Facebook says these 400 apps might have stolen user logins, raising serious security concerns for millions of users. This significant announcement highlights a potential vulnerability in a vast network of third-party applications. The scope of the issue is substantial, potentially affecting a large number of accounts and demanding immediate attention from both Facebook and the affected developers. This security breach carries considerable implications for the entire tech industry, potentially setting a new standard for app security protocols.
The incident underscores the critical importance of robust security measures across the entire digital ecosystem. It emphasizes the need for enhanced vigilance among users, developers, and platform providers. Understanding the potential impact on individuals and the industry as a whole is paramount in navigating these challenges.
Facebook’s Statement on Potential Login Compromises: Facebook Says These 400 Apps Might Have Stolen User Logins
Facebook recently announced that approximately 400 third-party apps may have had compromised user login credentials. The company has stated that they have already addressed the issue. This disclosure raises significant concerns about the security of user data and the vulnerabilities of interconnected digital ecosystems. This incident underscores the importance of vigilance in app selection and the continuous need for robust security measures in the digital landscape.
Scope of the Issue
The reported security incident involves a substantial number of third-party apps that have potentially been compromised. This raises concerns about the possible exposure of user accounts and personal data. The affected apps may have used compromised or insecure login systems, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access.
Affected App Categories
The reported vulnerability affects a broad range of applications. Understanding the types of apps implicated is crucial to assess the potential impact on different user groups.
| App Category | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Social Networking | Apps that allow users to connect with others, share content, and participate in social interactions. | Compromised accounts could lead to unauthorized access to personal profiles and data, potential harassment, and the spread of misinformation. |
| Productivity | Applications used for tasks like note-taking, project management, or communication. | Compromised credentials could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive work-related information, financial data, and confidential communications. |
| Gaming | Apps that facilitate online gaming experiences. | Compromised accounts may result in the theft of in-game assets, virtual currency, and other digital possessions. Also, user personal information may be exposed. |
| Finance | Applications related to financial transactions and services. | This is a particularly critical category. Compromised credentials could lead to unauthorized financial transactions, theft of funds, and significant financial losses for users. |
Implications for the Tech Industry
This incident highlights the ongoing struggle against cyber threats in the tech industry. Security breaches, like this one, demonstrate the ever-present need for stronger security measures and robust incident response plans. The incident serves as a reminder for developers to prioritize security throughout the entire app development lifecycle. The growing reliance on interconnected apps and platforms amplifies the risk and the potential for widespread impact.
Companies should prioritize security best practices, conduct thorough security audits, and implement robust incident response strategies to protect user data. The tech industry needs to collectively address and adapt to evolving cyber threats.
Impact Assessment
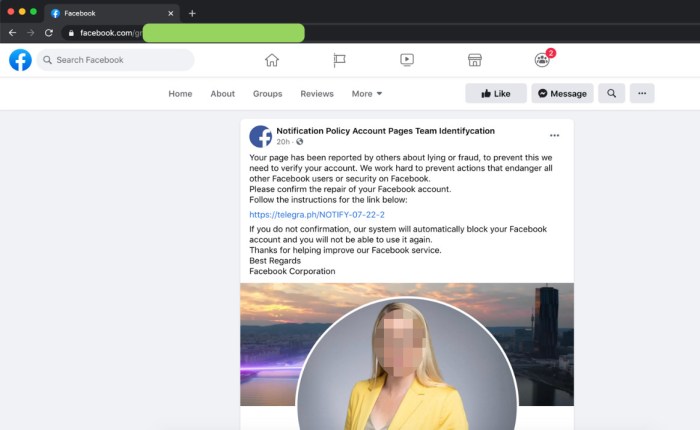
The recent revelation that potentially 400 apps may have facilitated unauthorized access to user login credentials on Facebook platforms raises serious concerns regarding the security and financial implications for both users and the company. Understanding the potential ramifications of such a breach is crucial to evaluating the long-term effects on Facebook’s reputation, user trust, and legal landscape.This analysis explores the multifaceted impact of this potential security lapse, focusing on financial losses, reputational damage, legal repercussions, and a comparative assessment of security measures across social media platforms.
