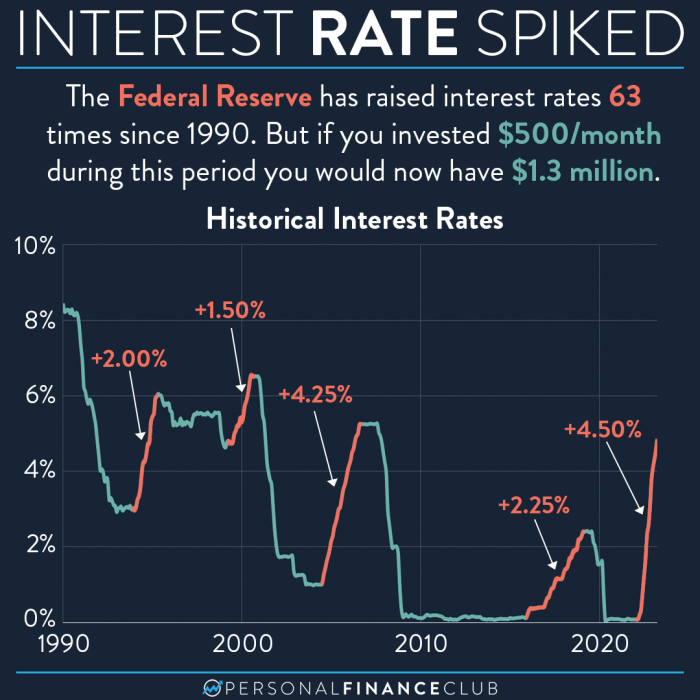
Fed expected to lower interest rates tomorrow with next year in limbo. This anticipated move by the Federal Reserve is poised to trigger a ripple effect throughout the economy. Current economic conditions, historical precedent, and potential market reactions are all factors influencing this decision. While a rate cut tomorrow may seem straightforward, the uncertainty surrounding 2024 interest rate adjustments adds another layer of complexity.
This deeper dive will explore the possible impacts on various sectors, from housing to investment strategies, while considering global factors that might shape the future direction of interest rates.
The Federal Reserve’s decision tomorrow is expected to lower interest rates. Several factors are driving this anticipation. Economic indicators suggest a need for stimulus to support the economy. Previous rate adjustments provide a historical context for analyzing potential impacts. This analysis will delve into the anticipated market reactions, considering how stocks, bonds, and currencies might respond.
A key element is the uncertainty surrounding next year’s interest rate adjustments, considering the potential influence of global events.
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decision Tomorrow: Fed Expected To Lower Interest Rates Tomorrow With Next Year In Limbo
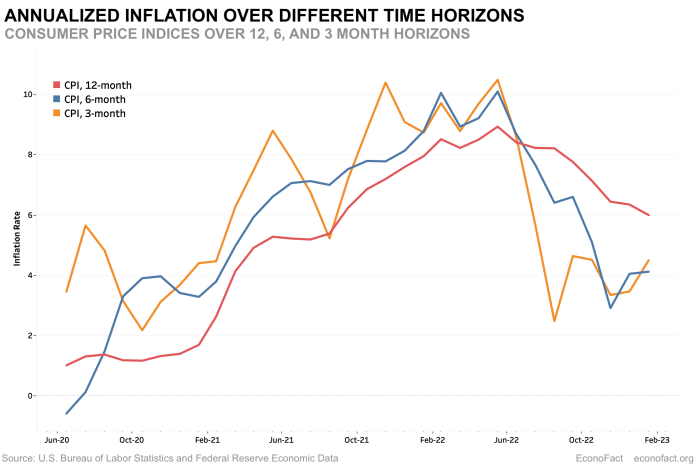
The Federal Reserve’s decision on interest rates tomorrow holds significant weight, impacting everything from the stock market to consumer spending. While the anticipated rate cut is well-telegraphed, the potential ripple effects on various economic sectors are still being analyzed. The global economic landscape, with ongoing geopolitical uncertainties and lingering inflation concerns, adds another layer of complexity to the situation.
