Securing applications VMware vSphere virtualized data center design guide provides a comprehensive blueprint for safeguarding applications within a virtualized environment. This guide dives deep into the complexities of securing applications in a VMware vSphere environment, addressing critical challenges and outlining best practices for a robust and secure virtualized data center. From understanding the security architecture of VMware vSphere to implementing secure network configurations and data protection, this guide equips you with the knowledge and strategies needed to navigate the evolving security landscape of virtualized environments.
The guide explores various crucial aspects, including VM security, network considerations, data security, identity and access management, application-specific measures, security auditing, disaster recovery, and essential security policies and procedures. It offers practical examples, actionable steps, and tables to illustrate key concepts and facilitate implementation. This is your one-stop resource for building a secure and reliable VMware vSphere data center.
Introduction to Application Securing in Virtualized Environments
Securing applications within a virtualized environment like VMware vSphere presents unique challenges compared to traditional physical deployments. This complexity stems from the dynamic nature of virtualization, where applications run in isolated virtual machines (VMs) that are often interconnected and share resources. Effective security strategies must account for these nuances to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of application data and functionality.Application security in a virtualized environment is paramount for maintaining business continuity and preventing data breaches.
Compromising a virtualized application can have far-reaching consequences, potentially affecting multiple applications or even the entire data center infrastructure. In the current threat landscape, where sophisticated attacks are becoming increasingly common, robust application security is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
Challenges Specific to VMware vSphere Application Security
Virtualization introduces new attack vectors and complexities. VM sprawl, resource contention, and the distributed nature of virtualized environments can make traditional security approaches less effective. Moreover, the dynamic nature of VM deployment and management introduces new vulnerabilities that need careful consideration. Maintaining consistent security posture across a constantly evolving virtualized infrastructure requires proactive strategies.
Potential Risks Associated with Insecure Applications
Insecure applications in a virtualized data center can lead to several critical risks. A compromised application could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt business operations, or even escalate privileges to other systems within the virtualized environment. The potential for data breaches and financial losses is significant. For example, a vulnerable e-commerce application could expose customer credit card information or allow unauthorized access to financial records.
Key Components and Considerations for Application Security in a VMware vSphere Design
Implementing robust application security in a VMware vSphere design requires a multi-faceted approach. The security strategy should encompass several key components, including:
- Network Segmentation: Isolating VMs and applications into secure segments based on their criticality and trust levels is essential. This limits the impact of a security breach to a contained area, reducing the risk of lateral movement. This segmentation approach is crucial for minimizing the blast radius of a potential attack.
- Access Control: Implementing granular access controls at the operating system, application, and network levels is critical to limit unauthorized access to application resources. This includes using strong authentication methods, least privilege principles, and regular access reviews.
- Vulnerability Management: Proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in applications and underlying infrastructure is crucial. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, along with patching and updates, are vital components of this strategy.
- Security Auditing: Establishing mechanisms for monitoring application activity and detecting anomalies is critical for identifying potential threats. Comprehensive logging, intrusion detection systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions are crucial in this context.
- Compliance and Governance: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations and security standards, like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR, is essential. The implementation of policies and procedures to meet regulatory compliance requirements should be integrated into the application security strategy.
VMware vSphere Security Architecture: Securing Applications Vmware Vsphere Virtualized Data Center Design Guide
VMware vSphere, the industry-leading virtualization platform, provides a robust foundation for securing applications within a virtualized data center. Its layered security approach protects against various threats, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of virtual machines (VMs) and the data they contain. This architecture, while complex, is designed to be manageable and adaptable to the ever-evolving threat landscape. Understanding the key components and functionalities is crucial for effective application security within a vSphere environment.The security architecture of VMware vSphere is not just about preventing attacks; it’s about establishing a secure operational environment.
It encompasses a range of technologies and practices designed to secure the entire virtualization infrastructure, from the underlying hardware to the applications running within the VMs. This comprehensive approach is crucial for maintaining business continuity and protecting sensitive data.
Security Features and Functionalities
VMware vSphere offers a wide array of security features to safeguard applications. These features are designed to mitigate various threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the virtualized environment. This robust set of functionalities addresses various security concerns, enabling organizations to protect their critical applications.
