS regulations. This, in turn, sparked intense controversy, raising concerns about the prioritization of economic interests over public health.
Trump Administration’s Stance on PFAS Regulations
The Trump administration demonstrated a more cautious and less stringent approach to PFAS regulations compared to previous administrations. This stance was characterized by a preference for a more measured and incremental approach to setting drinking water standards, often citing concerns about the economic impact of stringent regulations on various industries. Public health considerations were sometimes overshadowed by other priorities.
Specific Policies and Actions Regarding PFAS
The Trump administration’s actions concerning PFAS regulation in drinking water were marked by a series of pronouncements and policy decisions. These actions, though less decisive in terms of concrete standards, significantly impacted the timeline and direction of PFAS regulation.
- Reduced emphasis on stringent regulations: The administration’s policies leaned towards reducing the emphasis on setting stringent PFAS standards, prioritizing economic considerations and industry feedback over immediate public health concerns. This approach was met with significant opposition from environmental groups and public health advocates.
- Delayed action on EPA standards: The Trump administration delayed or significantly slowed down the EPA’s process of developing and implementing national drinking water standards for PFAS. This delay caused uncertainty and frustration for those advocating for stricter protections for public health.
- Emphasis on further research: The Trump administration highlighted the need for further research and scientific understanding of PFAS, although critics argued that this approach was used to stall or delay the establishment of clear standards. This approach emphasized a need for greater scientific understanding before setting stringent standards, but critics perceived it as a strategy to postpone action.
Statements and Pronouncements
The Trump administration’s pronouncements on PFAS frequently emphasized the need for a balanced approach to regulation, acknowledging both public health concerns and economic realities. These pronouncements were often characterized by a focus on industry input and economic considerations.
“We are committed to finding a balance between protecting public health and supporting our economy.”
A representative statement from the Trump administration.
Political Context
The political context surrounding the Trump administration’s actions on PFAS regulations was complex and often contentious. The administration’s approach faced criticism from environmental groups and public health advocates, who argued that it prioritized economic interests over public health concerns. The debate also reflected broader political divisions and differing perspectives on environmental regulation.
Summary Table of Key Actions and Statements
| Action/Statement | Description | Political Context |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced emphasis on stringent regulations | Prioritized economic concerns over immediate public health protection. | Facing criticism from environmental groups and public health advocates. |
| Delayed EPA standards | Slowed the development and implementation of national drinking water standards. | Caused uncertainty and frustration for advocates of stricter regulations. |
| Emphasis on further research | Highlighted the need for scientific understanding before setting standards. | Critics argued this was a tactic to delay action. |
| Statements emphasizing balance | Acknowledged public health and economic considerations. | Part of a broader political debate about environmental regulation. |
Impact of PFAS on Public Health
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of man-made chemicals used in various products. Their widespread use has led to their presence in the environment, including drinking water sources. Understanding the potential health impacts of PFAS exposure is crucial for public safety and the development of effective preventative measures. This section explores the potential health risks associated with PFAS exposure through drinking water, the scientific evidence linking PFAS to various health issues, and the mechanisms by which PFAS may impact human health.PFAS have been linked to a range of potential health problems, raising significant concerns about their long-term effects on human health.
Exposure to PFAS can occur through various pathways, including drinking water contaminated with these chemicals. The long half-lives of some PFAS compounds mean they persist in the environment and can accumulate in the human body. Consequently, understanding the potential risks of PFAS exposure is paramount to safeguarding public health.
Potential Health Risks of PFAS Exposure
PFAS exposure, particularly through drinking water, has been associated with a range of adverse health outcomes. Numerous studies have explored the relationship between PFAS levels in water and various health indicators. These studies provide crucial insights into the potential health consequences of PFAS exposure.
Scientific Evidence Linking PFAS to Health Issues
A substantial body of scientific research suggests a correlation between PFAS exposure and several health issues. Epidemiological studies, examining large populations, have demonstrated potential links between PFAS exposure and certain health outcomes. Animal studies have also shown similar effects, providing further evidence for potential health risks. These findings, although not definitive proof, strongly suggest a need for further investigation and public health measures.
Mechanisms of PFAS Impact on Human Health
The mechanisms by which PFAS exert their effects on human health are complex and not fully understood. However, research suggests several potential pathways. PFAS may interfere with hormone production, disrupt immune function, and potentially cause damage to organs and tissues. These potential mechanisms underscore the importance of understanding how PFAS interact with the human body.
The EPA’s stance on forever chemicals (PFAS) in drinking water standards under the Trump administration is a pretty hot topic. While the details are complex, it’s clear that there are significant concerns about public health. Meanwhile, did you know that the Tesla Cybertruck delivery livestream is coming up soon? You can find out the exact time and date, plus how to watch Elon Musk on this page.
