Android privacy sandbox Google Apple Facebook ad tracking is a complex issue, but one with huge implications for the future of mobile advertising. This initiative from Google is designed to change the way apps and websites track users, impacting everything from the ads you see to the performance of your favorite apps. This in-depth look examines the key players, exploring their approaches and potential impacts on user experience and the broader tech landscape.
The Android Privacy Sandbox aims to create a more privacy-respecting environment for mobile users. It seeks to balance the needs of advertisers with the growing concern over user data collection. This intricate system involves several key components and technologies, which will be explored in detail, alongside the potential benefits and drawbacks. Different approaches to ad tracking will be examined, from Google’s strategy to Apple’s privacy-focused approach and Facebook’s ad tracking practices.
Android Privacy Sandbox Overview: Android Privacy Sandbox Google Apple Facebook Ad Tracking
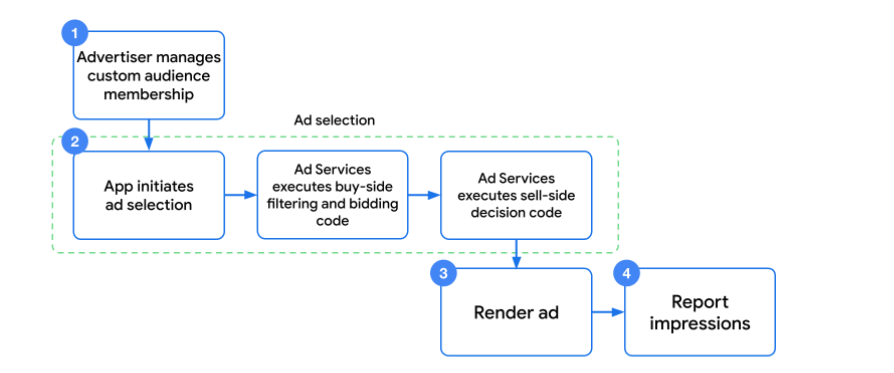
The Android Privacy Sandbox is Google’s initiative to improve user privacy while maintaining the functionality of personalized advertising on the Android platform. It aims to create a more privacy-respecting environment for users without sacrificing the value proposition of targeted advertising for developers. This shift reflects a broader societal trend toward increased user awareness and demand for control over their personal data.The Android Privacy Sandbox is designed to replace the reliance on direct user tracking with privacy-preserving alternatives.
This is achieved through a range of technical solutions that allow advertisers and developers to still gather valuable insights into user behavior without compromising user privacy. The sandbox approach allows for experimentation and gradual adoption of these new methods, providing a controlled environment for innovation and refinement.
Goals and Objectives of the Android Privacy Sandbox
The primary goal of the Android Privacy Sandbox is to empower users with greater control over their data while enabling developers to maintain a valuable ecosystem of advertising and personalization. Key objectives include: enabling effective advertising without intrusive tracking; ensuring a balance between user privacy and business interests; and fostering innovation in privacy-preserving technologies. It aims to achieve this by creating a more transparent and user-friendly advertising environment.
Google, Apple, and Facebook’s ad tracking practices within Android’s privacy sandbox are constantly evolving. Protecting user data is paramount, but the complexity of these systems is sometimes overwhelming. A recent development in phone safety, the mobile airbag drop phone, mobile airbag drop phone , aims to provide a new layer of protection. Ultimately, though, the real solution lies in a more transparent and user-friendly approach to ad tracking within the Android privacy sandbox.
Key Components and Technologies
The Android Privacy Sandbox leverages several key components and technologies to achieve its goals. These include federated learning of cohorts (FLoC), privacy-preserving APIs, and enhanced reporting tools. These technologies provide a framework for advertisers and developers to access user data without directly tracking individual users.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The Android Privacy Sandbox presents a potential shift towards a more privacy-conscious advertising ecosystem. Benefits include increased user privacy, a more robust advertising ecosystem for developers, and a more user-friendly advertising environment. However, drawbacks include the potential for reduced advertising effectiveness, the need for developers to adapt to new technologies, and the possibility of unintended consequences.
