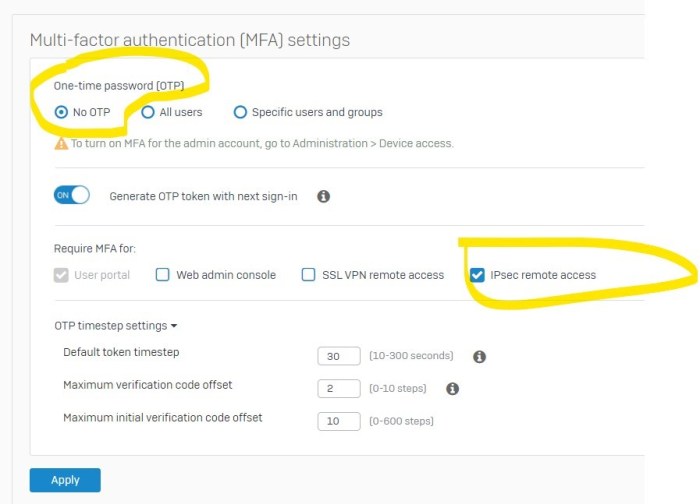
PingIdentity MFA NFGW Captive Portal Guide.viewer provides a comprehensive overview of securing network access using PingIdentity’s Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Network Access Gateway (NFGW) solutions. This guide explores the captive portal’s role in authentication, detailing its configuration, user experience, security considerations, and integration with other systems. It delves into the intricacies of deploying and maintaining the captive portal, offering a practical approach to managing network access for diverse devices and user groups.
The guide begins by explaining the fundamentals of PingIdentity MFA and NFGW, including their functions and how they work together. It then provides a detailed walkthrough of captive portal configuration, covering various authentication methods, customization options, and device compatibility. Further, it emphasizes user experience, troubleshooting common issues, and security best practices to ensure a seamless and secure network access process.
The guide also examines integration with other systems, deployment procedures, and advanced customization options, offering a complete picture of implementing a secure network access solution using PingIdentity’s platform.
Introduction to PingIdentity MFA and NFGW: Pingidentity Mfa Nfgw Captive Portal Guide.viewer
PingIdentity’s Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Network Access Gateway (NFGW) are crucial components for securing network access. MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond usernames and passwords, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before granting access. NFGW extends this security to the network itself, controlling and monitoring all network traffic. This combination creates a robust and adaptable security posture.These technologies are particularly important in today’s increasingly complex and distributed environments.
The need for secure remote access, and protection against unauthorized access attempts, has led to widespread adoption of these solutions. The integration of these systems with a captive portal further strengthens the security posture.
PingIdentity MFA Functionality
PingIdentity’s MFA solution verifies user identities using multiple factors. This approach dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized access, compared to relying solely on passwords. Typical verification methods include something the user knows (password), something the user has (a mobile device), or something the user is (biometric data). This multi-factor approach enhances security significantly.
Network Access Gateway (NFGW) Role
The NFGW acts as a central point of control for network access. It manages and enforces security policies, providing a critical layer of security between the network and external users. This is especially important for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to internal resources.
Captive Portal Integration
A captive portal acts as a gateway for network access, requiring users to authenticate before gaining access to the network. It’s a critical component of the PingIdentity MFA and NFGW solution, allowing for the enforcement of security policies and providing a secure onboarding experience for users.
I’ve been diving deep into the PingIdentity MFA NFGW captive portal guide.viewer, and honestly, it’s been a bit of a rabbit hole. The sheer volume of configurations is impressive, but after some head-scratching, I found a hidden gem. This guide seems crucial for securing access, but I had a momentary lapse in focus. I got sidetracked by the blazing speed of the Red Magic 8S Pro overclocked Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 processor redmagic 8s pro overclocked snapdragon 8 gen 2.
Now that my brain is back on track, I’m ready to finish tackling this PingIdentity MFA NFGW captive portal guide.viewer.
User Experience with Captive Portal
The user experience is streamlined. Users are directed to the captive portal upon attempting network access. They then enter their credentials, and if authenticated, they gain access to the network resources. The entire process is generally seamless, ensuring that only authorized users are granted access. This experience ensures that security is maintained while still being user-friendly.
