Enhance your vulnerability management is crucial in today’s digital landscape. This comprehensive guide delves into every facet, from defining vulnerability management and its importance to implementing robust strategies and using advanced tools. We’ll explore the entire lifecycle, from identification to remediation and reporting, equipping you with the knowledge to build a strong vulnerability management program.
This guide will help you understand the stages of vulnerability management, from identification and remediation to monitoring and reporting. We will also discuss the critical role of a dedicated team and how to continuously improve your program to adapt to evolving threats.
Introduction to Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is a crucial component of any robust cybersecurity strategy. It’s not just about identifying weaknesses; it’s about proactively addressing them to protect systems and data from malicious actors. In today’s interconnected world, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, a well-defined vulnerability management program is no longer a luxury, but a necessity.Vulnerability management encompasses the entire lifecycle of identifying, assessing, remediating, and monitoring vulnerabilities.
It’s a continuous process, not a one-time fix, that requires constant vigilance and adaptation to emerging threats. This approach not only safeguards critical infrastructure but also protects sensitive information and maintains the integrity of operations.
Definition of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is the systematic process of identifying, classifying, prioritizing, mitigating, and monitoring security vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure. It involves a coordinated effort across various teams, including security, development, and operations, to proactively address potential security breaches. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of exploitation by malicious actors and safeguards the organization’s digital assets.
Importance of Vulnerability Management in Today’s Digital Landscape
The modern digital landscape is characterized by an ever-increasing number of interconnected systems and devices. This interconnectedness, while facilitating innovation and efficiency, also exposes organizations to a wider range of potential vulnerabilities. Proactive vulnerability management is vital to mitigating these risks, preventing data breaches, and maintaining business continuity. Ignoring vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications.
Best Practices for Establishing a Robust Vulnerability Management Program
Implementing a robust vulnerability management program requires a multi-faceted approach. A key element is establishing clear policies and procedures that define roles, responsibilities, and reporting mechanisms. This structured approach ensures consistent actions and fosters a culture of security awareness. Regular training and communication are essential for all personnel to understand their roles in vulnerability management. Implementing automated tools and processes streamlines the workflow and increases efficiency.
Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact is crucial for focusing resources on the most critical issues.
- Policy and Procedure Development: Establish clear guidelines for identifying, reporting, and remediating vulnerabilities. These should include procedures for incident response and communication channels.
- Automated Tools and Processes: Employ automated vulnerability scanning tools to identify potential weaknesses across the organization’s systems and applications.
- Prioritization and Risk Assessment: Use risk assessment methodologies to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact. This ensures that resources are allocated effectively to address the most critical issues first.
- Collaboration and Communication: Encourage collaboration between security, development, and operations teams. Transparent communication channels facilitate the timely resolution of vulnerabilities.
Relationship between Vulnerability Management and Cybersecurity
Vulnerability management is an integral part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. It acts as a crucial component in reducing the attack surface by proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities. Effective vulnerability management significantly strengthens the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture and reduces the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
The vulnerability management lifecycle involves several key stages. A well-defined process ensures that vulnerabilities are identified, assessed, prioritized, and ultimately remediated in a structured manner. This approach minimizes the time between vulnerability discovery and remediation, thus reducing the risk of exploitation.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Identification | Identifying potential vulnerabilities through automated scans, penetration testing, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. |
| Assessment | Evaluating the severity, impact, and potential exploitability of identified vulnerabilities. |
| Prioritization | Ranking vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact. This ensures resources are allocated effectively. |
| Remediation | Developing and implementing solutions to mitigate or eliminate vulnerabilities. This can involve patching systems, configuring firewalls, or implementing security controls. |
| Monitoring | Continuously monitoring systems to ensure that vulnerabilities are not reintroduced and that newly discovered vulnerabilities are addressed quickly. |
Enhancing Vulnerability Identification
Identifying vulnerabilities is a crucial first step in a robust security posture. Effective vulnerability management relies heavily on proactive identification, enabling organizations to address potential weaknesses before malicious actors exploit them. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and system compromise.Vulnerability identification encompasses a range of techniques, from automated scans to in-depth penetration testing. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
Understanding the various methods and their strengths and weaknesses is vital for implementing a comprehensive vulnerability management strategy.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Automated vulnerability scanning tools are essential for identifying a wide range of vulnerabilities across a network. These tools automate the process of checking systems and applications for known security weaknesses, significantly reducing the manual effort required. Different scanning techniques have varying levels of effectiveness, and organizations must carefully evaluate the specific tools and approaches to best meet their needs.