- Virtual Machine (VM) Security: VMware provides mechanisms to isolate and secure individual VMs, preventing malicious code from spreading across the environment. This isolation is crucial for containing any potential security breaches within a VM. This feature safeguards the sensitive data and applications residing within the virtual machines.
- Network Security: vSphere leverages network virtualization to control and monitor traffic flow between VMs and the external network. This granular control enables organizations to implement security policies and firewall rules specific to each application or VM. Effective network segmentation plays a vital role in preventing lateral movement within the virtualized environment.
- Access Control: VMware vSphere allows administrators to define granular access controls for users and groups. This feature ensures that only authorized personnel can access and manage specific resources within the vSphere environment. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a key aspect of this, enabling fine-grained security policies.
- Data Protection: Data protection mechanisms are integrated within the vSphere architecture to ensure the availability and integrity of virtualized data. These mechanisms include features like encryption and data backups to mitigate the impact of data loss or corruption.
- Security Auditing: VMware provides logging and auditing capabilities to monitor activities within the vSphere environment. This allows administrators to track user actions, identify security events, and respond to potential threats proactively. This feature is critical for incident response and regulatory compliance.
Key Security Roles and Responsibilities
Effective security within a vSphere environment depends on clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Different roles within the organization have specific responsibilities regarding security and compliance.
- System Administrators: Responsible for the day-to-day management of the vSphere infrastructure, including installing, configuring, and maintaining security settings.
- Security Administrators: Focus on implementing and enforcing security policies, monitoring security events, and responding to security incidents.
- Application Owners: Responsible for securing applications running within the virtual machines. This includes ensuring the application code and configuration comply with security policies.
- Network Engineers: Responsible for securing the network infrastructure connecting the vSphere environment to the external network, implementing firewalls and network segmentation.
Comparison of VMware vSphere Versions
Security features and functionalities evolve with each new vSphere release. This evolution reflects the dynamic nature of the threat landscape and the need for enhanced security measures.
- Enhanced Security Features: Newer versions often incorporate improved security features, such as enhanced encryption options, improved access control mechanisms, and updated security patching mechanisms.
- Integration with Other Security Tools: Later versions often improve integration with other security tools and platforms, allowing for more comprehensive security management and threat detection.
- Increased Automation: Automation features within vSphere can be utilized for tasks like security audits and incident response, leading to more efficient and effective security management. This enhances operational efficiency and reduces the risk of human error.
Conceptual Diagram of vSphere Security Architecture
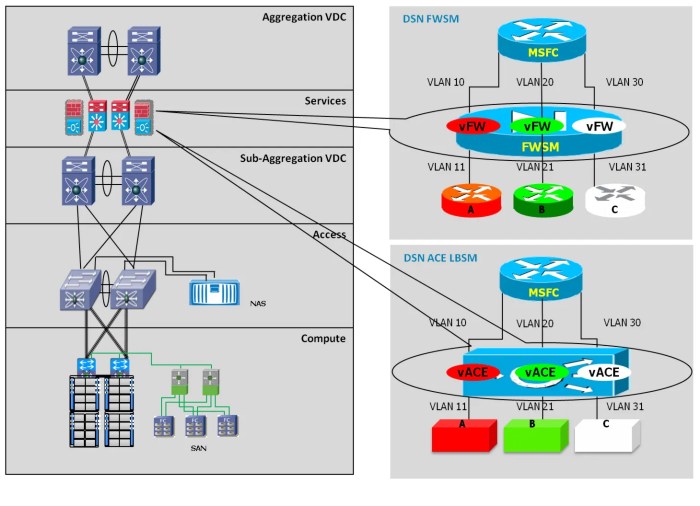
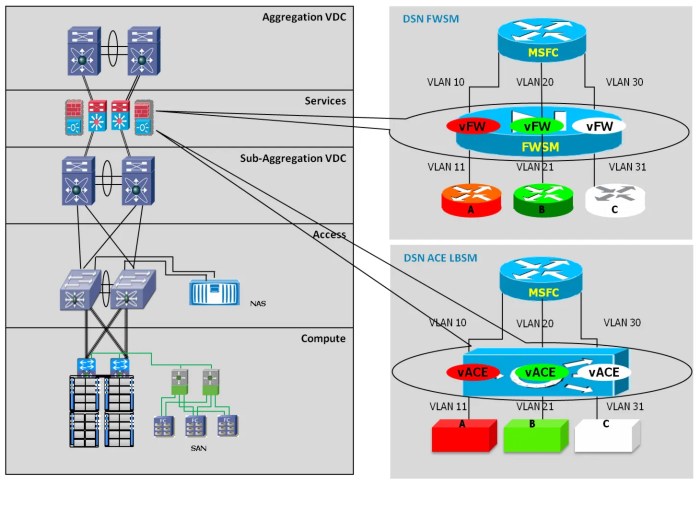
A conceptual diagram of a vSphere virtualized data center security architecture would show interconnected components, highlighting the security features mentioned previously. The diagram would illustrate the layers of security, from physical hardware security to application security within the VMs. It would visually represent the network segmentation, access control mechanisms, and data protection policies. This visual representation helps to understand the overall security posture and the interaction between different security components.