Key Components of PingIdentity MFA, NFGW, and Captive Portal
| Component | Description | Role | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| PingIdentity MFA | Provides multi-factor authentication, requiring users to present multiple verification factors (e.g., password, one-time code). | Verifies user identity. | Validates user credentials, often by prompting for additional factors after initial login credentials are provided. |
| NFGW | Acts as a gateway for network access, controlling and monitoring all network traffic. | Manages and enforces security policies. | Interacts with the captive portal to authenticate users before granting network access. |
| Captive Portal | A web page that requires users to authenticate before granting network access. | Provides a secure authentication point. | Presents login forms and redirects users to the NFGW for authentication. |
Captive Portal Configuration
Setting up a captive portal for PingIdentity NFGW access is crucial for secure network entry. This configuration allows you to control who gains access to your network and enforces MFA policies before granting network access. The process involves configuring authentication methods, customizing the portal’s appearance, and ensuring compatibility with various devices.The PingIdentity Network Access Gateway (NFGW) captive portal acts as a gateway for users attempting to access a network.
It presents a login screen (the captive portal) that requires users to authenticate before granting access to the network. This approach enhances security and helps ensure that only authorized users can access the network.
Configuring the PingIdentity NFGW Captive Portal, Pingidentity mfa nfgw captive portal guide.viewer
The NFGW captive portal configuration process involves several key steps. First, you select the authentication method, which can range from simple username/password to more secure certificate-based solutions. Next, you customize the portal’s visual elements and messages to match your organization’s branding and communication style. Finally, you ensure the portal’s compatibility with various devices.
Authentication Methods
Choosing the right authentication method is crucial for the security and usability of your captive portal. Different methods offer varying levels of security and convenience.
- Username/Password: This is a common authentication method. Users provide their credentials, which are verified against a directory service. While simple, this method can be less secure compared to certificate-based authentication if not managed correctly.
- Certificate-Based Authentication: This method uses digital certificates for authentication. Certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority (CA), ensuring a strong level of trust. This method is more secure than username/password and often preferred for sensitive networks.
Customizing the Captive Portal
The captive portal’s appearance and messaging are critical for user experience and brand consistency. You can customize various aspects, including branding elements, logos, and instructions.
- Branding and Logo: Integrating your company’s logo and colors into the captive portal design enhances brand recognition and reinforces a consistent user experience.
- Clear Instructions: Providing clear instructions on how to authenticate and the steps involved can improve user onboarding and reduce support requests.
- Error Messages: Providing clear and informative error messages when authentication fails can guide users through the process.
Device Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility across various devices, such as laptops, tablets, and mobile phones, is essential. Different devices might require different configurations or settings for optimal functionality.
- Laptops: Laptops typically require no special configuration beyond the standard authentication method selected.
- Mobile Phones: Mobile devices might need additional configuration to handle certificate-based authentication. This can involve installing certificates on the device.
Comparison of Authentication Methods
The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of different captive portal authentication methods.
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Username/Password | Traditional authentication using credentials. | Simple to implement. | Potentially less secure than certificate-based methods. |
| Certificate-Based | Authentication using digital certificates. | Highly secure, reduces reliance on passwords. | Requires certificate management and potentially device configuration. |
User Experience and Troubleshooting

A well-designed captive portal is crucial for a smooth user experience when accessing network resources. A user-unfriendly portal can lead to frustration and wasted time, especially when dealing with multi-factor authentication (MFA). This section delves into best practices for designing a positive user experience and provides solutions for common problems.The captive portal is the first point of contact for users connecting to your network.
A streamlined process, clear instructions, and readily available support will contribute to user satisfaction and a positive perception of your network.
Best Practices for a User-Friendly Captive Portal
A user-friendly captive portal should be intuitive and easy to navigate. Clear instructions, concise language, and visually appealing design are essential. Visual cues, like progress bars or informative messages, can help users understand the authentication process. Providing options for different authentication methods, like social logins or password recovery, can increase user convenience. Consider using a responsive design to ensure optimal viewing across various devices.
Accessibility features, such as alternative text for images and keyboard navigation, are critical for users with disabilities.
Common User Issues and Troubleshooting
Several issues can arise during the captive portal authentication process. Understanding these potential problems and having effective troubleshooting steps in place can significantly improve the user experience. Addressing these issues quickly and efficiently prevents user frustration and enhances network access.
Login Failure Troubleshooting
Login failures can stem from various causes. Incorrect usernames or passwords are common, but network connectivity issues or server problems can also be culprits. Troubleshooting login failures involves systematically checking these potential factors. First, ensure the user’s credentials are accurate. If the credentials are correct, check network connectivity to confirm stable internet access.
If network connectivity is stable, check for temporary network outages or server issues. In case of persistent login failures, contact the network administrator for further assistance.
Figuring out the PingIdentity MFA NFGW Captive Portal Guide.viewer can be tricky, but hey, sometimes you just need a little break. Thinking about getting a great deal on a refurbished Nintendo Switch? Check out this awesome deal for a refurbished Nintendo Switch for just $260 with a full year warranty! nintendo switch deal get it refurbished for 260 including a 1 year warranty Once you’ve got your gaming fix sorted, you can get back to mastering that PingIdentity MFA NFGW Captive Portal Guide.viewer! It’s all about balance, after all.