Tomorrow’s announcement will be crucial for understanding the Fed’s outlook on the economy and its strategy for the coming months.The current economic climate presents a mix of challenges and opportunities. Inflation, though showing signs of easing, remains a concern for policymakers. Simultaneously, growth indicators show some signs of weakening, potentially signaling a need for a more accommodative monetary policy.
The Federal Reserve will weigh these factors against potential risks, like the possibility of a sharper slowdown or a resurgence in inflationary pressures. The Fed’s decision will directly affect the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers.
Current Economic Conditions Influencing the Fed’s Decision
Recent economic data, including consumer spending reports, employment figures, and inflation rates, are crucial in shaping the Fed’s perspective. The overall trend in these indicators will guide the Fed’s assessment of whether a rate cut is appropriate. For instance, a persistent decline in consumer confidence could influence the Fed’s decision towards a more cautious approach. Conversely, signs of robust economic growth might prompt a different course of action.
These indicators paint a complex picture, suggesting the Fed will likely consider a nuanced approach to its rate adjustments.
Historical Precedent of Interest Rate Adjustments
The Federal Reserve has a history of adjusting interest rates to manage economic conditions. These adjustments have had significant impacts on various sectors, influencing borrowing costs and investment decisions. For instance, during periods of economic recession, the Fed has typically lowered interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending. Conversely, during periods of high inflation, the Fed has often raised interest rates to curb demand and cool down the economy.
Analyzing past instances of rate adjustments, and the subsequent economic outcomes, can provide valuable insights into the potential impact of tomorrow’s decision.
Potential Market Reactions to the Anticipated Rate Cut
The anticipated rate cut will likely generate specific responses across various financial markets. Stocks could potentially rise on expectations of increased investment and economic activity. Bond yields are also expected to decrease, as investors seek a lower-risk return. Currency markets will be closely monitored, as a rate cut might influence the exchange rate. The degree of market reaction will depend on the overall economic outlook and the strength of the Fed’s communication regarding the future of interest rates.
Comparison of Recent Interest Rate Adjustments with Corresponding Economic Indicators
| Date of Rate Adjustment | Interest Rate Change | Key Economic Indicator (e.g., Inflation Rate) | Economic Impact (e.g., Consumer Spending) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-Q4 | 0.5% increase | High Inflation (8.1%) | Slowed consumer spending, increased borrowing costs |
| 2023-Q1 | 0.25% increase | Inflation cooling (7.5%) | Moderate impact on consumer spending |
| Anticipated (Tomorrow) | 0.25% decrease | Potential softening in growth, moderate inflation | Potential boost to consumer spending and borrowing |
Potential Impact of a Rate Cut on Various Sectors
A rate cut can have various effects on different economic sectors. For example, the housing sector might experience increased demand for mortgages and home purchases due to lower borrowing costs. Consumer spending could also increase as borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating retail and related industries. Small businesses, often heavily reliant on loans and investments, could see a positive impact as credit becomes more accessible.
However, potential negative impacts include the possibility of decreased return on investments and increased risk for lenders.
Uncertainties Surrounding Next Year’s Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve’s decision tomorrow regarding interest rates sets the stage for a period of significant uncertainty surrounding future adjustments. While the immediate future appears clearer, the path for the coming year is shrouded in ambiguity, influenced by a multitude of interconnected global and domestic factors. Understanding these uncertainties is crucial for investors navigating the economic landscape.The upcoming year promises to be a complex period for interest rate policy.
Various economic forecasts paint divergent pictures, highlighting the difficulties in accurately predicting future economic trends. Global events and domestic economic data will continue to shape the Fed’s decisions, adding layers of complexity to the equation. This makes understanding the factors driving this uncertainty paramount for informed investment strategies.
Factors Contributing to Uncertainty
Several factors contribute to the uncertainty surrounding interest rate adjustments in the coming year. These include evolving economic data, global geopolitical tensions, and differing economic forecasts. The interplay of these factors creates a dynamic environment that makes precise predictions challenging.