Virtual Machine (VM) Security Best Practices
Securing individual VMs is crucial for maintaining the overall security posture of a virtualized data center. A robust VM security strategy considers the unique characteristics of virtualized environments, encompassing the hypervisor, guest operating systems, and application workloads. This approach must go beyond simply securing the physical host; each VM needs specific attention to protect its applications and data.Effective VM security practices extend beyond basic access controls, encompassing secure configurations, vulnerability management, and robust network segmentation.
A layered approach that integrates these elements is vital for comprehensive protection against various threats.
VM Hardening and Configuration
Proper VM hardening is essential for reducing attack surfaces and enhancing security. This involves configuring VMs with the necessary security controls and disabling unnecessary services. A hardened VM minimizes the potential for exploitation, making it significantly more resistant to malicious attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies. Regular checks and updates to configurations and patching are critical to maintaining a strong security posture. Examples include verifying firewall rules, checking for open ports, and ensuring proper user access control mechanisms are in place.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Implement the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks. This limits the potential damage from compromised accounts. For example, avoid assigning administrator privileges to users unless absolutely required.
- Strong Passwords and Authentication: Enforce strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all VM accounts. Implement robust authentication methods to verify the identity of users attempting to access VMs. Employing MFA significantly increases the security level compared to passwords alone.
Common VM Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Understanding common vulnerabilities in VMs and their corresponding mitigation strategies is essential for proactive security.
| Vulnerability | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Outdated Operating Systems | Using outdated guest operating systems exposes VMs to known vulnerabilities. | Regularly update guest operating systems and install security patches promptly. |
| Misconfigured Firewalls | Improperly configured firewalls allow unauthorized network access. | Configure firewalls to block unnecessary ports and traffic. Use a centralized firewall policy for consistency. |
| Default Credentials | Using default credentials for accounts makes VMs vulnerable. | Change default passwords for all accounts and enforce strong password policies. |
| Missing or Weak Encryption | Lack of encryption for sensitive data makes VMs vulnerable to data breaches. | Employ full disk encryption and encrypt data in transit using secure protocols. |
VM-Level Security Features in vSphere
vSphere provides various security features to enhance VM protection. Leveraging these features can significantly strengthen the security posture of the virtual environment.
Thinking about securing applications in a VMware vSphere virtualized data center design? It’s a complex topic, but one that’s becoming increasingly crucial. While Samsung is expanding the Galaxy Ring in five innovative new ways, this new approach to device integration might have some interesting implications for future data center security. Ultimately, a solid understanding of virtualization and robust security protocols remain key to a secure and reliable data center design.
- VMware vCenter Security: Centralized management and control over security policies across the vSphere infrastructure. It helps to enforce security configurations and monitor compliance across all VMs.
- VMware vShield Endpoint: Provides advanced threat protection and intrusion detection capabilities for VMs. This feature can be used to identify and respond to malicious activity within the VMs.
