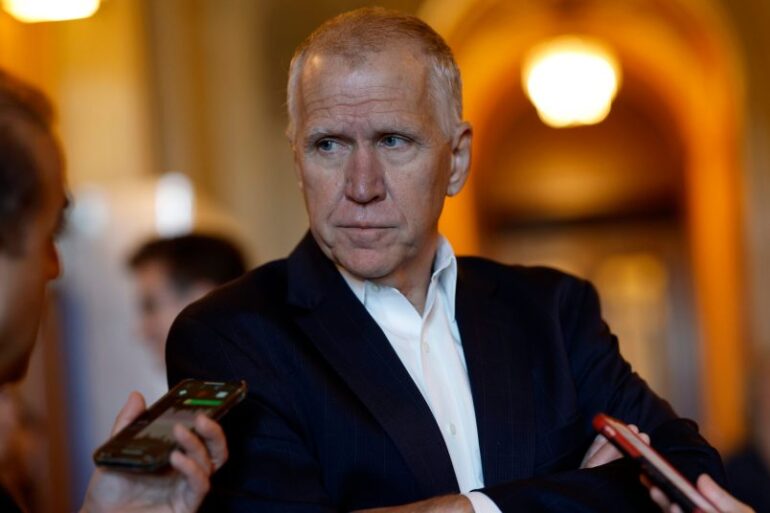
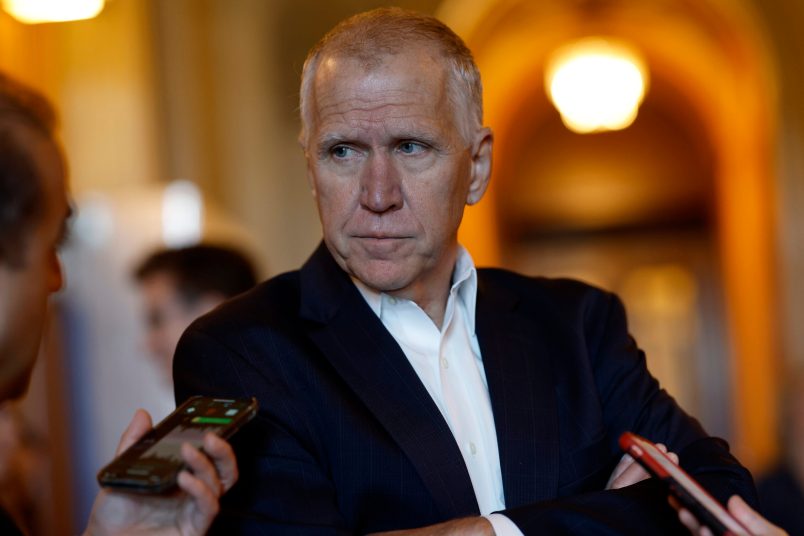
Congress dmca copyright reform hearing tillis coons big tech – Congress DMCA copyright reform hearing, Tillis, Coons, big tech – this is a complex issue with potential far-reaching consequences. The hearing scrutinizes the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and how it affects large tech companies. Senators Tillis and Coons are spearheading this reform, aiming to strike a balance between protecting creators and fostering innovation in the digital age.
The current state of copyright law is under intense pressure as big tech companies grapple with issues of content distribution, user-generated content, and potential copyright infringement. This reform will likely reshape the digital landscape, impacting everyone from artists and musicians to consumers and the tech giants themselves.
The hearing delves into specific concerns regarding copyright infringement and the need for updated legislation. Stakeholders, including artists, content creators, and big tech executives, will present their perspectives. This in-depth examination promises to reveal potential conflicts of interest and ethical dilemmas. The impact on big tech business models is significant, potentially leading to changes in how they operate.
The proposed reforms to the existing DMCA will be scrutinized for their benefits and drawbacks to various parties.
Background on the Hearing: Congress Dmca Copyright Reform Hearing Tillis Coons Big Tech
The recent DMCA copyright reform hearing, featuring Senators Tillis and Coons, highlights a long-standing debate about balancing copyright protection with innovation in the digital age. This hearing, and the ongoing efforts to modernize copyright law, reflect a complex interplay of interests between creators, content platforms, and the tech industry. The need for updates to the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) has been felt by many stakeholders, each with unique perspectives on how copyright law should adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape.