- Network vulnerability scanners scan for vulnerabilities in network devices, such as routers and firewalls. They typically use a variety of probes to simulate attacks, identifying potential weaknesses in configurations and services.
- Web application scanners focus on identifying vulnerabilities in web applications, probing for flaws like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and insecure authentication. These scanners often use techniques to simulate real-world attacks.
- Database scanners target vulnerabilities in database systems, probing for weaknesses in configurations and user access controls. They can uncover vulnerabilities like unauthorized access, improper data handling, and weak authentication procedures.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing goes beyond automated scanning by simulating real-world attacks. Ethical hackers use various techniques to attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and applications, providing a more in-depth understanding of potential attack vectors. This process helps identify vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
Comparing Vulnerability Scanning Techniques
Different scanning techniques offer varying levels of detail and coverage. Automated scanners are typically faster and can cover a larger scope, while penetration testing provides a more comprehensive and realistic assessment of security weaknesses. Automated scans are valuable for routine vulnerability assessments, but penetration testing offers more context and actionable insights.
Examples of Common Vulnerabilities and Their Impacts
Common vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and insecure authentication can have significant impacts. SQL injection, for instance, can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to databases, potentially compromising sensitive data. Cross-site scripting vulnerabilities can enable attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages, leading to the theft of user credentials or the redirection of users to malicious websites.
Want to enhance your vulnerability management? It’s crucial for protecting your digital assets, and sometimes the smallest details matter most. For example, consider grabbing some new accessories to bolster your security setup. You can save up to 50% off select accessories at Verizon, save up to 50 off select accessories at verizon , which could significantly impact your security posture.
Stronger devices and peripherals are a key step in your overall vulnerability management strategy.
Role of SIEM Systems in Vulnerability Identification
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems play a crucial role in vulnerability identification. By collecting and analyzing security logs from various sources, SIEM systems can detect suspicious activities that may indicate vulnerabilities or potential attacks. They can correlate events to identify patterns and anomalies, providing valuable insights into potential security weaknesses.
Vulnerability Scanning Tools Comparison
| Tool | Capabilities | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nessus | Network, web application, and database scanning | Wide range of scan types, comprehensive vulnerability database | Can be resource-intensive for large environments |
| OpenVAS | Network, web application, and database scanning | Open-source and highly customizable | Requires some technical expertise to configure effectively |
| Acunetix | Web application scanning | Specialized in web application security, comprehensive scan of web apps | Limited network scanning capabilities |
Improving Vulnerability Remediation: Enhance Your Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management isn’t just about finding flaws; it’s about fixing them effectively. A strong remediation process is crucial for maintaining a secure environment and minimizing the impact of potential attacks. This section dives into prioritizing vulnerabilities, patching systems, and understanding the critical role of timely remediation.Effective vulnerability remediation is more than just patching; it’s a strategic process that considers the broader context of your security posture.
Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on risk, implementing robust patching procedures, and maintaining a proactive remediation plan are key components of a successful vulnerability management program.
Prioritizing Vulnerabilities Based on Risk
Prioritizing vulnerabilities is essential for focusing resources on the most critical issues. This involves evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of exploitation for each vulnerability. A common method is using a risk matrix, which combines the severity of the vulnerability with the likelihood of it being exploited. This structured approach helps to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that the most dangerous weaknesses are addressed first.
A well-defined scoring system allows for a consistent evaluation process, leading to a clear and organized prioritization strategy.
Patching and System Configuration
Patching and system configuration are fundamental steps in mitigating vulnerabilities. Effective patching involves deploying security updates promptly and thoroughly testing the impact on systems and applications. This step requires a well-defined patching process, including clear communication channels for notifying affected users and ensuring smooth system updates. Thorough testing is critical to identify and resolve any unforeseen issues.
Configuration management plays a crucial role by ensuring systems are configured securely and adhering to best practices. This includes implementing strong passwords, enabling necessary security features, and limiting unnecessary access.
Boosting your vulnerability management is crucial, especially when dealing with software updates. A recent example highlights this – the Google Pixel Android 13 update, unfortunately, introduced some wireless charging battery drain bugs, as detailed in this article here. Addressing these kinds of issues, and proactively patching vulnerabilities, strengthens your overall system security. So, take the time to enhance your vulnerability management practices.