- Network Segmentation: Effective network segmentation can isolate VMs and limit the impact of security breaches. This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments.
Secure VM Configuration and Deployment Procedures
Consistent and secure deployment procedures are crucial for maintaining the security of VMs.
- Template-Based Deployment: Creating secure templates for VMs ensures consistent configuration across all deployed instances. This approach minimizes the chance of misconfigurations during VM deployment.
- Automated Patching: Automate the patching process to apply security updates promptly. This helps to maintain a secure posture for the VMs.
- Security Hardening Scripts: Employ scripts to automate the hardening process, applying consistent security configurations to all VMs.
Secure Network Segmentation Techniques for VMs
Implementing network segmentation within vSphere is essential for isolating VMs and limiting the scope of potential attacks.
- VLANs: Using VLANs to segment the network into isolated logical segments limits the impact of a breach. A compromised VM will not have access to resources in other VLANs.
- Virtual Switches: Using virtual switches to control network traffic between VMs can isolate them and restrict communications. This limits the potential for lateral movement of malware.
- Firewalls: Deploying firewalls at various points in the network isolates and controls access between different segments, preventing unwanted communication between VMs.
Network Security Considerations for Applications
Securing applications in a virtualized environment like VMware vSphere requires a multi-layered approach, focusing on the network as a crucial component. A robust network strategy isn’t just about preventing unauthorized access; it’s about ensuring application availability, data integrity, and compliance with security policies. Ignoring network security can leave applications vulnerable to breaches, data leaks, and service disruptions.Network security in a virtualized data center is paramount.
A compromised network segment can potentially affect multiple VMs and applications, leading to widespread disruption. Proper network segmentation, secure access controls, and intrusion detection mechanisms are essential to maintaining the overall security posture of the virtualized environment. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of security incidents and facilitates faster incident response.
Secure Network Segmentation
Effective network segmentation isolates applications and data based on their sensitivity and access requirements. This isolation minimizes the impact of a security breach within one segment. Virtual networks (vNets) and VLANs within vSphere enable this segregation, allowing administrators to define distinct security zones for different applications. For example, separating development, testing, and production environments in separate vNets enhances security by limiting the potential spread of malware or unauthorized access.
This segregation is vital for controlling access and isolating potential threats.
While delving into securing applications within a VMware vSphere virtualized data center design, I couldn’t help but notice the recent Garmin Venu SQ 2, Vivofit 3 Jr Special Edition launch. This new release highlights how technology is innovating in various sectors. Ultimately, strong data center security is crucial for maintaining robust systems, just like a reliable fitness tracker helps maintain a healthy lifestyle.
The complexities of securing applications in a virtualized environment require careful planning and meticulous execution, just like choosing the right tech for your fitness journey.
Firewall Configuration and Management
Firewalls act as the gatekeepers for network traffic, controlling ingress and egress based on predefined rules. Implementing robust firewall policies within a vSphere environment is crucial. These policies should be based on the principle of least privilege, allowing only necessary traffic to pass. Firewall rules should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changing application needs and security threats.
By carefully defining rules, administrators can control the flow of data into and out of the virtual environment, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Virtual Network Security Devices
Network security appliances can be virtualized to enhance security within vSphere. Virtual firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can be deployed within the virtual network infrastructure. These virtual appliances offer granular control over network traffic, providing a centralized security management point within the virtualized environment. Implementing these tools can enhance the overall security posture and facilitate efficient threat detection and response.
Securing Network Traffic Between VMs and External Resources
Traffic between VMs and external resources should be secured using appropriate protocols and encryption. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can extend the secure network to external connections. For example, remote access to applications running within VMs should utilize encrypted channels to protect sensitive data. Using HTTPS for web applications and secure protocols for data transfer is crucial for protecting data in transit.
Proper encryption is essential for maintaining data confidentiality and integrity when communicating between VMs and external systems.