Historical Overview of DMCA Copyright Reform Efforts
Copyright law has been constantly evolving since its inception. The DMCA, enacted in 1998, represented a significant shift in how copyright was addressed in the digital environment. Prior to the DMCA, there was a lack of clear legal frameworks for dealing with copyright infringement online. Subsequent efforts to refine and adapt the DMCA have focused on specific areas of concern, such as online piracy, content takedown procedures, and the responsibilities of online platforms.
This ongoing evolution is crucial to maintaining a balanced approach to protecting intellectual property rights while fostering a thriving digital ecosystem.
Key Legislative Actors Involved
Senators Tillis and Coons, representing different perspectives within the political spectrum, are instrumental in shaping the current discourse on copyright reform. Senators play a critical role in drafting and advocating for legislation that affects copyright law, often representing various constituencies and stakeholders. Their involvement in the hearing signifies the importance of this issue in contemporary policy discussions.
Current State of Copyright Law and its Impact on Big Tech Companies
The current copyright law framework places significant responsibilities on big tech companies to address copyright infringement on their platforms. These companies act as intermediaries, hosting user-generated content, and are increasingly expected to proactively identify and remove infringing material. This often involves complex algorithms and manual review processes, posing challenges to efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, the liability framework for big tech companies under the DMCA has spurred debates on how to balance their role as platforms with their potential liability for content hosted by users.
Context Surrounding the Hearing
The hearing takes place amidst a growing number of controversies surrounding copyright in the digital realm. Recent trends in online piracy and the rise of streaming services have further complicated the landscape, raising concerns about the effectiveness of existing copyright protections. The evolving nature of creative expression in the digital age, including new forms of content creation and distribution, necessitates a careful consideration of the need for adaptation in copyright law.
Table: Timeline of Copyright Reform Efforts
| Time Period | Key Event | Impacted Party |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Initial enactment of the DMCA | Big Tech, Artists, Content Creators |
| 2000s-2010s | Incremental amendments and legal interpretations | Big Tech, Artists, Content Creators |
| 2020s | Renewed focus on copyright reform, including the current hearing | Big Tech, Artists, Content Creators, Streaming Services |
Issues Addressed in the Hearing
The recent congressional hearing on DMCA copyright reform, featuring Senators Tillis and Coons, delved into the complex relationship between copyright law, big tech platforms, and content creators. The debate highlighted the need for updated legislation to address the evolving digital landscape and balance the interests of all stakeholders. The hearing sought to define the precise scope of copyright protections in the digital age, particularly regarding user-generated content and platform liability.
Copyright Concerns Raised by Senators
Senators Tillis and Coons voiced concerns regarding the current copyright framework’s ability to adequately address the challenges presented by the rise of user-generated content and the prevalence of online platforms. They specifically questioned the balance between platform liability and the rights of content creators. The senators sought to find a middle ground that would protect creators’ intellectual property while not unduly burdening platforms with the responsibility for policing content.
A core concern was the perceived difficulty in enforcing copyright in the digital environment, leading to potential exploitation of content and hindering fair compensation for creators.
Potential Impacts on Big Tech Companies
The proposed changes could significantly impact big tech companies’ business models. If the legislation places greater emphasis on platform responsibility for copyright infringement, it could lead to increased costs and administrative burdens for these companies. They may be required to implement more robust systems for content identification, monitoring, and takedown procedures. Increased liability could also discourage the hosting of user-generated content, potentially altering the platforms’ functionality and user experience.
The impact on platform revenue streams, particularly those reliant on user-generated content, is also a key consideration. For example, YouTube’s reliance on user-uploaded videos would be affected by stricter enforcement.
Perspectives of Various Stakeholders
Content creators often advocate for stronger copyright protections to ensure fair compensation for their work. They may see the proposed changes as a positive step towards increased revenue streams and reduced piracy. Big tech companies, conversely, may express concerns about the financial implications of increased liability and the potential impact on user experience. They may argue that the existing framework is sufficient or that the proposed changes are overly burdensome.
Civil society groups and organizations representing smaller creators may support stronger protections for user-generated content, particularly for creators who lack the resources to monitor and address copyright infringement.
Potential Conflicts of Interest or Ethical Dilemmas
Potential conflicts of interest arise when balancing the interests of content creators and big tech companies. The proposed changes may place a disproportionate burden on smaller platforms, potentially stifling innovation and the growth of smaller content creators. Determining the appropriate level of platform liability is critical, as is ensuring that creators receive fair compensation without imposing unreasonable costs on platforms.
Further, the enforcement mechanisms must be designed to avoid bias or discrimination, ensuring fair application across all users.