Regardless of the electric vehicle excitement, the ongoing debate over PFAS levels in our water supply is crucial, demanding careful consideration and responsible action.
Summary of Potential Health Effects of PFAS
| PFAS Compound | Potential Health Effects |
|---|---|
| PFOA | Possible immune system suppression, liver damage, developmental issues in children, increased cholesterol levels, thyroid problems, and increased risk of certain cancers. |
| PFOS | Similar to PFOA, including immune system suppression, liver damage, developmental issues in children, and increased risk of certain cancers. |
| Other PFAS | Varying potential health effects depending on the specific PFAS compound. Some may have similar effects as PFOA and PFOS, while others might have different or less well-understood impacts. |
Research on PFAS is ongoing, and the full spectrum of health effects is still being elucidated. Further studies are essential to fully understand the long-term health consequences of PFAS exposure.
Public Awareness and Concerns
The public’s understanding and response to PFAS contamination in drinking water are crucial factors in the ongoing effort to address this environmental challenge. Public concern is directly linked to the perceived health risks associated with these chemicals, driving demand for action and influencing policy decisions.The public’s understanding of PFAS contamination and its potential health impacts is constantly evolving, shaped by information from various sources.
This dynamic understanding is fundamental to the success of mitigation efforts and policy changes.
Public Concerns Regarding PFAS Contamination
Public concerns regarding PFAS contamination in drinking water stem from a multitude of factors. These range from the persistent nature of these chemicals in the environment to the potential long-term health effects they might pose. The lack of definitive long-term health studies further fuels public apprehension. Additionally, the presence of PFAS in seemingly ubiquitous sources, from food packaging to firefighting foam, adds to the sense of pervasive contamination and potential exposure.
Factors Contributing to Public Awareness
Several factors have contributed to increasing public awareness of PFAS contamination. The growing body of scientific research linking PFAS to various health issues, including immune system and developmental problems, is a key catalyst. Moreover, the media’s increased coverage of PFAS contamination incidents and investigations has amplified public awareness. Concerned citizens and advocacy groups have also played a critical role in raising awareness through campaigns and educational initiatives.
Role of Media and Advocacy Groups
The media plays a pivotal role in disseminating information about PFAS contamination to the public. News reports, documentaries, and investigative journalism have exposed the extent of the problem and highlighted the potential risks to public health. Advocacy groups, with their dedicated efforts to raise public awareness and advocate for policy changes, have been equally instrumental in bringing the issue to the forefront.
These groups often organize community meetings, disseminate information, and actively engage in political advocacy.
Public Response to EPA Standards
The public’s response to the EPA’s drinking water standards for PFAS has been varied and complex. Some individuals and groups have praised the EPA’s efforts, viewing the standards as a crucial step towards protecting public health. Others have criticized the standards, either for not being stringent enough or for the process through which they were established. These differing perspectives reflect the varying degrees of understanding and concern regarding the risks associated with PFAS.
Public Response to PFAS Contamination (Illustrative Table)
| Public Response Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Supportive | Individuals and groups who believe the EPA’s standards are adequate and beneficial. | Environmental organizations that support the EPA’s stance, individuals who trust the EPA’s scientific assessments. |
| Critical | Individuals and groups who believe the EPA’s standards are insufficient, either due to inadequate stringency or questionable procedures. | Advocacy groups that are demanding more stringent standards, individuals concerned about potential health risks not adequately addressed by the standards. |
| Concerned/Cautious | Individuals and groups who are uncertain about the EPA’s standards, expressing reservations about the potential long-term health effects. | Individuals who seek more research and evidence, individuals who are wary of potential industry influence on the standards. |
PFAS Contamination Case Studies

PFAS contamination has emerged as a significant environmental and public health concern, impacting communities across the globe. Understanding specific contamination events, their consequences, and the challenges in remediation is crucial for developing effective strategies to address this pervasive issue. This section delves into detailed case studies, examining the varied impacts and highlighting the complexities involved in cleaning up PFAS-tainted water.
The EPA’s drinking water standards for forever chemicals, PFAS, under the Trump administration are definitely a hot topic. While we’re all concerned about the potential health risks of these chemicals in our water, it’s fascinating to see how a seemingly unrelated topic like the Xiaomi 12 Ultra’s rear panel design leak Xiaomi 12 ultra rear panel design leak can still draw our attention.
Ultimately, though, the persistent danger of PFAS contamination remains a serious concern, and the ongoing debate about these standards deserves our continued attention.
Specific PFAS Contamination Events
Numerous instances of PFAS contamination have been documented in various locations. These events often involve industrial facilities, military bases, and firefighting training areas. The contamination pathways can range from direct discharge into water sources to the leaching of PFAS-containing materials into the environment.