- Evolving Economic Data: Recent economic data, such as inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth, will continue to play a significant role in shaping the Fed’s decisions. The direction and magnitude of these indicators will heavily influence the Fed’s stance on interest rates. For instance, persistent high inflation could prompt further rate hikes, while a significant downturn in economic activity could lead to a pause or even a reduction in rates.
- Global Geopolitical Tensions: International conflicts, trade disputes, and other geopolitical events can significantly impact global economic conditions. These events can disrupt supply chains, affect commodity prices, and create uncertainty about future economic growth. For example, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has influenced global energy markets and commodity prices, impacting inflation and potentially influencing the Fed’s rate decisions.
- Differing Economic Forecasts: Various economic institutions and analysts offer contrasting forecasts for the coming year. Some predict continued economic growth, while others anticipate a recession. These divergent forecasts highlight the inherent difficulty in accurately predicting the future economic trajectory, thereby impacting interest rate adjustments.
Comparison of Economic Forecasts
Different economic forecasting models and institutions often present divergent views on the future economic landscape. The varying predictions reflect the inherent complexities and uncertainties surrounding global economic conditions.
- Contrasting Outlooks: Some forecasts project sustained economic growth, pointing to a healthy labor market and robust consumer spending. Other forecasts anticipate a potential recession, citing rising interest rates, high inflation, and global uncertainties. This contrast highlights the difficulty in pinpointing a single accurate economic trajectory.
- Impact on Rate Adjustments: The divergence in economic forecasts directly influences the expected interest rate adjustments. Sustained growth might lead to further interest rate increases, while a predicted recession could result in rate cuts. The impact on investment strategies is notable, depending on the predicted outcome.
Impact of Global Events
Global events, including geopolitical tensions and international trade conflicts, have significant implications for future interest rate decisions. These events can disrupt supply chains, influence commodity prices, and affect investor confidence.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Geopolitical tensions and trade conflicts can disrupt global supply chains, leading to higher prices and reduced production. These disruptions can impact inflation and influence the Fed’s response.
- Commodity Price Volatility: Fluctuations in commodity prices, particularly energy and raw materials, are directly linked to global events and economic conditions. These price fluctuations affect inflation and, in turn, influence the Fed’s interest rate decisions.
- Investor Confidence: Uncertainty stemming from global events can negatively impact investor confidence, leading to decreased investment and economic activity. This can further influence the Fed’s decision-making process regarding interest rates.
Investor Challenges and Opportunities
A period of economic uncertainty presents both challenges and opportunities for investors. Investors need to adapt their strategies to navigate these unpredictable market conditions.
- Adapting Strategies: Investors need to adapt their strategies to the current economic conditions. Diversification, risk management, and thorough research are essential in this period of uncertainty.
- Identifying Opportunities: Periods of uncertainty can also create investment opportunities. Investors who carefully analyze the market and identify undervalued assets can capitalize on these opportunities.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and Fed’s Response
The Federal Reserve’s historical response to economic indicators provides insights into potential future actions. This correlation helps investors understand the potential impact of economic trends on interest rate adjustments.
| Economic Indicator | Historical Fed Response |
|---|---|
| High Inflation | Increased interest rates to curb inflation |
| Low Inflation | Lowered interest rates to stimulate economic growth |
| High Unemployment | Lowered interest rates to stimulate employment |
| Strong GDP Growth | Potential for increased interest rates to manage inflation |
Impact on Different Sectors of the Economy
The Federal Reserve’s potential interest rate cut tomorrow carries significant implications across various sectors. While the immediate impact might be muted due to the uncertainty surrounding next year’s rate trajectory, the long-term effects on everything from housing affordability to business investment could be profound. Understanding these impacts is crucial for investors, consumers, and businesses alike.