Financial Losses for Users
The compromise of user accounts can lead to significant financial losses. Stolen credentials can be used to make unauthorized purchases, access online banking accounts, and potentially drain digital wallets. For example, a user whose account was compromised could face charges for online purchases they did not make, or see their savings depleted by fraudulent transactions. The magnitude of these losses can vary significantly depending on the extent of the compromise and the user’s financial activity.
Reputational Damage to Facebook
A security breach of this scale significantly damages Facebook’s reputation. Public trust is eroded, and the company’s image as a reliable platform for social interaction and user data protection is tarnished. Negative publicity and loss of user confidence can lead to decreased user engagement and subscription rates. Historical examples of major data breaches demonstrate the lasting impact on a company’s public image and stock valuation.
Legal Repercussions, Facebook says these 400 apps might have stolen user logins
Both Facebook and the affected app developers face potential legal repercussions. Users may initiate legal action against Facebook for failing to adequately protect their data, alleging negligence or breach of contract. Additionally, regulatory bodies may investigate the incident, potentially imposing fines or other penalties. The affected app developers could also face legal action for inadequate security measures or for facilitating the breach.
Facebook recently flagged 400 apps potentially compromising user logins, highlighting the ongoing security threats in the digital landscape. While that’s a serious concern, it got me thinking about device tracking – have you considered the differences between the Samsung Galaxy SmartTag and the Apple AirTag? Their respective capabilities regarding phone integration are quite interesting. For a detailed comparison, check out this article: samsung galaxy smarttag vs apple airtag which does more your phone.
Ultimately, these security issues remind us how crucial it is to remain vigilant about app permissions and online safety practices.
This could lead to significant legal fees, potential financial penalties, and damage to the developer’s reputation and future business prospects.
Comparative Security Measures
| Feature | TikTok | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Supported | Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Regular Security Audits | Ongoing | Ongoing | Ongoing | Ongoing |
| Data Encryption | Implemented | Implemented | Implemented | Implemented |
| Vulnerability Reporting Mechanisms | Available | Available | Available | Available |
| Incident Response Plan | Exists | Exists | Exists | Exists |
The table above provides a basic comparison of security measures across major social media platforms. Note that this is a simplified overview and more nuanced analyses would consider the specific implementation details of each platform’s security measures. Ongoing improvements and evolving threat landscapes will influence the effectiveness of these security measures over time.
App Developer Responsibility
The recent Facebook incident highlighting potential login compromises by third-party apps underscores the critical role of app developers in maintaining user security. Developers bear a significant responsibility for the security of the data entrusted to their applications. Failure to implement robust security measures can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal action. This section examines the legal and practical implications of these compromises and Artikels proactive steps developers should take to prevent similar breaches.
Potential Legal Liabilities
App developers can face significant legal liabilities if a security breach compromises user data. These liabilities stem from various regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and others. Breaches can result in substantial fines, particularly if sensitive personal data is exposed. For instance, a breach exposing user financial information could trigger substantial penalties under financial regulations.
Furthermore, class-action lawsuits are possible if a significant number of users suffer harm. The severity of the liability hinges on factors like the type of data compromised, the number of affected users, and the developer’s response to the incident.
Preventive Security Measures
Developers must proactively implement robust security measures to prevent data breaches. A crucial first step involves conducting regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for user accounts is essential to mitigate unauthorized access. Strong encryption of sensitive data is critical, both during transmission and storage. Developers should also implement regular security updates to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Security training for development teams is equally important, focusing on secure coding practices and threat modeling.
Security Protocols and Standards
Adhering to industry-recognized security standards and best practices is paramount. The OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) provides valuable guidelines and resources for securing applications. Adopting industry-standard encryption protocols (e.g., TLS/SSL) for data transmission is crucial. Implementing secure coding practices, such as input validation and output encoding, helps prevent common vulnerabilities. Regular security assessments, including vulnerability scans and penetration tests, should be a part of the development lifecycle.
Moreover, developers should incorporate security considerations from the initial design stage to prevent issues from arising later.