Significance of Timely Vulnerability Remediation
Timely vulnerability remediation is crucial for preventing exploitation. Delayed remediation increases the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit the vulnerability, leading to potential data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. For instance, a recent study demonstrated that organizations with a delayed patching policy had a significantly higher rate of successful attacks. Proactive remediation strategies can reduce this risk, minimizing the potential impact of security incidents.
Factors Influencing Remediation Effectiveness
Several factors influence the effectiveness of vulnerability remediation. These include:
- Automated Remediation Tools: Automation tools streamline the patching process, improving efficiency and reducing human error. This leads to faster deployment of updates, thereby reducing the exposure window.
- Proactive Security Policies: Clearly defined security policies and guidelines, along with established processes for addressing vulnerabilities, ensure consistency and reduce errors. This proactive approach can prevent a recurrence of similar vulnerabilities.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices helps prevent human error. It includes proper handling of suspicious emails and links, enabling the team to act in line with established procedures.
- Comprehensive Change Management: Proper change management processes minimize disruptions during patching and configuration updates, maintaining service continuity.
- System Monitoring and Alerting: Continuous monitoring of systems for signs of compromise can help identify and respond to vulnerabilities faster. This ensures that any unexpected issues are caught promptly, mitigating risks.
Examples of Successful Remediation Processes
Many organizations have successfully implemented robust remediation processes. For example, a company that automated patching procedures and implemented strict change management protocols saw a significant reduction in vulnerabilities and security incidents. Similarly, a company that proactively trained its employees about phishing attempts and security best practices reported a decrease in the number of successful social engineering attacks. These real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of proactive and consistent remediation efforts.
Creating a Remediation Plan
A clear remediation plan is crucial for effectively addressing identified vulnerabilities. This plan should Artikel specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities for each vulnerability. The plan should include:
- Vulnerability Identification and Analysis: A detailed assessment of the vulnerability, including its impact, likelihood, and potential remediation steps.
- Prioritization and Categorization: Ranking vulnerabilities based on risk, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first.
- Patching and Configuration Management: Detailed steps for applying patches and updating configurations, including testing and validation.
- Timeline and Resources: A clear timeline for completion, along with the resources required for each step.
- Communication Plan: Defining the communication channels for notifying stakeholders and users about the remediation process.
Implementing Enhanced Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous vulnerability monitoring and effective reporting are critical for proactive security posture management. Robust reporting mechanisms enable organizations to track the effectiveness of vulnerability remediation efforts, identify emerging trends, and prioritize remediation activities based on risk. This proactive approach strengthens overall security posture and mitigates potential threats.Effective vulnerability management hinges on a constant watch for emerging vulnerabilities and timely communication to relevant stakeholders.
Implementing a robust monitoring system coupled with clear reporting procedures is crucial for maintaining a secure environment.
Strategies for Establishing Continuous Monitoring of Vulnerabilities
Continuous vulnerability monitoring requires a proactive approach that goes beyond periodic scans. Implementing automated vulnerability scanning tools, integrating security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and utilizing threat intelligence feeds are key components of a robust monitoring strategy. These tools and techniques provide real-time insights into emerging vulnerabilities, allowing for faster identification and response.
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: Scheduled scans, combined with on-demand scans triggered by specific events or changes in the environment, offer comprehensive coverage. This approach proactively identifies vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. For instance, integrating vulnerability scanners with CI/CD pipelines ensures that new code deployments are thoroughly assessed for vulnerabilities.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: SIEM systems correlate security events and logs to detect anomalies, unusual patterns, and suspicious activities, which can often indicate a vulnerability or a breach. For instance, an unusually high number of failed login attempts from a specific IP address could trigger an alert and a vulnerability scan.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Utilizing threat intelligence feeds provides valuable insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations can proactively adjust their security posture to address potential risks before they materialize.
Significance of Reporting and Communication in Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management reporting and communication are essential for stakeholder engagement, informed decision-making, and ultimately, enhanced security. Regular reports provide visibility into the organization’s security posture, allowing for the identification of vulnerabilities and effective prioritization of remediation efforts.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Transparent and consistent communication keeps stakeholders informed about the organization’s security posture and any potential risks. This fosters a shared understanding of the importance of vulnerability management.
- Informed Decision-Making: Comprehensive reporting allows stakeholders to make informed decisions about resource allocation and prioritization of remediation activities based on risk assessments.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Effective communication and reporting facilitate a proactive approach to security, ensuring that the organization is constantly aware of its vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate countermeasures.