The Fed is expected to lower interest rates tomorrow, leaving next year’s economic outlook a bit uncertain. This move, while seemingly positive for some sectors, could also be impacted by recent developments like the California governor’s veto of the self-driving truck safety driver bill, Assembly Bill 316, concerning autonomous vehicles. This veto highlights the complex interplay between technological advancements and regulatory frameworks, potentially influencing investment and, consequently, the overall trajectory of interest rate adjustments in the coming year.
It’s all a bit of a puzzle, isn’t it? The Fed’s decision tomorrow could be interesting to watch, given the broader context.
Impact on the Housing Market
Lower interest rates typically lead to more affordable mortgages, boosting demand for housing. Borrowing becomes cheaper, making homeownership more accessible. This can lead to increased home sales and rising property values. However, the current market’s overall health, including existing inventory levels and inflation, will play a crucial role in how the housing market responds. For example, if the market is already saturated, a rate cut might not significantly stimulate demand.
A recent study by the National Association of Realtors indicates that buyer demand is influenced not just by rates but also by affordability and economic confidence.
Effect on Consumer Spending and Borrowing Behavior
Lower interest rates often translate to lower borrowing costs for consumers. This can stimulate consumer spending, as individuals have more disposable income or feel more comfortable taking on debt for purchases like cars or appliances. Credit card interest rates may also decrease, further encouraging spending. However, the impact depends heavily on consumer confidence and the overall economic outlook.
The Fed is expected to lower interest rates tomorrow, but next year’s economic outlook remains uncertain. While waiting for the Fed’s decision, I’ve been diving into the Final Fantasy 15 Platinum Demo on PS4 and Xbox One. It’s pretty awesome, and a great distraction from the economic anxieties, giving me some much-needed escapism. The demo definitely holds up well against the broader interest rate concerns, but I’m still keeping a close eye on the overall economic picture, and wondering how the Fed’s decision tomorrow will impact things further.
final fantasy 15 platinum demo ps4 xbox one. Hopefully, everything will be smooth sailing soon!
A recent report from the Bureau of Economic Analysis highlighted a correlation between consumer confidence and discretionary spending, indicating that consumer sentiment significantly affects spending decisions.
Influence on Businesses, Especially SMEs
Lower interest rates can encourage businesses, particularly SMEs, to borrow and invest more in expansion, equipment, and new ventures. Access to cheaper capital can boost productivity and job creation. However, businesses may be hesitant to invest if the economic outlook is uncertain, or if other factors like supply chain disruptions or labor shortages persist. Many small businesses have historically been more vulnerable to economic downturns, and this has often been amplified by the current economic situation.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw many small businesses struggle to access capital.
The Fed is expected to lower interest rates tomorrow, but next year’s outlook remains uncertain. This potential rate cut, while seemingly positive for the economy, might be overshadowed by the ongoing complexities of Brexit’s impact on science research collaborations between the UK and EU. For example, brexit impact science research uk eu funding collaboration is creating a ripple effect that could potentially impact funding opportunities and research partnerships, adding another layer of uncertainty to the already complex economic picture.
Ultimately, tomorrow’s rate cut might be a small victory in a much larger, and potentially challenging, economic landscape.
Potential Influence on Financial Markets and Investor Sentiment
Lower interest rates can often lead to an increase in the price of stocks and bonds, as investors seek higher returns. The expectation of future economic growth due to the rate cut often fuels this optimistic sentiment. However, if investors anticipate the rate cut to be short-lived or if there are other macroeconomic concerns, the effect on financial markets may be less pronounced.
For instance, the 2020 pandemic saw fluctuating investor sentiment and market volatility.