Table of Common Network Security Threats and Countermeasures in vSphere
| Threat | Description | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Unprivileged users gain access to network resources. | Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, role-based access control. |
| Malware Infection | Malicious software compromises VMs or network infrastructure. | Regular security updates, antivirus software, intrusion detection/prevention systems. |
| Denial-of-Service Attacks | Attackers flood network resources, disrupting service. | Load balancing, intrusion prevention systems, network monitoring. |
| Man-in-the-Middle Attacks | Attackers intercept and manipulate network traffic. | Secure protocols (SSL/TLS), VPNs, network segmentation. |
Data Security and Compliance
Protecting sensitive data in a virtualized environment like VMware vSphere is paramount. Data breaches can have severe financial and reputational consequences, impacting both the organization and its customers. Robust data security measures are essential to ensure compliance with industry regulations and maintain trust. Implementing a comprehensive strategy that includes encryption, access controls, and regular audits is crucial for mitigating risks.Data security in a virtualized environment demands a layered approach.
It’s not enough to secure individual VMs; the entire infrastructure, including storage, networks, and access points, must be considered. Compliance mandates dictate specific requirements for data protection, and adhering to them is critical for maintaining operational integrity and avoiding penalties. This necessitates a detailed understanding of the security measures required within a vSphere environment and how to implement them effectively.
Importance of Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental component of data security in a virtualized data center. Encrypting data at rest and in transit safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access. This protects against data breaches during transmission and storage, reducing the risk of exploitation. Strong encryption algorithms and robust key management practices are vital for maintaining data confidentiality.
Access Control Mechanisms
Implementing granular access controls is essential for managing who can access specific data within the virtualized environment. Role-based access control (RBAC) provides a framework for defining user permissions, limiting access to only necessary resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access. Properly configured access controls help maintain data integrity and prevent unauthorized modification or deletion of sensitive information.
Compliance with Data Security Regulations
Adherence to data security regulations is critical for maintaining operational integrity and avoiding penalties. Different industries and jurisdictions have specific requirements for data protection. These regulations often mandate data encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
Table of Data Security Regulations and vSphere Compliance
| Regulation | Key Compliance Requirements | vSphere Implementation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) | Protecting Protected Health Information (PHI) | Encrypting VMs containing PHI, implementing strict access controls, logging all access attempts. |
| GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) | Protecting personal data of EU citizens | Ensuring compliance with data minimization, data retention policies, and access requests, encryption of VMs containing personal data. |
| PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) | Protecting payment card information | Implementing strong encryption for cardholder data, access controls for sensitive applications, regular security assessments, and vulnerability management. |
| CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) | Protecting California residents’ personal data | Complying with data subject rights, including access, deletion, and portability, and using encryption to protect personal data. |
Handling Sensitive Data within VMs
Handling sensitive data within VMs requires specific considerations. Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) tools can help detect and prevent sensitive data from leaving the environment. Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the security posture. Data sanitization procedures should be established for decommissioned or retired VMs to ensure that sensitive data is permanently removed.
Best Practices for Sensitive Data Handling
- Employing strong encryption algorithms for both data at rest and in transit is crucial.
- Implementing RBAC ensures that users only have access to the data and resources they need.
- Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Establishing a clear data handling policy, including procedures for data sanitization and disposal, is critical for compliance.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in vSphere
Securing virtualized environments like VMware vSphere necessitates robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) practices. Proper IAM ensures that only authorized users and applications have access to critical resources, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Effective IAM implementation in vSphere significantly enhances the overall security posture of the virtualized data center.Implementing strong IAM policies within a vSphere environment is crucial for maintaining control over access to virtual machines, networks, and data.
A well-defined IAM strategy is a cornerstone of a secure vSphere architecture, ensuring that only authorized personnel and applications can interact with sensitive resources.
Role-Based Access Controls for Application Access
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a fundamental principle in securing vSphere. It enables granular control over access to resources by assigning roles to users and groups. These roles define the specific actions that users and applications are permitted to perform. By associating specific privileges with roles, administrators can precisely control what each user or application can do within the vSphere environment.
For example, a development team role might grant access to specific virtual machines and networks but restrict access to production resources.
Multi-Factor Authentication in vSphere Security
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a critical security measure to enhance the security posture of vSphere. It requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, typically a password combined with a one-time code from a token or mobile device. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access to accounts even if they have compromised passwords.