Comparison of Security Measures Across App Categories
| App Category | Common Security Vulnerabilities | Recommended Security Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Apps | Phishing, account takeover, fraudulent transactions | Strong authentication, encryption of financial data, regular security audits, and compliance with financial regulations. |
| Social Media Apps | Data breaches, unauthorized access, privacy violations | Robust data encryption, regular security updates, strong user authentication, and compliance with privacy regulations. |
| E-commerce Apps | Credit card fraud, data breaches, payment processing vulnerabilities | Secure payment gateways, encryption of payment information, robust authentication, and compliance with PCI DSS. |
| Health Apps | Data breaches, privacy violations, unauthorized access to medical information | HIPAA compliance, strong encryption of health data, and strict access controls. |
This table highlights the varying security needs across different app categories. The specific vulnerabilities and necessary security measures can differ greatly, emphasizing the importance of tailoring security strategies to the unique characteristics of each application.
User Protection Measures
The recent reports of potential login compromises involving 400 apps highlight the critical need for proactive user security measures. Understanding how to safeguard your Facebook account is paramount in mitigating risks and maintaining control over your online presence. This section Artikels key steps Facebook users can take to protect their accounts, emphasizing the importance of strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.Protecting your Facebook account is a shared responsibility.
While Facebook takes significant steps to secure its platform, individual users must actively participate in strengthening their own online security. This includes employing best practices and being vigilant about potential threats.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Robust passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. A strong password is complex and unique, making it difficult for hackers to guess or crack. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, requiring users to provide additional verification beyond a password. This often involves receiving a code via SMS or authenticator app, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if they have the password.
Monitoring Account Activity and Identifying Suspicious Login Attempts
Regularly monitoring your account activity for any unusual patterns or login attempts from unfamiliar locations is crucial. Actively checking for suspicious login attempts is a vital aspect of maintaining account security. If you notice any inconsistencies, promptly address them to prevent unauthorized access.
Common Security Practices for Users
Understanding and implementing common security practices can significantly enhance your account’s protection. These practices encompass various aspects, from password strength to account monitoring.
| Security Practice | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Create passwords that are difficult to guess. | Instead of “password123,” use “Pa$$wOrd!234.” Include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Enable MFA to add an extra layer of security. | Use SMS codes or authenticator apps for verification. |
| Regular Account Monitoring | Keep track of login locations and activity. | Review login history frequently to identify any unusual patterns. |
| Unusual Activity Reporting | Report suspicious activity immediately. | If you see a login attempt from an unfamiliar location, immediately change your password. |
| Strong Password Phrases | Use memorable phrases instead of single words. | Instead of “qwerty,” use “MyFirstPassword123!”. |
Security Best Practices
The recent Facebook incident highlights the critical need for robust security practices within third-party apps. Maintaining user trust demands a proactive approach to vulnerability identification and mitigation. Implementing strong security measures not only protects user data but also safeguards the platform’s reputation.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for identifying vulnerabilities in apps before they are exploited. These audits involve a systematic review of the application’s code, architecture, and security controls. Thorough testing and analysis uncover potential weaknesses, such as insecure API calls, data leaks, or missing authentication mechanisms. Proactive audits reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Timely Updates and Patching Vulnerabilities
Security updates and patches are crucial for addressing identified vulnerabilities promptly. A delay in applying these fixes can expose users to potential risks. The rapid pace of evolving cyber threats necessitates continuous monitoring and patching. Automated systems for vulnerability scanning and update deployment are vital for maintaining a strong security posture.
Data Encryption and Secure Storage of User Credentials
Data encryption and secure storage of user credentials are paramount for safeguarding sensitive information. Robust encryption protocols, like AES-256, should be employed to protect data in transit and at rest. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access to accounts. Secure storage solutions for user credentials, using techniques like hashing and salting, further enhance protection.