Table: Potential Sector Reactions to a Rate Cut
| Sector | Potential Reaction | Factors Influencing Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | Increased demand, potentially rising prices | Mortgage affordability, existing inventory, overall economic outlook |
| Consumer Spending | Potential increase | Consumer confidence, disposable income, borrowing costs |
| Businesses (SMEs) | Potential increase in investment and expansion | Economic outlook, access to capital, other macroeconomic factors |
| Financial Markets | Potential increase in stock and bond prices | Investor sentiment, expectation of future growth |
Historical Context and Comparisons
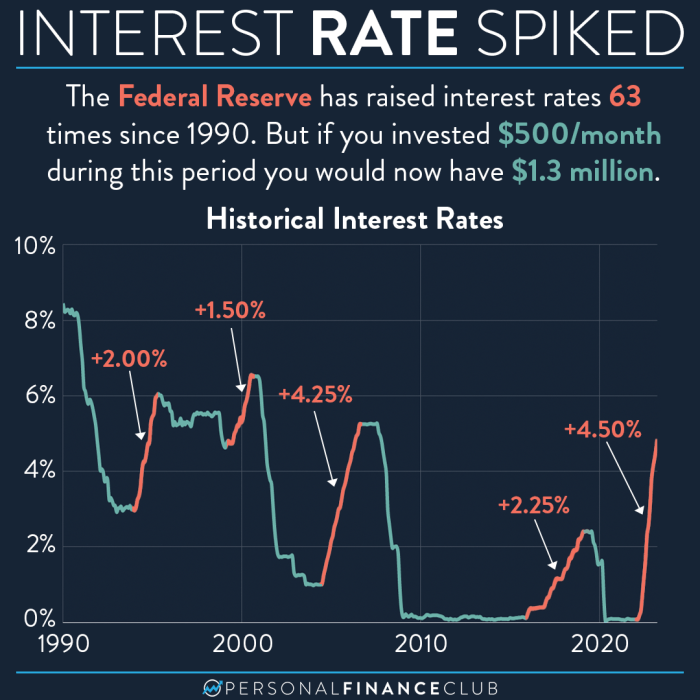
The Federal Reserve’s decision to potentially lower interest rates tomorrow marks a significant moment in the ongoing economic landscape. Understanding the historical context surrounding such adjustments is crucial to assessing the potential impact. Previous interest rate adjustments have had far-reaching effects on various sectors, from consumer spending to investment activity. Analyzing past trends can illuminate potential outcomes of the upcoming decision.
Historical Overview of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Adjustments
The Federal Reserve has a long history of adjusting interest rates in response to economic fluctuations. These adjustments aim to maintain price stability and full employment. Notable events include the Volcker disinflation of the 1980s, the Greenspan era of the late 20th century, and the post-2008 financial crisis period. Each period presented unique economic challenges and the Fed’s response varied accordingly.
The complexity of the current economic situation makes comparison to past events nuanced.
Key Events and Outcomes
Numerous instances of interest rate adjustments have shaped the economic trajectory of the United States. The 1980s saw Paul Volcker’s aggressive interest rate hikes combat inflation, leading to a recession but ultimately stabilizing prices. The Greenspan era, marked by periods of both rate increases and decreases, saw the economy navigate technological advancements and global market integration. More recently, the post-2008 crisis period witnessed significant rate cuts to stimulate economic growth, followed by gradual increases as the recovery progressed.
Each event illustrates the intricate relationship between monetary policy and economic performance.
Comparison to Current Economic Climate
The current economic climate differs from previous periods in several key aspects. Inflation rates, while still present, have moderated compared to the 1980s. Global uncertainty and geopolitical tensions add another layer of complexity. The current labor market, while showing some signs of cooling, remains relatively robust. Comparing these elements to past adjustments requires careful consideration of these differing factors.
Potential Consequences of the Fed’s Decision
The Fed’s decision to lower interest rates tomorrow could have various consequences. Lower rates could stimulate borrowing and spending, potentially boosting economic growth. However, lower rates could also lead to increased inflation if not carefully managed. Conversely, maintaining or increasing rates could curb inflation but potentially hinder economic growth. The unpredictable nature of the global economy makes precise predictions difficult.