Implementing MFA for vSphere administrators and users dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens the overall security of the virtualized environment. This practice is becoming a standard in enterprise security.
Enforcing Least Privilege Access
Implementing the principle of least privilege is paramount in vSphere security. This means granting users and applications only the minimum necessary access rights to perform their required tasks. Restricting access to resources limits the potential damage from a compromised account. For instance, an administrator should not have access to all vSphere resources if their role only requires modifying specific virtual machines.
This approach significantly minimizes the impact of a security breach, limiting the scope of potential harm.
Securing applications in a VMware vSphere virtualized data center design takes careful planning. Choosing the right screen protector for your OnePlus Nord N200 5G is crucial for preventing scratches and damage, just like robust security measures are crucial for your virtual infrastructure. Finding the best ones can be a challenge, but thankfully, this guide will help you navigate the options.
Ultimately, a well-protected device and a well-designed virtual environment are both important for a successful operation.
Comparison of IAM Solutions for vSphere
| IAM Solution | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| VMware vCenter Security | Integrated with vCenter, providing robust role-based access controls. | Ease of management, tightly integrated with vSphere ecosystem. | Limited customization options compared to third-party solutions. |
| Third-Party Identity Providers (e.g., Okta, Azure AD) | Integrate with vSphere using APIs or connectors. | Broader customization options, integration with existing enterprise identity systems. | Requires integration effort and potentially higher upfront costs. |
| Open Source Solutions (e.g., OpenID Connect) | Flexible and potentially cost-effective. | Highly customizable, potentially lower costs. | Requires expertise to configure and maintain. |
Application-Specific Security Measures
Application security is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Virtualized environments, while offering flexibility and scalability, introduce unique security challenges that require tailored approaches. Protecting applications within vSphere necessitates a granular understanding of each application’s vulnerabilities and the specific security measures needed to mitigate them. This includes proactive identification of potential threats and the implementation of robust security controls specific to the application’s functionality and data handling.Application-specific security goes beyond general network and host security measures.
It demands a deep dive into the application’s code, architecture, and operational processes. This approach helps pinpoint vulnerabilities that might be overlooked by generic security protocols, ensuring a more comprehensive and effective security posture.
Common Application Vulnerabilities
Applications, irrespective of their function, are susceptible to a variety of vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities often stem from coding errors, inadequate input validation, and lack of proper access controls. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for proactively addressing them within a virtualized environment. Common vulnerabilities include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), and insecure direct object references.
- SQL Injection: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in applications that interact with databases to execute malicious SQL queries. This can lead to unauthorized data access, modification, or deletion. Mitigation strategies involve parameterized queries, input validation, and secure coding practices.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. This can steal user credentials, redirect users to malicious websites, or deface web pages. Mitigation involves validating and sanitizing user inputs, output encoding, and secure coding practices.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): Attackers trick users into performing unwanted actions on a web application by submitting forged requests. Mitigation involves using anti-CSRF tokens, validating user requests, and implementing robust authentication protocols.
- Insecure Direct Object References: Applications might expose internal objects or resources directly through URLs or other interfaces. Attackers can exploit this to access unauthorized resources or manipulate data. Mitigation involves using proper access control mechanisms and secure coding practices to restrict access to resources.
Implementing Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS), Securing applications vmware vsphere virtualized data center design guide
IDS/IPS systems are crucial for detecting and preventing malicious activities targeting applications. These systems monitor network traffic and application logs for suspicious patterns or anomalies. Implementing IDS/IPS for applications in vSphere necessitates careful configuration to avoid false positives and ensure minimal impact on application performance. Consider using specialized application-aware IDS/IPS solutions that can identify and block malicious traffic tailored to the application’s specific communication protocols.
Security Tools for Application Security in vSphere
Numerous security tools are available for enhancing application security in a vSphere environment. These tools range from general-purpose vulnerability scanners to application-specific security testing tools.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): WAFs filter and monitor HTTP traffic to web applications, protecting against common web attacks. They can be deployed as separate devices or integrated into application servers.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems: SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, including applications running in vSphere. They help identify potential threats and security incidents.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Tools like Nessus or OpenVAS can scan applications for known vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation.
- Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST/DAST) tools: These tools analyze application code and runtime behavior to identify vulnerabilities. They can help identify vulnerabilities before deployment or during runtime.
Securing Web Applications in vSphere
Web applications are frequently targeted by attackers. Ensuring their security within vSphere requires a layered approach. This involves implementing secure coding practices, input validation, output encoding, and utilizing WAFs to filter malicious requests.
- Secure Coding Practices: Following secure coding guidelines helps prevent common vulnerabilities in application code. These practices include using parameterized queries, avoiding direct object references, and sanitizing user inputs.
- Input Validation: Validate all user inputs to prevent malicious data from being processed by the application. This includes checking for data type, length, and format.
- Output Encoding: Encoding output data before displaying it to users helps prevent XSS attacks.
- WAF Deployment: Deploying a WAF in front of web applications can help mitigate common web attacks.
Security Auditing and Monitoring
Regular security audits and robust monitoring are crucial for maintaining the integrity and resilience of a virtualized data center. They provide a proactive approach to identify vulnerabilities, assess compliance, and ensure the ongoing effectiveness of security measures. By actively tracking security events and analyzing trends, organizations can proactively address potential threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Importance of Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations within the vSphere environment. These audits assess the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify areas needing improvement. They verify compliance with industry standards, regulatory requirements, and internal policies. The findings from these audits form the basis for implementing corrective actions and preventing future security breaches.
Implementing Security Monitoring Tools in vSphere
Several tools are available to implement security monitoring in vSphere. VMware vCenter Security provides built-in capabilities for monitoring security events. Third-party security information and event management (SIEM) solutions can integrate with vCenter to provide a comprehensive view of security events across the entire virtualized environment. These tools collect logs from various vSphere components, including virtual machines, network devices, and storage systems.
Best Practices for Log Management and Analysis
Effective log management and analysis are critical for detecting security threats and responding to incidents. Centralized log aggregation is essential for efficient analysis. Establish clear log retention policies to comply with regulatory requirements and minimize storage costs. Develop automated alerts for critical security events, enabling proactive response to threats. Use security analytics tools to correlate events, identify patterns, and generate actionable insights.
Regularly review and update security policies based on log analysis findings.
Security Incident Response Plans for vSphere
A well-defined security incident response plan is crucial for handling security incidents effectively. The plan should Artikel procedures for detecting, containing, responding to, and recovering from security incidents within the vSphere environment. It should define roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and escalation paths. Regularly test and update the incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness in a real-world scenario.
Key Security Audit Points and Tools for vSphere
| Audit Point | Description | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| VM Configuration | Reviewing VM settings for security best practices, such as firewall rules, access controls, and security patches. | vCenter Server, vSphere Client, Security Hardening tools |
| Network Security | Evaluating network configurations for vulnerabilities and compliance with security policies. | Network analyzers, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), VMware NSX |
| Data Security | Assessing data encryption, access controls, and compliance with data protection regulations. | Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools, encryption tools |
| User and Role Management | Reviewing user access rights and permissions to ensure appropriate access levels. | vCenter Server, Active Directory, Identity Management tools |
| Security Compliance | Ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS). | Compliance management tools, vCenter Security |
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity

Virtualized environments offer significant advantages, but the potential for disruption due to hardware failures, software glitches, or even malicious attacks remains. Robust disaster recovery (DR) planning is crucial for ensuring business continuity in a virtualized data center. This section explores the critical elements of DR for vSphere applications, focusing on backup and recovery strategies, replication, failover mechanisms, and best practices for maintaining uptime.Effective DR planning minimizes downtime and financial losses by allowing applications to resume operation quickly and efficiently after a disruption.
It encompasses a range of measures, from preventative maintenance to complete disaster recovery procedures.
Importance of Disaster Recovery Planning for Virtualized Applications
Disaster recovery planning is paramount for maintaining operational stability and minimizing financial losses in a virtualized environment. Without a well-defined plan, disruptions can lead to significant downtime, impacting productivity, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, profitability. Proactive planning ensures business continuity and enables quick resumption of critical services after an outage.