Consequences for Affected Communities
The consequences of PFAS contamination extend far beyond the immediate environmental impact. Exposure to PFAS can have detrimental effects on human health, potentially leading to various health issues, including immune system problems, developmental delays in children, and certain types of cancer. Affected communities often face significant financial burdens as they grapple with the costs of remediation and health monitoring.
These communities may experience decreased property values and difficulty attracting businesses due to the stigma associated with contamination.
Challenges in Addressing PFAS Contamination
Addressing PFAS contamination in drinking water presents substantial challenges. The persistence of PFAS in the environment, their widespread use in various products, and the complex analytical techniques required for detection are key hurdles. Furthermore, the high costs associated with remediation and the long-term monitoring needed to ensure the effectiveness of cleanup efforts create additional difficulties. Regulatory frameworks often lag behind the evolving scientific understanding of PFAS, further complicating remediation efforts.
Remediation Methods for PFAS Contamination
Several remediation methods are being explored and implemented to address PFAS contamination. These methods often involve combinations of techniques tailored to the specific site conditions and the nature of the contamination. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), which use chemical reactions to break down PFAS, are increasingly employed. Activated carbon adsorption, membrane filtration, and bioaugmentation are also utilized in certain cases.
Summary Table of PFAS Contamination Case Studies
| Case Study | Contaminant Source | Affected Communities | Consequences | Remediation Methods | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superfund Site in Ohio | Industrial Discharge | Residential areas downstream of the facility | Elevated PFAS levels in drinking water, potential health concerns | Combination of AOPs and activated carbon adsorption | High cost of remediation, long-term monitoring required |
| Military Base in California | Fire-fighting training activities | Surrounding residential communities | PFAS detected in groundwater, concerns about potential health risks | Membrane filtration systems and enhanced natural attenuation | Difficulty in determining the full extent of contamination, long-term effectiveness of remediation |
| Agricultural Runoff in Iowa | Agricultural Practices | Rural communities relying on well water | PFAS detected in surface water and groundwater, concerns about potential health impacts | Construction of retention ponds and optimized drainage systems | Limited funding for remediation, regulatory uncertainties regarding agricultural PFAS use |
Future of PFAS Regulations
The future of PFAS regulations hangs in the balance, a complex interplay of scientific advancements, political will, and public pressure. Current EPA standards are a crucial first step, but their limitations and the evolving understanding of PFAS toxicity necessitate a more comprehensive and adaptable regulatory framework. The path forward is not straightforward, and the potential impact on public health and the environment will depend on the decisions made in the coming years.
Potential Future Developments in PFAS Regulations
The ongoing research into PFAS’s long-term effects and its widespread contamination in various environments are driving the need for more stringent and comprehensive regulations. Expect to see a shift from focusing on individual chemicals to considering the mixture of PFAS in the environment. Further, regulators may prioritize developing remediation strategies for contaminated sites and implementing more robust monitoring programs.
The potential for emerging PFAS compounds will require adaptive management approaches in regulations.
Challenges for Future Regulation
Several challenges will likely hinder the swift development of effective PFAS regulations. Scientific uncertainty about the long-term health effects of PFAS mixtures and the varying degrees of exposure across populations will make establishing safe limits challenging. Defining clear exposure pathways and quantifying their impacts in diverse ecosystems will be crucial. Furthermore, navigating the complex legal and political landscape, including differing opinions on regulatory timelines and enforcement strategies, will pose significant hurdles.
International cooperation will also be essential due to the global nature of PFAS contamination.
Opportunities for Future Regulation
Despite the challenges, opportunities exist for improving PFAS regulations. Advancements in analytical techniques and monitoring technologies offer more accurate and sensitive detection methods for PFAS, allowing for better tracking and assessment of contamination. The public’s growing awareness and advocacy efforts are creating pressure for stronger regulations. Innovative remediation technologies and approaches will also play a key role.
This could lead to cost-effective and efficient methods for removing PFAS from water sources and contaminated environments.
Possible Scenarios for Future PFAS Standards, Forever chemicals pfas drinking water standards epa trump
Different scenarios for future PFAS standards are possible. One scenario envisions a phased approach, starting with stricter standards for drinking water, followed by regulations for other environmental media like soil and air. Another scenario involves setting a comprehensive maximum contaminant level (MCL) for the entire PFAS group of chemicals. A third scenario could involve tiered standards based on the toxicity and concentration levels of specific PFAS compounds.
The selection of the most suitable scenario will depend on the available scientific data and the political priorities of regulatory bodies.