Table: Economic Indicators During Similar Interest Rate Adjustments
| Economic Indicator | 1980s Volcker Era | Post-2008 Crisis | Potential Current Outcome (hypothetical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | High (double-digit) | Elevated, then gradually declining | Moderating, but with potential for future spikes |
| Unemployment Rate | Increased | Decreased | Potentially stabilizing or slightly increasing |
| GDP Growth Rate | Negative | Positive, but variable | Moderate positive growth |
| Consumer Confidence | Declining | Variable | Likely to fluctuate depending on the rate decision |
Market Implications and Predictions
The anticipated interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve tomorrow presents a complex set of implications for various asset classes and investment strategies. While the move is generally seen as supportive of economic growth, the uncertainty surrounding next year’s rate path adds a layer of complexity to market reactions. Investors are now carefully assessing the potential impact on stocks, bonds, and real estate, and are adjusting their portfolios accordingly.
Potential Impact on Asset Classes
The interest rate cut is likely to have a ripple effect across different asset classes. Lower rates typically boost demand for riskier assets like stocks, as borrowing costs decrease and investment opportunities seem more attractive. Conversely, bond yields are expected to fall, as the attractiveness of existing bonds diminishes with lower returns on offer. Real estate could see increased demand, as mortgages become cheaper, potentially driving up prices in certain sectors.
However, the overall effect will depend on various economic factors and investor sentiment.
Investor Reactions and Market Volatility
Investors are likely to react to the rate cut with varying degrees of enthusiasm. Some may see it as a positive signal for economic recovery, driving stock prices higher. Others may remain cautious, given the uncertainty surrounding future interest rate movements. This divergence in opinions could lead to periods of increased market volatility. The reaction will be influenced by the specific details of the Fed’s statement and the overall economic outlook.
Historically, interest rate cuts have been followed by mixed reactions in the market, with periods of both gains and losses.
Investment Strategies, Fed expected to lower interest rates tomorrow with next year in limbo
The anticipated interest rate cut creates both opportunities and risks for various investment strategies. A shift towards growth stocks could be a potential strategy, given the reduced cost of borrowing. Conversely, investors might consider repositioning their portfolios to mitigate potential losses in bond yields. It is crucial to consider the potential impact on different sectors and adjust investment strategies accordingly.
Impact on Different Market Segments
The impact of the rate cut will likely vary among different market segments. Retail investors, with their diverse investment goals and risk tolerances, may react to the news in different ways. Institutional investors, with their large portfolios and sophisticated investment strategies, are likely to adopt more analytical approaches, analyzing the Fed’s communication and future expectations. The rate cut’s effect on these segments depends on how each perceives the future path of interest rates.
Potential Investment Strategies Table
| Investment Strategy | Rationale | Potential Opportunities | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth Stock Focus | Lower rates stimulate economic growth, boosting company earnings and stock valuations. | Higher potential returns compared to other asset classes. | Increased volatility, potential for sharp corrections if economic outlook deteriorates. |
| Bond Portfolio Adjustment | Lower rates decrease bond yields, making current bonds less attractive. | Rebalancing to newer bonds with higher yields can provide a hedge against falling yields. | Potential for losses if bond prices don’t appreciate as expected. |
| Real Estate Investment | Lower mortgage rates increase affordability and drive demand for housing. | Increased demand can drive up real estate prices. | Potential for overvaluation and price corrections if the economic outlook changes. |
| Defensive Investment Strategy | Focus on low-volatility assets, such as high-quality bonds and dividend stocks. | Protection against market volatility and potential losses. | Potential for lower returns compared to more aggressive strategies. |
Final Wrap-Up
The Fed’s potential rate cut tomorrow, coupled with the uncertainty surrounding 2024, presents both opportunities and risks for investors and the economy as a whole. While a lower rate might stimulate growth in certain sectors, such as housing, the unpredictable nature of next year’s economic landscape necessitates careful consideration of potential risks. Understanding the historical context of similar rate adjustments and the potential impact on various economic sectors will help navigate this period of uncertainty.
Ultimately, the Fed’s decision tomorrow and the subsequent trajectory of interest rates in 2024 will be critical factors in shaping the economic landscape.