Comparison of Proposed Changes to Existing Copyright Laws
| Aspect | Existing Copyright Laws | Proposed Changes | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform Liability | Generally limited; platforms not typically held liable for user-generated content infringement | Potentially increased platform liability for user-generated content infringement | Increased incentives for platforms to actively combat copyright infringement | Increased costs and administrative burden on platforms; potential chilling effect on user-generated content |
| Content Identification | Often relies on manual takedown requests; less efficient for large-scale infringement | Potentially mandates more sophisticated content identification technologies | More efficient and effective detection of infringement; improved copyright enforcement | Cost of implementation for platforms; potential for false positives; concerns about data privacy |
| Enforcement Mechanisms | Reliance on legal action; potentially slow and costly | Potential for streamlined dispute resolution processes | Faster and more accessible enforcement mechanisms; potentially lower costs for creators | Potential for disputes regarding enforcement procedures; concerns about due process |
Big Tech’s Role and Response

The ongoing debate surrounding copyright reform in the US Congress has significant implications for major technology companies, particularly concerning their role in facilitating and managing user-generated content. The proposed changes could fundamentally alter how these companies operate, impacting their revenue streams, legal liabilities, and long-term strategies. Big Tech companies are not simply passive recipients of these reforms; they are active participants in shaping the future of digital copyright.The proposed copyright reforms aim to create a more balanced ecosystem for both creators and users, but the practical application of these reforms will directly affect the day-to-day operations and business models of major technology platforms.
Big Tech companies will need to adapt their current practices to comply with the new regulations, potentially leading to changes in their policies, user experiences, and financial outcomes.
Predicted Impact on Big Tech Companies
The impact of copyright reform will vary significantly depending on the specific company and its business model. For example, companies like YouTube and Facebook, which heavily rely on user-generated content, face the most significant potential challenges. The need to better identify and manage copyrighted material will likely require substantial investment in new technology and personnel. Conversely, companies that primarily provide tools for creators may see opportunities to improve their offerings and attract new users.
Potential Legal and Financial Implications
Big Tech companies face significant legal and financial implications from the proposed changes. Increased liability for copyright infringement could lead to substantial legal costs and potential settlements. Moreover, the need to implement new systems and procedures for content moderation and takedown requests could require substantial financial investments. The potential for lawsuits from creators or rights holders will likely increase, and the costs associated with defending against these lawsuits could become substantial.
Big Tech Adaptation Strategies
Companies will likely employ various strategies to adapt to the changes. Investment in advanced technology for automated copyright identification and management is a likely response. This could include employing sophisticated algorithms and artificial intelligence to detect and flag potential copyright violations in real-time. Re-evaluation of current user agreements and content policies to reflect the new legal landscape will also be crucial.
Many companies may also seek to partner with rights management organizations to streamline the process of identifying and managing copyrighted content.
Table: Big Tech Company Analysis
| Company | Predicted Impact | Adaptation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| YouTube | Increased costs for content moderation, potential for more takedown requests, potential for increased liability for copyright infringement. Loss of revenue if creators leave due to issues with copyright enforcement. | Invest in advanced technology for copyright identification, implement stricter content policies, partner with rights management organizations to streamline takedown procedures. Implement measures to empower creators with tools for managing their own content. |
| Increased costs for content moderation, potential for more takedown requests, potential for increased liability for copyright infringement. Impacts on user engagement due to restrictions on content. | Invest in advanced technology for copyright identification, implement stricter content policies, partner with rights management organizations to streamline takedown procedures, potentially create a system for creators to easily claim ownership and enforce rights. | |
| Google (including Google Photos, Google Drive) | Potential legal challenges and liability for user-uploaded copyrighted material, increased costs for content management. | Implement stricter policies regarding uploaded content, improve content identification systems, provide tools to creators to facilitate proper copyright management. |
Potential Outcomes and Future Implications
The Copyright Reform hearing, particularly the focus on big tech’s role in content distribution, promises significant shifts in the digital landscape. The proposed reforms aim to address imbalances in power, but the practical implications for creators, consumers, and the tech giants are multifaceted and potentially disruptive. Understanding these potential outcomes is crucial for anticipating the future of online content.
Congress’s DMCA copyright reform hearing, featuring Tillis and Coons tackling big tech, is definitely interesting. It’s got me thinking about how sampling impacts music creation, though. For example, importing samples for Roland TR-8s Rhythm Performer, like 808s, Roland TR-8s Rhythm Performer import samples 808 , raises some copyright questions. Ultimately, the complexities of copyright reform in the digital age are still a hot topic, no matter the musical tools used.