Vulnerability Management Reporting Metrics
Reporting metrics provide a quantifiable measure of the effectiveness of vulnerability management programs. These metrics are critical for assessing the security posture, identifying areas needing improvement, and demonstrating the value of security investments.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of vulnerabilities identified | Counts the total number of vulnerabilities found during scans. |
| Number of vulnerabilities remediated | Indicates the number of vulnerabilities successfully addressed. |
| Vulnerability remediation time | Measures the time taken to remediate identified vulnerabilities. |
| Vulnerability severity distribution | Categorizes vulnerabilities based on severity levels, providing insight into critical issues. |
| Vulnerability exploitability | Indicates the ease with which vulnerabilities can be exploited. |
Effective Communication of Vulnerability Information to Stakeholders
Effective communication ensures stakeholders understand the severity and potential impact of vulnerabilities. This involves tailoring the communication to the specific audience and utilizing various formats to enhance clarity and comprehension. Tailored reports, presentations, and visual aids can improve comprehension.
- Audience-Specific Communication: Tailoring communication to different stakeholder groups (e.g., IT staff, executive management, compliance officers) ensures that the information is relevant and actionable.
- Multiple Communication Channels: Utilizing various channels, such as email, dedicated dashboards, and security awareness training, can enhance the reach and impact of vulnerability management information.
- Visual Aids and Dashboards: Visualizations of vulnerability data provide a concise overview of security posture, highlighting trends and areas requiring attention.
Dashboards and Visualizations in Monitoring and Reporting
Dashboards and visualizations provide a centralized and interactive view of vulnerability data, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp critical information. These tools offer a streamlined way to monitor and report on vulnerability status, providing an overview of the security posture. They can highlight trends and patterns, allowing for proactive mitigation.
Want to enhance your vulnerability management? It’s crucial for overall system security, just like mastering the combat mechanics in God of War Ragnarok New Game Plus on PlayStation. Thorough vulnerability assessments are key to proactive defense, much like strategically planning your attacks in the game. Understanding potential weaknesses allows you to fortify your systems and prevent future threats.
- Centralized View: Dashboards consolidate key vulnerability metrics and provide a comprehensive overview of the security posture.
- Interactive Visualization: Interactive dashboards allow stakeholders to drill down into specific vulnerabilities, examining details like severity, affected systems, and remediation status.
- Trend Analysis: Visualizations can highlight trends in vulnerability identification and remediation, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
Different Reporting Formats for Vulnerability Data
Different reporting formats cater to specific needs and stakeholder preferences. Regular vulnerability reports, dashboards, and automated alerts all play crucial roles in disseminating critical security information.
- Regular Vulnerability Reports: Detailed reports provide a comprehensive overview of identified vulnerabilities, including their severity, affected systems, and recommended remediation steps.
- Dashboards: Interactive dashboards present key vulnerability metrics in a visual format, facilitating quick analysis and trend identification.
- Automated Alerts: Automated alerts notify stakeholders about critical vulnerabilities or significant changes in the security posture, enabling timely responses.
Vulnerability Management Tools and Technologies
Choosing the right vulnerability management tools is crucial for a robust security posture. These tools automate the identification, assessment, and remediation of security vulnerabilities, significantly reducing the risk of cyberattacks. Effective vulnerability management tools empower organizations to proactively address potential weaknesses, ensuring continuous security improvement.
Popular Vulnerability Management Tools
Various vulnerability management tools cater to different needs and budgets. Leading providers offer comprehensive solutions encompassing vulnerability scanning, risk assessment, and remediation guidance. Key players in this space include Nessus, Qualys, Rapid7, and OpenVAS, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these tools’ capabilities and limitations is vital for informed decision-making.
Features and Functionalities of Leading Solutions
Leading vulnerability management solutions offer a suite of features, enabling automated vulnerability scanning, prioritizing risks, and facilitating remediation workflows. These features often include:
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: Tools automatically scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities, identifying potential weaknesses. This helps organizations proactively address potential security issues.
- Risk Assessment and Prioritization: Tools assess the severity and impact of identified vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts based on potential harm. This prioritization is crucial for focusing resources on the most critical vulnerabilities.
- Remediation Guidance and Reporting: Tools often provide detailed remediation steps and guidance for fixing identified vulnerabilities, ensuring efficient and effective patching. Comprehensive reporting allows organizations to track their progress and measure the effectiveness of their vulnerability management program.
- Integration with Other Security Solutions: Modern vulnerability management tools frequently integrate with other security solutions, such as SIEMs and incident response platforms. This integration enhances the overall security posture by providing a holistic view of the security landscape.