Network Access Problems Troubleshooting
Network access problems can manifest in several ways, including slow connection speeds or complete inability to access network resources. These issues can arise from network congestion, firewall restrictions, or outdated device drivers. Troubleshooting network access problems involves systematically identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate solutions. First, check for network congestion by observing network traffic or by contacting the network administrator.
If network congestion is not the issue, ensure that the firewall settings allow access to the required network resources. In cases where the problem persists, review the user’s device drivers and ensure they are up-to-date.
Table of Common User Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Login Failure | User unable to log in to the captive portal. | Verify username and password. Check network connection. Contact network administrator if problem persists. |
| Network Access Problems | User experiences slow connection or cannot access network resources. | Check network congestion. Ensure firewall settings allow access. Update device drivers. Contact network administrator if problem persists. |
Security Considerations
Securing your captive portal is paramount for protecting user data and maintaining a trustworthy environment. This section delves into crucial security best practices, potential risks, and mitigation strategies to ensure the safety and integrity of your PingIdentity MFA and NFGW implementation.A well-designed captive portal acts as the first line of defense, safeguarding network access and preventing unauthorized entry. Proper configuration and robust security measures are vital to prevent exploitation and ensure a secure user experience.
Security Best Practices for Captive Portals
Implementing strong security practices for captive portals is essential. These practices include using strong passwords, enforcing two-factor authentication (2FA), and managing certificates meticulously. Effective security measures deter malicious actors and protect sensitive user information.
- Strong Passwords: Enforce a password policy requiring a minimum length, complexity (uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols), and regular password changes. Educate users on creating strong, unique passwords for each account. A strong password policy is a cornerstone of robust security, making it difficult for attackers to crack passwords.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement 2FA for all user accounts. This adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification method (e.g., a code sent to a mobile device) beyond a username and password. 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
- Certificate Management: Use trusted certificate authorities (CAs) and ensure certificates are regularly renewed and revoked when necessary. Maintain a robust certificate management system to prevent certificate compromise and ensure the authenticity of communications.
Potential Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Captive portals are vulnerable to various security threats. Understanding these risks and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial.
| Risk | Description | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|
| Man-in-the-Middle Attack | An attacker intercepts communication between the user’s device and the captive portal, potentially capturing credentials or modifying data. | Employ HTTPS encryption for all portal communications. Verify the authenticity of the captive portal using digital certificates. Regularly update the captive portal software to patch known vulnerabilities. |
| Password Cracking | Attackers attempt to guess or deduce user passwords using various techniques. | Enforce strong password policies. Implement robust password hashing algorithms to protect stored passwords. Employ account lockout mechanisms to prevent brute-force attacks. |
| Phishing Attacks | Attackers attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames and passwords, by impersonating legitimate entities. | Educate users about phishing tactics. Implement a robust security awareness training program. Use security awareness tools to monitor for suspicious user activity. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Attackers flood the captive portal with requests, overwhelming its resources and making it unavailable to legitimate users. | Implement rate limiting and access control mechanisms to prevent DoS attacks. Use load balancers to distribute traffic across multiple servers. Configure firewall rules to block malicious traffic. |
Encryption in Securing Captive Portal Communications
Encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding communications between the user’s device and the captive portal. HTTPS is crucial for encrypting data transmitted over the network. This protects sensitive information, such as login credentials, from eavesdropping and tampering.
Integration with Other Systems
PingIdentity MFA and NFGW are designed to seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure, particularly identity providers like Active Directory and LDAP. This integration allows for a unified and secure authentication process, streamlining user access and management. This capability is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage existing investments and avoid costly re-platforming efforts.Integrating with other systems empowers organizations to leverage their existing directory services, thereby enhancing security and efficiency.
The ability to integrate with Active Directory, for example, simplifies user provisioning and management, making it easier to manage user accounts across different systems. By automating user access management, organizations can minimize errors and improve overall security.
Active Directory Integration
Active Directory is a widely used directory service for managing user accounts and permissions. Integrating PingIdentity MFA and NFGW with Active Directory enables organizations to enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) requirements on users already managed within their Active Directory infrastructure. This approach provides a streamlined and efficient way to enhance security without requiring significant modifications to existing Active Directory setups.
A key benefit of this integration is the ability to leverage existing user information and policies, reducing configuration complexity.