Approaches to Address Ad Tracking, Android privacy sandbox google apple facebook ad tracking
The Android Privacy Sandbox utilizes various approaches to address ad tracking. These approaches aim to strike a balance between personalized advertising and user privacy.
| Approach Name | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federated Learning of Cohorts (FLoC) | FLoC groups users into cohorts based on browsing behavior. Advertisers can target ads to cohorts without identifying individual users. | Preserves user privacy by not tracking individual users. Enables advertisers to target ads to broader segments. | May result in less targeted advertising. Accuracy of cohort representation may vary. |
| Privacy-Preserving APIs | These APIs provide access to user data without requiring direct tracking. These APIs offer various ways to analyze user behavior and preferences. | Enables access to user data while respecting user privacy. Provides flexibility for developers to tailor advertising strategies. | Requires developers to adapt to new APIs. Learning curve for implementation. |
| Enhanced Reporting Tools | Provides aggregated data on user behavior without individual user identifiers. This data can be used to understand overall trends and patterns. | Allows for analysis of broader user trends without violating privacy. Useful for understanding user engagement. | Limited insights into individual user behavior. May not be as effective for highly targeted advertising. |
Google’s Role in Ad Tracking

Google plays a significant role in ad tracking on Android devices, acting as both a facilitator and a participant in the process. Their extensive reach within the mobile ecosystem gives them unique insights into user behavior, which is crucial for the targeted advertising model. This influence, however, has raised concerns about user privacy and the potential for data misuse.Google’s strategies for ad tracking within the Android Privacy Sandbox center on developing alternative methods that respect user privacy while still enabling relevant and effective advertising.
These methods focus on federated learning of cohorts and other privacy-preserving techniques, aiming to balance the needs of advertisers with user rights. The Sandbox’s goal is to ensure that advertisers can still target users effectively, but without collecting personally identifiable information.
Google’s Strategies for Ad Tracking within the Android Privacy Sandbox
Google’s strategies within the Android Privacy Sandbox emphasize a shift away from reliance on individual user data. They aim to aggregate user data in a way that maintains user anonymity while providing advertisers with useful insights for targeting. This approach seeks to respect user privacy and promote fairness in the ad ecosystem. Key strategies include employing federated learning of cohorts, which allows for machine learning models to be trained on data distributed across multiple devices without ever needing to collect or share individual user data.
Google’s Stance on User Privacy in Relation to Ad Tracking
Google’s official stance on user privacy regarding ad tracking is that they prioritize user data protection. They assert that the Android Privacy Sandbox is designed to balance the needs of advertisers with user rights. Google emphasizes their commitment to transparency and user control over their data. They claim that the Sandbox allows for a more privacy-respecting approach to advertising, without sacrificing the effectiveness of the advertising system.
Comparison of Google’s Ad Tracking Methods on Android to Other Platforms
Google’s ad tracking methods on Android differ significantly from those on iOS. Apple’s approach to privacy on iOS prioritizes user control over their data, limiting the ability of third-party advertisers to track user activity across different apps. Google’s Android Privacy Sandbox aims for a middle ground, enabling targeted advertising while mitigating some of the concerns raised by user privacy advocates.
While both platforms strive for different solutions to privacy, both aim to strike a balance between targeted advertising and user privacy.
Google’s Ad Tracking Methods Across Different Android Versions
| Android Version | Ad Tracking Method | Privacy Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Android 10 | Focus on device-level data and aggregation of user data for ad targeting | Potential for broader data collection compared to later versions |
| Android 12 | Introduction of Privacy Sandbox features, emphasizing federated learning of cohorts, and other privacy-respecting techniques | Reduced collection of individual user data, improved user privacy |
| Android 13 (and beyond) | Continued evolution of Privacy Sandbox features and enhancements | Further refinement of ad tracking strategies, ongoing emphasis on user privacy |
The table above provides a general overview of the evolving nature of Google’s ad tracking methods across Android versions. Each update reflects Google’s ongoing commitment to balancing user privacy and advertising effectiveness.
Apple’s Approach to Privacy
Apple’s approach to user privacy on iOS has been a defining characteristic, contrasting sharply with the strategies employed by other tech giants like Google. This difference is particularly evident in their handling of ad tracking, emphasizing user control and transparency over data collection. Apple’s stringent policies have significantly impacted the digital advertising landscape, forcing a re-evaluation of data collection methods and user experience.
Apple’s Privacy Policies on iOS
Apple’s iOS operating system prioritizes user privacy above all else. This is reflected in its stringent policies regarding ad tracking, emphasizing user control and transparency. Apple’s approach fundamentally differs from Google’s on Android, which allows for a more extensive use of data for targeted advertising. This difference is not just a matter of preference; it directly impacts the user experience and the way applications are developed.