Comparing Strengths and Weaknesses of Tools
A comprehensive comparison requires evaluating various factors. Consider the tool’s scalability, ease of use, and reporting capabilities, alongside factors like the cost of implementation and maintenance. A detailed comparison can be presented in a table, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of different solutions.
Real-World Examples of Enhanced Vulnerability Management, Enhance your vulnerability management
Numerous organizations have successfully enhanced their vulnerability management through the use of these tools. For instance, a financial institution leveraging a robust vulnerability management solution identified and mitigated critical vulnerabilities in their online banking platform before they could be exploited. This proactive approach prevented significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Table Comparing Vulnerability Management Tools
| Tool | Features | Pricing | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nessus | Comprehensive scanning, reporting, and remediation guidance | Variable, based on licensing | Strong reputation for accuracy and extensive coverage | Can be complex to configure for some users |
| Qualys | Cloud-based platform, extensive integrations, excellent reporting | Variable, based on licensing and usage | Scalable, suitable for large organizations | Learning curve for full feature utilization |
| Rapid7 | Wide range of scanning options, detailed reporting, and incident response capabilities | Variable, based on licensing and usage | Strong incident response and threat intelligence integration | Might be less cost-effective for smaller organizations |
| OpenVAS | Open-source platform, highly customizable | Free | Cost-effective solution for smaller organizations | Requires significant technical expertise for setup and maintenance |
Integration with Other Security Solutions
Integration with other security solutions is critical for a holistic security approach. For example, integrating a vulnerability management tool with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system provides a centralized view of security events, enabling organizations to correlate vulnerabilities with suspicious activities. This integration can improve incident response and threat detection capabilities.
Building a Strong Vulnerability Management Team
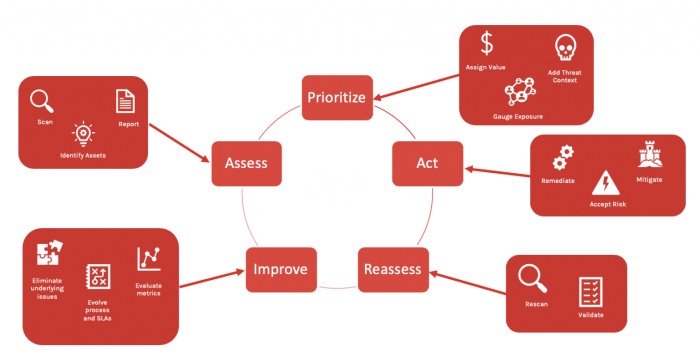
A robust vulnerability management program relies heavily on a skilled and well-organized team. This team is the engine driving proactive security posture, and their effectiveness directly impacts an organization’s overall security resilience. Building a strong team involves not just assembling individuals with the right technical skills, but also fostering a culture of collaboration, communication, and continuous learning.
Essential Skills and Knowledge
A successful vulnerability management team needs members with a deep understanding of security principles, tools, and processes. This includes proficiency in identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing vulnerabilities, as well as the knowledge to effectively remediate them. Critical skills include: proficiency in various security tools (e.g., vulnerability scanners, penetration testing tools), understanding of operating systems and applications, and experience in security best practices.
Knowledge of industry standards and regulations, like NIST frameworks and GDPR, is also invaluable. Furthermore, strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and the ability to effectively communicate complex technical information to non-technical stakeholders are crucial.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration is paramount for a vulnerability management team. Team members must be able to share information, coordinate efforts, and work together seamlessly to address vulnerabilities efficiently. Open communication channels, regular meetings, and clear roles and responsibilities are essential for maintaining a smooth workflow. A culture of trust and respect, where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns, is vital for effective collaboration.
Clear communication strategies, both internal and external, are needed to ensure everyone understands the process and progress.
Team Structures
Several team structures can be implemented for vulnerability management, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. A centralized team, reporting directly to a security manager, allows for streamlined decision-making and consistent application of security policies. A distributed approach, where team members are embedded within various business units, can enhance collaboration and improve the understanding of the impact of vulnerabilities within different operational contexts.
A hybrid structure combines elements of both centralized and distributed models, allowing for a balance of efficiency and localized knowledge. The optimal structure depends on the size and complexity of the organization and its specific security needs.
Training and Development
Continuous training and development are essential for maintaining the expertise of the vulnerability management team. Regular training sessions on new tools, techniques, and industry best practices can help the team stay current with the evolving threat landscape. Mentorship programs and opportunities for professional development can further enhance individual skills and encourage career growth within the team. This includes training on compliance requirements and ethical hacking techniques.