Potential Impact on Public Health and the Environment
The impact of future PFAS regulations on public health will be substantial. Reduced exposure to PFAS through improved drinking water standards and remediation efforts will likely lead to a decrease in health issues linked to PFAS exposure. The potential long-term impacts, however, will require continued monitoring and research. Future regulations will also impact the environment by preventing further contamination and promoting remediation efforts.
The success of these efforts will be vital for safeguarding ecosystems and protecting wildlife.
Table of Possible Future PFAS Regulations
| Regulation Type | Focus | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Phased Approach | Start with drinking water, then expand to other environmental media. | Addresses immediate health concerns while allowing for further research. |
| Comprehensive MCL | Set a single maximum contaminant level for all PFAS compounds. | Provides clear and consistent standards but may require extensive remediation. |
| Tiered Standards | Standards based on toxicity and concentration of specific PFAS. | Addresses the varying risks posed by different PFAS compounds. |
Comparing Different Remediation Strategies
Tackling PFAS contamination in drinking water requires a multifaceted approach. Different remediation methods offer varying degrees of effectiveness, cost-efficiency, and environmental impact. Choosing the optimal strategy hinges on the specific characteristics of the contaminated water source, the extent of contamination, and the available resources.Various methods are employed to remove PFAS from contaminated water sources, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding these differences is crucial for developing a comprehensive remediation plan. This section delves into the diverse techniques, their effectiveness, and associated costs.
Methods for PFAS Removal
Several techniques are employed to remove PFAS from water, ranging from simple filtration to advanced chemical treatments. The selection of the appropriate method depends on the concentration of PFAS, the type of PFAS present, and the desired level of removal.
- Activated Carbon Adsorption: This method utilizes activated carbon materials to adsorb PFAS from water. The effectiveness depends on the type of activated carbon and the specific PFAS contaminants. High-surface-area activated carbons generally provide better removal rates, but the process can be expensive and require ongoing maintenance. Activated carbon adsorption is often a first-line defense in PFAS remediation due to its relative simplicity and cost-effectiveness compared to other methods for lower concentrations.
- Membrane Filtration: Membrane filtration, including reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF), is another common technique. These processes use semi-permeable membranes to separate PFAS from water. RO is typically used for high-concentration PFAS removal, while NF is more suitable for lower concentrations. Membrane filtration methods generally yield high PFAS removal rates but can be expensive to implement and maintain, particularly for large-scale applications.
Furthermore, membrane fouling is a potential issue that can impact long-term effectiveness and require frequent maintenance.
- Chemical Oxidation: This method involves using chemical oxidants to break down PFAS molecules into less harmful substances. Ozone and hydrogen peroxide are commonly used oxidants. This approach can be effective in degrading PFAS, but the process can be complex and may generate byproducts that need further treatment. The cost of chemical oxidants and the need for careful monitoring of byproduct formation are significant factors to consider.
Moreover, the efficiency of chemical oxidation depends on the specific PFAS and the conditions of the treatment.
- Bioaugmentation: Bioaugmentation involves introducing microorganisms to the water that can degrade PFAS. This method can be effective, but the process is slow and may require significant time to achieve desired results. The long-term sustainability of this approach is still being evaluated, and specific microorganisms need to be identified to effectively target different PFAS structures. The costs associated with bioaugmentation can be considerable and require specialized expertise and infrastructure.
Comparison of Remediation Techniques
Evaluating the effectiveness of different remediation techniques necessitates a comprehensive comparison. This comparison considers the efficiency of PFAS removal, operational costs, and environmental impact.
| Remediation Method | Effectiveness | Cost | Feasibility | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated Carbon Adsorption | Moderate to high, depending on carbon type | Relatively low to moderate | High, especially for initial stages | Low, minimal impact if properly managed |
| Membrane Filtration (RO/NF) | High | High | High, but may be more expensive for larger-scale projects | Low, but potential membrane fouling issues |
| Chemical Oxidation | High, but potential for byproducts | Moderate to high, depending on oxidant cost | Moderate, requires specialized infrastructure and monitoring | Moderate, depending on byproduct treatment |
| Bioaugmentation | Moderate, potentially low | Moderate to high, depending on implementation | Low, slow process and requires expertise | Low, but requires long-term monitoring |
This table provides a general overview. The specific effectiveness, cost, and feasibility of each method will vary depending on the specific context of the contamination.
Epilogue: Forever Chemicals Pfas Drinking Water Standards Epa Trump
In conclusion, the forever chemicals PFAS and their presence in drinking water pose significant challenges for public health and the environment. The EPA’s efforts to establish and update standards, the Trump administration’s actions, and public concerns all contribute to a complex narrative. Looking ahead, the future of PFAS regulation will likely depend on continued scientific research, public awareness, and effective remediation strategies.
Understanding the multifaceted issues surrounding PFAS is crucial for safeguarding public health and ensuring clean water for all.