Contrast with Google’s Approach on Android
Apple’s policies regarding ad tracking stand in stark contrast to Google’s approach on Android. Google’s Android Privacy Sandbox aims to improve privacy while maintaining the effectiveness of targeted advertising. However, Apple’s more restrictive approach has led to the development of alternative solutions for ad tracking and user experience on iOS. This difference is highlighted in the distinct frameworks each company has developed for handling user data.
Impact on the Ad Technology Landscape
Apple’s stringent privacy policies have significantly reshaped the ad technology landscape. Developers are forced to adapt their strategies for collecting and using user data, leading to the emergence of alternative solutions for ad tracking on iOS. This has spurred innovation in areas like privacy-preserving technologies and alternative advertising models. The shift away from reliance on granular user data has led to new challenges and opportunities for advertisers and developers alike.
Differences in Ad Tracking Frameworks
| Platform | Framework | User Privacy Approach | Data Collection Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | SKAdNetwork, App Tracking Transparency (ATT) | Prioritizes user control over data collection. Users are explicitly asked for permission to track their activity. | Limited data collection. Focus on aggregated data and less reliance on individual user data points. |
| Android | Android Privacy Sandbox | Aims to balance privacy with targeted advertising by limiting the ability to track individual users. | Allows for targeted advertising based on contextual data and user profiles, while restricting direct tracking of individual users. |
The table above summarizes the key differences in ad tracking frameworks between Apple and Google. Note the significant emphasis on user control and limited data collection in Apple’s approach, contrasting with Google’s more comprehensive approach to targeted advertising, albeit with privacy safeguards in place. These differing approaches highlight the ongoing debate about the balance between user privacy and the effectiveness of advertising models.
Facebook’s Ad Tracking Practices
Facebook’s ad platform is a powerful engine for targeted advertising, but its extensive data collection practices raise significant privacy concerns. Understanding Facebook’s strategies for tracking users, both across different platforms and within the Android Privacy Sandbox, is crucial for assessing the impact on individual privacy and online experiences. This analysis will explore Facebook’s methods, potential privacy implications, and strategies for mitigating these concerns.
Facebook’s Ad Tracking Strategies
Facebook employs a multifaceted approach to ad tracking, leveraging a combination of techniques to build detailed user profiles. This allows them to tailor advertisements to individual interests and behaviors, optimizing their advertising effectiveness. These strategies are deeply integrated with the platform’s core functionalities, making them a pervasive aspect of the user experience.
Google’s Android privacy sandbox is a big deal, especially when considering how Apple and Facebook handle ad tracking. It’s all about trying to limit how apps can access your personal data. If you’re looking for a phone that prioritizes your privacy and still packs a punch, check out some amazing deals on the OnePlus 9, one of our favorite phones of the year.
Save over 200 on the OnePlus 9 – it’s a fantastic option for anyone concerned about data privacy, and it offers a great user experience. Ultimately, the ongoing debate about how much control users have over their data in the digital age is something we all need to pay attention to.
Data Collection and Use for Ad Targeting
Facebook gathers a vast amount of data from users to inform ad targeting. This data includes information directly provided by users (e.g., profile details, interests), interactions within the platform (e.g., posts, comments, likes, and shares), and data collected through third-party integrations and partnerships. This comprehensive data collection allows Facebook to create detailed profiles of users, enabling precise ad targeting.
For example, if a user frequently interacts with posts about gardening, Facebook might display ads for gardening tools and supplies. Similarly, if a user shares articles about travel, Facebook might show ads for travel packages and destinations. Furthermore, Facebook’s use of data extends beyond its platform, leveraging information from other websites and apps through its extensive network of partners and integrations.
Ad Tracking within the Android Privacy Sandbox
Facebook’s strategy within the Android Privacy Sandbox focuses on adapting its ad tracking methods to respect user privacy while maintaining effective advertising. This involves utilizing privacy-preserving technologies, like those enabled by the Android Privacy Sandbox, to ensure user data isn’t tracked in ways that compromise their privacy. Crucially, Facebook’s efforts must ensure that the shifting landscape of user privacy doesn’t impede its ability to provide relevant and engaging advertising experiences.