LDAP Integration
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is another prevalent directory service often used for user authentication and authorization. The integration of PingIdentity MFA and NFGW with LDAP allows organizations to enforce MFA on users authenticated through LDAP directories. This integration enables a consistent security posture across various systems, regardless of the directory service used. The integration process typically involves configuring the PingIdentity MFA and NFGW components to interact with the LDAP server, including specifying the necessary authentication credentials and user attributes.
Configuration Process
The configuration process for integrating PingIdentity MFA and NFGW with other systems, such as Active Directory and LDAP, varies slightly but generally involves similar steps. These steps typically include:
- Identifying the relevant user attributes from the external system.
- Configuring the PingIdentity MFA and NFGW components to communicate with the external system.
- Defining the mapping between user attributes in the external system and the attributes required by PingIdentity MFA and NFGW.
- Testing the integration thoroughly to ensure correct functionality and user experience.
Example Integrations
Consider a scenario where an organization wants to enforce MFA on all users accessing a web application. They can integrate PingIdentity MFA and NFGW with their Active Directory. This setup ensures that only authenticated users, validated by both Active Directory credentials and a multi-factor authentication challenge, gain access to the application. Another example involves a company utilizing LDAP to manage user accounts.
Integrating PingIdentity MFA and NFGW with LDAP allows the company to require MFA for all users accessing internal network resources, strengthening the security posture across their entire network.
Common System Integrations
The following table Artikels common system integrations and their configuration steps. Note that specific steps might vary depending on the PingIdentity MFA and NFGW version and the specific external system.
| System | Description | Configuration Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Active Directory | Integrates with existing Active Directory infrastructure for user authentication and management. | Configure PingIdentity MFA to communicate with the Active Directory server, map user attributes, and enforce MFA requirements. |
| LDAP | Integrates with LDAP directory services for user authentication and authorization. | Configure PingIdentity MFA to communicate with the LDAP server, map user attributes, and enforce MFA requirements. |
Deployment and Maintenance
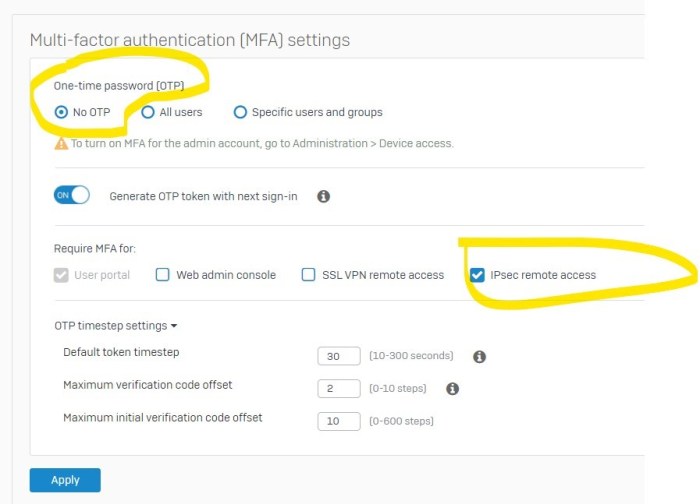
Deploying and maintaining a PingIdentity NFGW captive portal requires careful planning and execution to ensure a secure and reliable user experience. Proper configuration, ongoing monitoring, and proactive maintenance are crucial for optimal performance and prevent potential issues. This section will detail the necessary steps, hardware/software requirements, and monitoring/logging tools to achieve this.
Deployment Steps
Careful planning and execution are essential for a smooth deployment. The process involves several key steps, each with its own considerations. These steps ensure the portal is configured correctly and seamlessly integrates into the existing network infrastructure.
- Network Configuration: The NFGW needs to be correctly configured within the network, including firewall rules and routing configurations. This step ensures the portal is accessible to authorized users and the communication between the NFGW and other systems is secure.
- Service Integration: The NFGW should be integrated with relevant services, such as Active Directory or other identity providers, to allow proper authentication and authorization of users. This ensures only authorized users gain access to the network.
- Captive Portal Configuration: The captive portal’s configuration should align with the organization’s branding and security policies. This involves setting up the login page, branding elements, and any specific security requirements.
- Testing and Validation: Comprehensive testing of the entire deployment is critical. This involves testing user authentication, access to network resources, and the captive portal’s overall functionality with different user roles and devices.
Hardware and Software Requirements
The hardware and software requirements for the NFGW should be carefully considered during deployment. The selection of hardware and software directly impacts the portal’s performance, scalability, and security.
- NFGW Appliance: The Ping Identity NFGW appliance is the core component, and its specifications (CPU, RAM, storage) should align with expected user traffic and portal complexity. This ensures optimal performance.