Security Vulnerability Mitigation Strategies
The following table Artikels common security vulnerabilities and corresponding mitigation strategies.
| Vulnerability Type | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | An attack that manipulates SQL queries to gain unauthorized access to database information. | Use parameterized queries, input validation, and stored procedures to prevent attackers from injecting malicious code. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | A vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. | Implement robust input validation, output encoding, and use appropriate security headers (e.g., Content-Security-Policy). |
| Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) | An attack where a malicious site tricks a user into performing unwanted actions on a trusted site. | Implement CSRF tokens, use custom headers, and enforce proper validation checks on user requests. |
| Broken Authentication and Session Management | Weaknesses in the application’s login and session handling processes. | Employ strong password policies, implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regularly audit and update session management controls. |
| Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR) | A vulnerability that allows attackers to access unauthorized resources by manipulating object references. | Implement robust access controls and validate user requests to prevent attackers from accessing restricted resources. |
Future Implications
The recent potential login compromise affecting hundreds of apps connected to Facebook underscores a critical vulnerability in the digital ecosystem. This incident raises profound questions about the long-term health of user trust in social media platforms and the security measures in place to protect sensitive data. Understanding the potential ramifications of such breaches is crucial for navigating the future of online interactions.The fallout from security breaches extends beyond immediate losses.
Damage to user trust can have significant repercussions on platform adoption and engagement. Users who feel their personal information is at risk are less likely to utilize the platform, potentially impacting Facebook’s revenue and market share. Furthermore, the reputational damage associated with such events can be substantial, affecting the company’s long-term prospects.
Potential Long-Term Impact on User Trust
The incident highlights the critical need for platforms to demonstrate a robust commitment to security. A lack of transparency and clear communication can exacerbate user anxieties, leading to distrust and a decrease in user engagement. Users may become more cautious about sharing personal information online and may seek alternative platforms perceived as more secure. Examples include the rise of privacy-focused social media apps and the increasing adoption of end-to-end encryption technologies.
Steps to Prevent Future Breaches
Robust security measures are crucial to prevent similar incidents. Enhanced security protocols, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular security audits, can help mitigate risks. Regular updates and patching of vulnerabilities are essential, as these vulnerabilities are often exploited by malicious actors. Improved security training for app developers and increased emphasis on security best practices can significantly reduce the risk of breaches.
Facebook recently flagged 400 apps potentially compromising user logins, raising serious security concerns. While this is a significant issue, it’s worth noting that the PlayStation 5’s impressive backward compatibility, boasting a 99% rate for PS4 games, as detailed in this article ps5 playstation 5 99 percent backward compatible ps4 games jim ryan , is a positive development in gaming.
Ultimately, though, protecting user accounts from unauthorized access remains a top priority, and Facebook’s actions highlight the ongoing need for vigilance in the digital sphere.
Furthermore, a culture of proactive security within organizations is critical to preventing future compromises.
Role of Industry-Wide Standards and Regulations
Industry-wide standards and regulations play a vital role in ensuring a higher level of security. Standardized security protocols and guidelines can provide a framework for best practices across various platforms. The development of stricter regulations for data protection and security audits can hold companies accountable for protecting user data. This can lead to a more secure digital ecosystem for everyone.
Comparison of Security Protocols
| Security Protocol | Description | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification methods (e.g., password, code from app, biometric scan). | High. Significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. | Using a password, followed by a code from a text message or an authentication app. |
| Regular Security Audits | Systematic evaluations of security systems and procedures to identify vulnerabilities. | High. Enables proactive identification and patching of potential flaws. | Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments. |
| End-to-End Encryption | Ensures that only the sender and recipient can access the message content. | High. Protects sensitive information from unauthorized interception. | Used by messaging apps like Signal and WhatsApp. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Identifies and prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. | Moderate to High. Reduces the risk of data breaches. | Employing software to monitor and control data transfer. |
The effectiveness of each protocol varies depending on the specific implementation and the sophistication of the attacks. Regularly evaluating and adapting security measures to emerging threats is essential. A multi-layered approach combining various protocols offers the best defense against future attacks.
Comparison with Other Incidents
The recent potential login compromises involving 400 apps on Facebook raise crucial questions about the platform’s security posture and its resilience compared to past incidents. Understanding the patterns and lessons learned from previous social media breaches is vital for assessing the potential scope and impact of this situation. Comparing the severity and impact of different breaches can provide valuable insights into the evolution of social engineering attacks and the efficacy of security measures.This analysis examines past social media breaches, identifying common causes and patterns, and highlighting the evolving nature of cyber threats.