Comparison of Ad Tracking Practices Across Platforms
Facebook’s ad tracking practices vary slightly across different platforms, such as Android, iOS, and desktop. While the fundamental principle of using user data for targeted advertising remains consistent, the specifics of data collection and the available tools for tracking may differ. For instance, iOS’s stricter privacy controls may necessitate different techniques compared to Android or desktop platforms. This flexibility allows Facebook to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and technological advancements on each platform.
Google’s Android privacy sandbox and the ongoing debate about Apple’s and Facebook’s ad tracking practices are definitely interesting. While we’re seeing efforts to control how apps collect user data, it’s also fascinating to see how the entertainment world is changing. For example, Logic’s signing an exclusive partnership deal with Twitch ( logic twitch signing deal exclusive partnership ) is a big deal, showing how streaming platforms are evolving.
Ultimately, these developments highlight the ever-shifting landscape of how tech companies collect and use user data, especially when it comes to Android privacy features.
Facebook’s Ad Tracking Methods and Potential Privacy Concerns
| Ad Tracking Method | Potential Privacy Concerns | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Cookies and tracking pixels | Potential for tracking user activity across multiple websites and platforms, creating a detailed profile of online behavior. | Employing privacy-enhancing technologies like federated learning of cohorts and differential privacy, which enable data analysis without compromising user anonymity. |
| Data from third-party apps and websites | Potential for misuse of data from third-party sources, potentially revealing sensitive personal information. | Implement stricter data access controls and transparency mechanisms, ensuring users are informed about how their data is being collected and used. |
| Data aggregation and analysis | Potential for misuse of aggregated data to identify individual users, revealing their personal preferences and behaviors. | Implementing data anonymization techniques and strict data security measures to protect user privacy. |
| Behavioral targeting | Potential for creating a detailed profile of user interests and behaviors, potentially leading to targeted advertising that is not relevant or is intrusive. | Improving transparency in ad targeting practices and giving users more control over their data through options for opt-out or granular control over data sharing. |
Impact on User Experience
The Android Privacy Sandbox, a suite of technologies designed to enhance user privacy, is poised to significantly alter the mobile landscape. This shift in ad tracking mechanisms will undoubtedly impact the user experience, presenting both opportunities and challenges for app developers and users alike. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for navigating this evolving environment.
Potential Positive Impacts on User Experience
Improved user privacy is a core benefit of the Privacy Sandbox. By reducing the ability of advertisers to track users across apps and websites, the sandbox aims to limit the collection and use of personal data. This can lead to a more private and secure mobile experience for users. Moreover, users may feel more comfortable interacting with apps and websites knowing their data is being handled responsibly.
Reduced tracking could also lead to a more focused and targeted advertising experience, potentially eliminating irrelevant ads and improving user engagement with relevant content.
Potential Negative Impacts on User Experience
While privacy gains are substantial, the transition to the Android Privacy Sandbox may present challenges. Reduced ad personalization could result in less relevant advertisements, potentially impacting user engagement. Apps reliant on targeted advertising for revenue might see a decrease in income. This shift could affect the ability of apps to provide free services, potentially leading to a rise in in-app purchases or subscriptions as a means of revenue generation.
The change in ad tracking models could also lead to a less optimized user experience for some apps and websites.
Impact on App and Website User Experience
Changes to ad tracking can dramatically affect the user experience of apps and websites. Apps and websites heavily reliant on personalized advertising might see a decline in user engagement and revenue. For example, a news app that depends on targeted ads to remain free might need to adjust its revenue model to accommodate the shift. Similarly, e-commerce platforms could face challenges in delivering personalized recommendations if their ad tracking capabilities are diminished.
Ultimately, the success of the Android Privacy Sandbox in maintaining a positive user experience will depend on the adaptability of developers and the effectiveness of the new ad tracking models.
Examples of Influencing User Engagement
Reduced ad personalization could negatively impact user engagement. For example, if a user frequently uses a fitness app, personalized ads for relevant workout gear or nutrition products might increase user engagement. With the sandbox, these personalized ads might decrease, leading to a potential decline in app usage or the need for other revenue generation strategies. Conversely, a more targeted advertising experience could result in users encountering ads for products they are more likely to be interested in, thereby increasing engagement and improving user satisfaction.
User Frustration and Dissatisfaction
Users might experience frustration due to a perceived reduction in ad personalization. If a user finds that ads are less relevant to their interests, they may perceive a less enjoyable user experience. This could lead to a decline in user engagement with apps and websites. However, the reduction in data collection might also foster a sense of privacy and control, potentially offsetting the perceived loss of personalized ads.