Onboarding New Members
A structured onboarding process is crucial for integrating new team members effectively. This should include clear communication of roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines. New team members should be provided with access to necessary resources, tools, and documentation. Initial training on existing processes, tools, and the organization’s security policies will ensure a smooth transition and maximize the new member’s contributions.
Pairing new members with experienced mentors can also expedite their learning curve and ensure a successful integration.
Job Roles and Responsibilities
| Job Role | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability Analyst | Identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing vulnerabilities; assessing impact and risk; documenting findings; coordinating remediation efforts. |
| Security Engineer | Developing and implementing security controls; configuring and maintaining vulnerability management tools; conducting penetration testing; supporting remediation efforts. |
| Security Manager | Overseeing the vulnerability management program; defining policies and procedures; allocating resources; reporting on program performance; collaborating with stakeholders. |
| Compliance Officer | Ensuring adherence to relevant industry regulations and standards; coordinating with compliance teams; monitoring regulatory changes. |
Continuous Improvement in Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process demanding continuous evaluation and adaptation. A static approach to vulnerability management will inevitably fall behind emerging threats and evolving attack vectors. This necessitates a commitment to continuous improvement, incorporating feedback, and leveraging data-driven insights to optimize the entire process.Continuous improvement in vulnerability management is not just about fixing flaws; it’s about creating a proactive and resilient security posture.
This requires a systematic approach that incorporates learning from successes and failures, proactively adapting to changing threats, and fostering a culture of continuous learning within the security team.
Strategies for Ongoing Assessment and Improvement
A proactive approach to vulnerability management requires consistent assessment of the process. This includes regular audits of existing procedures, tools, and team capabilities. Assessing the effectiveness of current tools and procedures is crucial. Are the tools still appropriate for the evolving threat landscape? Are the procedures efficient and up-to-date?
By regularly evaluating the effectiveness of current tools, teams can identify potential areas for improvement and streamline the process.
Methods for Evaluating the Effectiveness of Vulnerability Management Initiatives
Evaluating the effectiveness of vulnerability management initiatives requires establishing clear metrics and benchmarks. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential for tracking progress and identifying areas needing attention. Measuring the time taken to remediate vulnerabilities, the number of vulnerabilities discovered, and the rate of successful remediation are crucial metrics. Regular reporting on these metrics allows for objective assessments and helps pinpoint bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the process.
Examples of Continuous Improvement Methodologies in Vulnerability Management
Several methodologies can be employed to achieve continuous improvement in vulnerability management. The Deming Cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) is a powerful tool. This cyclical process encourages proactive planning, execution, evaluation, and adaptation to improve efficiency and effectiveness. Agile methodologies can also be beneficial, enabling rapid response to emerging threats and adapting to changing priorities. This iterative approach allows for adjustments based on real-time feedback and data.
Adapting the Vulnerability Management Program to Evolving Threats
The threat landscape is dynamic, demanding a corresponding adaptation in vulnerability management programs. Regularly reviewing and updating the vulnerability database is essential. This includes adding new vulnerabilities as they are discovered and patching known weaknesses. Staying informed about emerging threats through industry news, threat intelligence feeds, and security advisories is vital for proactive defense. Integrating threat intelligence into the vulnerability management process allows for a more proactive approach to identifying and mitigating potential risks.
Gathering Feedback from Stakeholders on Vulnerability Management Effectiveness
Regular feedback from stakeholders is critical to the success of any vulnerability management program. This includes end-users, developers, and other stakeholders. Surveys, questionnaires, and regular meetings can be used to collect feedback. Gathering this feedback allows for identifying areas of concern or improvement in the process from a stakeholder’s perspective. Feedback from stakeholders provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the program from different viewpoints.
Using Metrics to Track and Measure Vulnerability Management Progress
Metrics provide a concrete way to track and measure the effectiveness of vulnerability management initiatives. These metrics can be used to measure the efficiency of the entire process. Common metrics include the number of vulnerabilities identified, the time taken to remediate them, and the rate of successful remediation. Tracking these metrics provides a clear picture of progress and identifies areas requiring attention.
Regular analysis of these metrics allows for the identification of trends, the assessment of program performance, and the adjustment of strategies for future improvements.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, enhancing your vulnerability management isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about proactively safeguarding your digital assets. By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can build a resilient system that anticipates and mitigates potential threats. Remember, continuous improvement and adaptation are key to staying ahead of ever-evolving cyber risks. The future of your digital security depends on it.