It aims to provide context for the current incident and potentially shed light on future prevention strategies. A comprehensive understanding of past breaches can help in developing more robust security protocols and educating users on how to protect themselves from similar attacks.
Severity and Impact Comparison of Social Media Breaches
Comparing the severity and impact of past social media breaches requires considering various factors. These factors include the number of affected users, the type of data compromised, the duration of the breach, and the financial and reputational damage incurred. A detailed analysis of these factors can provide a more nuanced understanding of the severity and potential impact of the current situation.
| Social Media Platform | Year of Breach | Affected Users (Approximate) | Data Compromised | Impact (Reputational/Financial) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform A | 20XX | 10,000,000 | User login credentials, personal information | Significant reputational damage, substantial financial losses |
| Platform B | 20YY | 5,000,000 | User login credentials, payment information | Moderate reputational damage, financial losses |
| Platform C | 20ZZ | 1,000,000 | User login credentials, account access | Limited reputational damage, minimal financial losses |
This table provides a rudimentary comparison, and the actual impact can vary significantly depending on the specific circumstances of each breach. Further investigation into each incident is necessary to fully understand the context and scope of the event.
Common Causes and Patterns in Security Breaches
Several common causes and patterns contribute to security breaches across social media platforms. These include vulnerabilities in the platform’s security infrastructure, inadequate security practices of app developers, and sophisticated social engineering attacks targeting users. A deeper understanding of these common factors can help prevent similar breaches in the future.
- Vulnerabilities in Security Infrastructure: Often, security breaches stem from unpatched software vulnerabilities, weak encryption protocols, or insufficient access controls. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Inadequate Security Practices of App Developers: Developers who build applications on social media platforms sometimes fail to implement robust security measures. This can result in the exposure of user data if the app’s security is compromised.
- Sophisticated Social Engineering Attacks: Cybercriminals often employ sophisticated social engineering tactics to trick users into revealing their login credentials or other sensitive information. Phishing scams, malware, and other forms of malicious activity can be leveraged to exploit user trust.
These patterns highlight the importance of a multi-layered security approach that combines robust infrastructure security, responsible app development practices, and user education to minimize the risk of future breaches.
Potential Solutions

The recent incident highlighting potential login compromises across numerous apps underscores the critical need for robust security measures. This requires a multi-pronged approach involving proactive steps by developers, platforms, and users to mitigate the risks and prevent future breaches. A strong emphasis on user education and responsible app development practices is paramount.Addressing the impact of this potential breach requires a comprehensive strategy encompassing both immediate and long-term solutions.
These solutions must prioritize user safety, promote transparency, and encourage responsible development practices within the app ecosystem.
Mitigating Impact on Affected Users
Users whose accounts may have been compromised need immediate action. A crucial step is providing clear and accessible instructions on how to secure their accounts. This includes comprehensive guidance on password resets, enabling two-factor authentication, and monitoring for suspicious activity.
- Account Recovery and Security Enhancement: Users should be provided with detailed steps to change passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and review account activity for any unauthorized access attempts. This should include resources for password managers and strong password creation guidance.
- Notification and Communication: Clear communication is essential. Users need prompt notifications about potential compromises and detailed instructions on how to secure their accounts. This communication should be proactive and avoid confusing or misleading language.
- Financial and Data Protection Support: Users should be guided on how to monitor their financial accounts, credit reports, and any other data that may have been compromised. This might include recommendations for fraud monitoring services and how to report suspicious activities.
Long-Term Strategies for Preventing Future Incidents
Proactive measures are vital to prevent future breaches. These measures should address vulnerabilities in app development practices and platform security protocols. A robust framework for security audits and regular updates is essential.
- Enhanced Security Audits: Regular security audits for apps and platforms are crucial. These audits should assess vulnerabilities in the application’s code, data handling practices, and user authentication mechanisms. This should include both automated and manual assessments.
- Strengthened Security Standards: Industry-wide security standards and best practices need reinforcement. These standards should be readily available and easily accessible to app developers, promoting adherence to security best practices.