- Operating System: The NFGW’s operating system needs to be compatible with the application and its supporting services. Up-to-date versions ensure security patches and optimal performance.
- Network Connectivity: The NFGW must have appropriate network connectivity to reach the necessary resources, such as identity providers and network devices. A stable network connection is crucial.
Monitoring and Logging Tools
Implementing appropriate monitoring and logging tools is essential for proactively identifying and resolving potential issues. These tools provide insights into portal performance, security events, and user activity.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitoring tools should track key metrics like response times, connection rates, and user sessions to detect performance bottlenecks or anomalies. This proactive approach prevents issues from escalating.
- Security Logging: Security logs should record all significant events, including login attempts, failed authentication, and access to network resources. This data aids in detecting and responding to security threats.
- User Activity Monitoring: Monitoring user activity provides insights into usage patterns, which helps in identifying potential problems or unauthorized access attempts. This provides crucial information for maintaining the portal.
Deployment and Maintenance Checklist
A checklist provides a structured approach to ensure all necessary steps are completed during deployment and maintenance.
Figuring out the PingIdentity MFA NFGW captive portal guide.viewer can be tricky, but thankfully, there are resources available. While you’re diving into the details of that, did you know you can now uncover fascinating facts about your favorite songs? Amazon Music’s new X-Ray experience lets you explore the stories behind the tunes, from the artists’ inspirations to the songs’ creation.
It’s a cool distraction from the complex configurations of the PingIdentity MFA NFGW captive portal guide.viewer, but it’s all good! You’ll get back to the nuts and bolts of the viewer in no time.
- Pre-Deployment Planning: Ensure all necessary hardware, software, and network configurations are in place before initiating deployment.
- Configuration Validation: Verify all settings are correct and according to security policies before activating the portal.
- Post-Deployment Testing: Rigorous testing across different user roles and devices to ensure functionality and security.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a schedule for software updates, security patching, and performance monitoring.
Advanced Features and Customization
Beyond the basic configuration, PingIdentity NFGW captive portals offer a wealth of advanced features for tailoring the user experience and enhancing security. These features allow administrators to customize the portal’s appearance, enforce specific access policies, and integrate with existing systems seamlessly. This deep dive explores the powerful customization options available.The flexibility of PingIdentity NFGW captive portals extends beyond standard configurations.
Administrators can significantly customize the user experience, security policies, and branding to align with specific organizational needs and branding guidelines. This enhanced control ensures a secure and user-friendly environment for accessing network resources.
Custom Branding
Custom branding options allow administrators to integrate the portal’s visual identity with the organization’s existing design elements. This personalized approach enhances brand recognition and user familiarity.Implementing custom branding involves replacing default elements like logos, colors, and fonts with company-specific assets. This personalized touch fosters a more consistent user experience, reducing confusion and enhancing brand recognition. Specific branding elements like logos, colors, and fonts can be tailored.
Custom Policies
Custom policies provide granular control over user access to network resources. They enable administrators to implement specific access rules based on user roles, departments, or other criteria.Implementing custom policies involves defining rules for authentication, authorization, and access control. For example, a policy could require users in the “Sales” department to complete additional security training before accessing specific resources.
A policy can mandate the use of multi-factor authentication for high-security resources. Another example could restrict access to certain resources for users who haven’t logged in for a certain period. These policies can be tailored for specific user groups, allowing for differential access control.
Advanced User Experience Customization
Beyond branding, administrators can personalize the portal’s user interface to meet specific organizational needs. This involves tailoring the portal’s layout, navigation, and information displayed to users.Administrators can create a customized user experience by modifying the portal’s structure and information displayed to meet user needs. This can include modifying the order of steps, adding or removing sections, or providing context-sensitive information.
Customizable elements like page layouts, input fields, and the overall user interface can be adjusted.
Example Custom Policies
| User Group | Policy |
|---|---|
| Sales Team | Requires completion of a sales-specific training module before accessing sales data. |
| Executives | Bypass certain authentication steps for faster access to critical resources. |
| External Contractors | Limited access to specific network resources and time-bound access restrictions. |
These policies demonstrate the granularity and control afforded by custom policies. By tailoring access based on user groups, administrators can create a secure and streamlined experience for everyone.
Epilogue
In conclusion, this PingIdentity MFA NFGW Captive Portal Guide.viewer serves as a valuable resource for understanding and implementing secure network access using PingIdentity’s MFA and NFGW. By thoroughly examining configuration, user experience, security, and integration aspects, the guide empowers users to effectively manage and secure network access. The guide’s practical approach and detailed explanations provide a strong foundation for implementing a robust and reliable security solution.