Possible Outcomes of the Hearing
The hearing’s outcome hinges on the specific proposals adopted. If the reform focuses on clarifying copyright ownership in digital spaces, it could lead to greater accountability for platforms hosting user-generated content. Conversely, if the reform is overly prescriptive, it might stifle innovation and creativity. The hearing’s success will depend on finding a balance between protecting creators and fostering a dynamic online environment.
The outcome could also influence international copyright agreements and standards.
Long-Term Consequences for the Digital Ecosystem
The digital ecosystem, already complex, will likely face significant adjustments. Changes to copyright rules could alter how platforms operate, potentially leading to shifts in revenue models and user engagement. This, in turn, could impact the content creation and consumption landscape, forcing adaptation by all stakeholders. The influence of the hearing extends beyond the immediate implications for copyright reform, influencing future regulations concerning intellectual property in the digital sphere.
Potential Effects on Content Creation and Consumption
Content creators will likely see changes in their revenue streams and the legal frameworks surrounding their work. The ability of independent artists and creators to monetize their work on platforms might be affected. Consumers might experience variations in access to content and potentially higher costs for some digital services. The overall experience could be impacted by changes to content distribution methods, from the availability of certain types of content to the format in which it’s presented.
Prediction of Shaping Future Legislative Discussions, Congress dmca copyright reform hearing tillis coons big tech
The hearing’s outcome will undoubtedly shape future legislative discussions. The arguments presented and the reforms proposed will likely influence future debates on copyright, intellectual property, and the role of technology in society. The success of the reforms will be judged not only by their immediate effect but also by their capacity to stimulate future conversations and adaptations to a changing digital environment.
Potential Consequences on Different Groups
| Group | Potential Positive Consequences | Potential Negative Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Creators | Increased compensation, clearer ownership rights, better control over content usage. | Reduced flexibility in content distribution, higher compliance costs, possible decrease in platform access. |
| Consumers | Wider access to content, improved quality and innovation, reduced piracy. | Higher costs for digital services, restricted access to certain content, potential for censorship. |
| Big Tech Companies | Increased accountability, potential for improved content moderation, clear legal guidelines for content. | Increased operational costs, need for changes in platform policies, potential for legal challenges. |
This table illustrates the potential ramifications of the proposed copyright reforms on different stakeholders. The actual outcomes will likely involve a mix of positive and negative consequences for each group, and the extent of each will depend on the specific reforms adopted.
The Congress DMCA copyright reform hearing, featuring Tillis, Coons, and big tech, is definitely grabbing headlines. While that’s happening, it got me thinking about the whole iOS 11 Apple battery performance slow-down update saga. This update really highlighted how tech companies can sometimes make decisions that affect users without full transparency. Ultimately, back to the copyright reform hearing, it seems like the same underlying issues of power dynamics and user impact are at play in both situations.
Illustrative Examples and Case Studies
The digital landscape presents unique challenges for copyright enforcement. Big tech platforms, with their vast user bases and complex algorithms, often find themselves entangled in copyright disputes. Understanding these cases is crucial to evaluating the effectiveness of current laws and the need for reform. These examples illuminate the difficulties of enforcing copyright in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
Copyright Infringement on Streaming Services
Streaming services often face accusations of copyright infringement, particularly regarding music and film content. The sheer volume of content available on these platforms makes it challenging to ensure all material is licensed appropriately. Users may upload copyrighted material, and algorithms may inadvertently surface unlicensed content. The sheer scale of these platforms, coupled with the rapid pace of content distribution, often overwhelms traditional copyright enforcement mechanisms.
- One prominent example involves a streaming service accused of hosting numerous unauthorized uploads of copyrighted music videos. This case highlights the challenges in proactively identifying and removing infringing content on a large scale.
- Another instance involves a streaming service accused of facilitating the distribution of pirated films. This case demonstrates the difficulty in monitoring user activity and preventing the unauthorized sharing of copyrighted content, particularly in a system designed for user-generated uploads and content sharing.
Copyright Infringement on Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms are another area where copyright infringement is a significant concern. Users routinely share copyrighted material without permission, and platforms often struggle to address this issue effectively. Determining fair use and the intent of the user can be complex and difficult to adjudicate. The vast volume of content and the rapid pace of sharing make proactive enforcement challenging.