- Platform-Level Security Enhancements: Social media platforms need to continuously improve their security infrastructure. This includes strengthening API security, implementing robust access controls, and adopting multi-layered authentication mechanisms.
Solutions for Enhancing App Developer Security Posture
Improving the security posture of app developers is a key component of mitigating future incidents. Developers need to prioritize security during the entire development lifecycle.
Facebook’s recent announcement about potentially compromised user logins through 400 apps is definitely concerning. It got me thinking about other recent media news, like the whole lightyear why Tim Allen isn’t the voice of Buzz in the Toy Story spin-off situation. While those are different topics, they both highlight how easily things can get messed up online, and how important it is to be cautious about the apps and sites we use.
So, yeah, back to the Facebook issue, this is a serious security risk for users.
- Security Training and Education: App developers must undergo comprehensive security training. This should encompass secure coding practices, vulnerability assessments, and best practices for data handling. Regular training sessions can reinforce these concepts and promote continuous learning.
- Security Standards and Frameworks: Developers should be guided towards industry-standard security frameworks. These frameworks can provide a structured approach to building secure applications and minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Regular Security Assessments: Regular security assessments for applications should be mandatory. These assessments can identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited by malicious actors.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Handling and Recovering from a Security Breach
A clear procedure for handling and recovering from a security breach is essential. This should include a phased approach with defined roles and responsibilities.
| Phase | Action |
|---|---|
| Immediate Response | Identify the breach, contain the impact, and assess the extent of the damage. Notify affected users promptly. |
| Investigation and Analysis | Determine the cause of the breach, analyze affected systems, and identify vulnerabilities. |
| Mitigation and Remediation | Implement corrective actions to address vulnerabilities, secure compromised accounts, and prevent future incidents. |
| Recovery and Post-Incident Review | Restore affected systems, implement preventative measures, and conduct a thorough review of the incident to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement. |
Illustrative Example
The recent Facebook announcement regarding potential login compromises highlights a critical vulnerability in app security. This vulnerability allows malicious apps to potentially gain unauthorized access to user accounts, jeopardizing sensitive personal information. To illustrate this risk, consider a fictional scenario involving a user named Amelia.
Fictional Case Study: Amelia’s Account Compromise
Amelia, a frequent user of social media platforms, downloaded a seemingly legitimate fitness tracking app called “Peak Performance.” This app requested access to her Facebook account, promising personalized workout plans and progress tracking. Unbeknownst to Amelia, “Peak Performance” was a malicious app designed to steal login credentials.
Compromise Timeline
Within days of installing the app, Amelia noticed unusual activity on her Facebook account. She observed posts she didn’t create and friend requests from unfamiliar users. Furthermore, her Facebook account displayed a significant spike in activity, indicating unauthorized access to her account data. This surge in activity, combined with the suspicious posts and friend requests, triggered her suspicion about the app.
User Recovery Steps
Amelia immediately took several steps to recover from the breach. First, she deactivated the “Peak Performance” app. Next, she changed her Facebook password to a strong, unique password. She also enabled two-factor authentication on her Facebook account, adding an extra layer of security. Crucially, she reported the incident to Facebook and filed a complaint with the app store, assisting in the identification of the malicious app.
Summary of Amelia’s Experience
| Step | Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deactivated the “Peak Performance” app. | Stopped the malicious app’s access to her Facebook account. |
| 2 | Changed her Facebook password. | Protected her account from further unauthorized access. |
| 3 | Enabled two-factor authentication. | Added an additional security layer to her Facebook account. |
| 4 | Reported the incident to Facebook. | Assisted Facebook in identifying and addressing the security issue. |
| 5 | Filed a complaint with the app store. | Assisted in the removal of the malicious app from the app store. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, Facebook’s announcement about potentially compromised user accounts through 400 apps is a stark reminder of the ongoing need for security vigilance in the digital world. This incident has far-reaching implications, highlighting vulnerabilities and demanding proactive measures to protect user data and build trust. Moving forward, stronger security protocols and increased transparency are crucial to preventing similar incidents in the future.