Potential Impacts Categorized
| Category | Potential Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| App Performance | Apps relying heavily on targeted advertising may see a decline in revenue, potentially leading to changes in the free-to-use model. | A news app might have to introduce a subscription model to maintain its current content offerings. |
| User Engagement | Reduced ad personalization could lead to a decrease in user engagement with apps and websites, particularly if users find ads less relevant to their interests. | A user might stop using a fitness app if they no longer see ads for products related to their workouts. |
| Ad Relevance | Ads might become less relevant to users’ interests, potentially leading to a less satisfying user experience. | A user browsing an e-commerce site might not find relevant product recommendations, decreasing the likelihood of a purchase. |
Future Trends in Ad Tracking
The Android Privacy Sandbox is reshaping the landscape of mobile advertising, forcing a fundamental shift in how advertisers reach users. This evolution necessitates a proactive understanding of future trends, challenges, and opportunities in ad tracking. The sandbox’s focus on user privacy demands innovative approaches that respect user choices while enabling effective advertising.The future of ad tracking on Android hinges on the ability to balance user privacy with the need for advertisers to effectively target their audiences.
This delicate equilibrium requires the development of new technologies and strategies that respect user preferences while allowing for targeted advertising. The sandbox’s influence extends beyond Android, prompting similar changes in other ecosystems, which suggests a broader trend towards user-centric advertising.
Predicting Future Trends in Ad Tracking
The Android Privacy Sandbox necessitates a shift from reliance on identifiers like the IDFA to more nuanced, privacy-preserving methods. Future ad tracking trends will likely emphasize federated learning and privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs). These techniques aim to aggregate data across multiple devices without compromising individual user privacy. For instance, the use of encrypted data pools for user profiles can allow for more targeted advertising while respecting user privacy.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The transition to a privacy-focused advertising ecosystem presents both challenges and opportunities. Challenges include the need to develop new ad-serving models, adjust existing business strategies, and adapt to evolving regulatory frameworks. However, opportunities include the development of more innovative and sophisticated advertising technologies that are aligned with user privacy. One opportunity is to find creative ways to collect data while being transparent about how it is used.
This will build trust with users and foster greater adoption of these new technologies.
Potential Future Technologies and Innovations
New technologies like federated learning, privacy-preserving machine learning, and differential privacy are poised to play a critical role in the future of ad tracking. Federated learning allows for machine learning models to be trained on decentralized data without requiring the central collection of sensitive user data. Privacy-preserving machine learning techniques can enable sophisticated analysis of user behavior while keeping individual data secure.
Differential privacy adds random noise to data, making it difficult to infer individual data points.
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Ad Tracking Practices
Regulatory changes, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other evolving privacy laws, are significantly influencing ad tracking practices. These regulations are driving a shift towards more transparent and user-controlled data handling practices. For example, GDPR mandates that users have the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal data. These regulations will continue to evolve, shaping the future of ad tracking and the development of new privacy-enhancing technologies.
Potential Future Trends Table
| Technology | Impact on Privacy | Potential Market Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Federated Learning | Improved user privacy by avoiding central data collection. | Increased trust and adoption of advertising platforms. |
| Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning | Enhanced data analysis while respecting user privacy. | Development of more targeted and relevant advertising campaigns. |
| Differential Privacy | Aggregation of user data while preserving individual anonymity. | Improved data accuracy and model performance without compromising user privacy. |
| Contextual Advertising | Focuses on user behavior and surroundings to personalize ads. | Improved user experience and reduced intrusive advertising. |
| Zero-party data | User-provided data enabling more personalized advertising. | Greater transparency and control over user data. |
Conclusive Thoughts
The Android Privacy Sandbox, Google’s initiative to improve user privacy, is a significant shift in the mobile advertising landscape. This new approach impacts not only how ads are tracked but also the performance of mobile apps and websites. Apple’s contrasting approach highlights the tension between user privacy and the need for effective advertising models. Facebook’s ad tracking practices, while subject to scrutiny, also warrant consideration.
The future of ad tracking is undeniably intertwined with user experience, privacy concerns, and regulatory changes. This exploration offers a comprehensive view of the Android Privacy Sandbox and its profound impact.