The congressional DMCA copyright reform hearing, featuring Tillis and Coons, and big tech’s involvement, has me thinking about innovation. My first 48 hours with the Galaxy S25 Ultra has me in awe here of its capabilities, making me wonder how tech advancements are influencing copyright discussions. Ultimately, the future of copyright reform is intertwined with the rapid pace of technological change.
- A case involving a social media platform hosting numerous unauthorized reposts of copyrighted articles highlights the issue of user-generated content and the difficulty of tracking down and removing unauthorized content in real time.
- Another instance involves a social media platform being accused of hosting copyrighted material without proper licensing agreements. This case demonstrates the challenges of establishing and enforcing licensing agreements for user-generated content on a global scale.
Court Decisions and Legal Precedents
Several court decisions have shaped the understanding of copyright enforcement in the digital age. These rulings have addressed issues like fair use, digital rights management (DRM), and the liability of online platforms.
| Case | Key Issues | Outcome | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| A&M Records, Inc. v. Napster | Peer-to-peer file-sharing and copyright infringement | Napster was found liable for copyright infringement. | Established a precedent for holding online platforms liable for copyright infringement. |
| MGM Studios, Inc. v. Grokster, Ltd. | Peer-to-peer file-sharing and copyright infringement | Grokster was found liable for inducement to copyright infringement. | Further clarified the liability of online platforms for facilitating copyright infringement. |
Visual Representation of Data

The copyright reform hearing illuminated the critical role of data visualization in understanding the complex issues at play. Effective graphics can distill complex financial and legal realities, making them accessible to a wider audience and fostering informed debate. This section presents visualizations to better grasp the financial ramifications of copyright infringement, the growth of big tech’s revenue streams, takedown requests, and the market valuation of content platforms.
Financial Impact of Copyright Infringement on Creators
Visualizing the financial impact of copyright infringement on creators is crucial for demonstrating the tangible losses incurred. A bar graph, for example, could display the estimated annual revenue lost by various categories of creators due to unauthorized use of their works. The graph’s vertical axis would represent the estimated revenue loss, and the horizontal axis would categorize the creators (e.g., musicians, filmmakers, writers).
Different shades or colors could differentiate between different types of infringement (e.g., streaming services, social media platforms). This visual representation would powerfully illustrate the cumulative financial impact of widespread copyright infringement, a key point in the hearing.
Growth of Big Tech Revenue Streams
Tracking the growth of big tech companies’ revenue streams provides valuable context. A line graph is an ideal choice for this purpose. The horizontal axis would represent the years (e.g., 2018-2023), and the vertical axis would display the revenue in billions of dollars. Different colored lines could represent different revenue streams, such as advertising, subscription fees, and in-app purchases.
This visual aids in understanding the exponential growth of these revenue streams and how they’ve potentially facilitated the scale of copyright infringement. For instance, a significant jump in revenue from streaming services might correspond to a surge in takedown requests.
Number of DMCA Takedown Requests by Big Tech Companies
Visualizing the number of DMCA takedown requests filed by big tech companies over time can reveal patterns and trends. A line graph, similar to the revenue stream chart, would illustrate the trend over the years. The horizontal axis would represent the years, and the vertical axis would display the number of takedown requests. Color-coding different tech companies would make comparisons clear.
This visualization could reveal whether there’s a correlation between the growth of big tech platforms and the increasing number of takedown requests, highlighting the need for better enforcement mechanisms.
Comparison of Market Value of Content Platforms
A bar graph effectively compares the market capitalization or valuation of various content platforms. The horizontal axis would list the different platforms (e.g., Netflix, YouTube, Spotify), and the vertical axis would represent the market value in billions of dollars. Different colors for each bar would allow for easy comparison. This visualization provides a clear picture of the significant economic clout of these companies and their potential responsibility in the copyright infringement landscape.
Such a visual aids in understanding the economic incentive behind these platforms’ behavior and the scale of the potential financial repercussions for creators.
Final Conclusion
The Congress DMCA copyright reform hearing, spearheaded by Senators Tillis and Coons, is poised to fundamentally alter the digital ecosystem. The future of content creation and consumption will likely be profoundly shaped by the outcome of this hearing. The potential consequences for content creators, big tech companies, and consumers are vast. Ultimately, the hearing aims to establish a more balanced and equitable framework for copyright in the digital age.
The implications of this reform will resonate for years to come, influencing future legislative discussions and potentially impacting the global digital economy.