Backup and Recovery Strategies for vSphere Applications
Implementing robust backup and recovery strategies is essential for safeguarding virtual machine (VM) data. Regular backups of VMs, including operating systems, applications, and data, provide a crucial recovery point. Backup frequency, retention policies, and recovery procedures must be carefully defined and regularly tested. A tiered backup strategy, using different backup types and frequencies, allows for various recovery options based on data criticality.
The choice of backup tools should align with the vSphere environment’s specific needs.
Replication and Failover Technologies in vSphere
Replication and failover technologies play a critical role in ensuring high availability and disaster recovery in a vSphere environment. Replication allows for real-time or near real-time data mirroring to a secondary site. This allows for quick failover to the secondary site in case of a primary site outage. Failover mechanisms automate the switching of applications and data to the secondary site, minimizing downtime.
vSphere Replication and other third-party solutions provide various levels of replication and failover capabilities.
Best Practices for Ensuring Business Continuity in a Virtualized Environment
Implementing best practices for business continuity ensures a smooth transition to alternative systems in case of disaster. These practices include:
- Regular Testing and Validation: Regularly test DR procedures to validate the effectiveness of backup and recovery processes, replication, and failover capabilities. Simulated failures help identify potential issues and optimize recovery times.
- Multi-site Deployments: Consider a multi-site deployment strategy to geographically distribute critical applications and data. This enhances resilience to localized disruptions. Geographic redundancy enhances the overall system resilience.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of all DR procedures, including backup schedules, recovery plans, and contact information. Detailed documentation facilitates a smooth recovery process. Ensuring all relevant personnel have access to this documentation is critical.
Disaster Recovery Procedures for a vSphere Environment
A comprehensive DR procedure for a vSphere environment should Artikel the steps to follow in case of a disaster. This includes:
- Identification of Critical Applications: Identify and categorize critical applications and VMs based on their business impact. Prioritize recovery procedures for mission-critical applications.
- Backup and Recovery Execution: Execute pre-defined backup and recovery procedures. This involves restoring VMs and data from backups to a secondary site. Thorough verification of data integrity and application functionality is necessary.
- Failover Activation: Activate failover mechanisms to transfer operations to the secondary site. Automated failover procedures are highly recommended.
- Post-Recovery Validation: Validate the successful restoration of applications and data at the secondary site. Verify functionality and data integrity.
Security Policy and Procedures
A robust security policy is the bedrock of any successful application security strategy, especially within a virtualized environment like VMware vSphere. It establishes clear guidelines and procedures for protecting applications, data, and infrastructure. A well-defined policy acts as a crucial reference point for all personnel, ensuring consistent security practices across the entire organization.A comprehensive security policy for vSphere applications Artikels acceptable use, access controls, incident response protocols, and compliance requirements.
This framework not only mitigates risks but also fosters a security-conscious culture within the organization. Its effectiveness hinges on clear communication, consistent enforcement, and continuous review and adaptation.
Importance of a Comprehensive Security Policy
A comprehensive security policy is vital for defining and enforcing security standards within the vSphere environment. It establishes clear guidelines for all personnel, minimizing the likelihood of security breaches. This document sets the tone for secure practices, reducing the risk of accidental or intentional data breaches.
Creating a Security Policy for Application Security in vSphere
Developing a security policy for vSphere applications involves several key steps. First, conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities within the environment. Next, define clear security objectives and measurable goals. The policy should cover access controls, data encryption, incident response, and compliance requirements. A well-defined policy Artikels specific procedures for addressing security incidents and breaches, ensuring a structured approach to remediation.
Finally, ensure the policy is reviewed and updated regularly to adapt to emerging threats and technological advancements.
Regular Security Awareness Training for Personnel in vSphere
Regular security awareness training is crucial for personnel in a virtualized environment. This training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to potential security threats. It helps foster a culture of security awareness, enabling employees to identify phishing attempts, understand the importance of strong passwords, and recognize suspicious activity. Training should cover topics such as identifying malware, protecting sensitive data, and reporting security incidents.
Key Security Policy Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Control | Defines who can access what resources and under what conditions. |
| Data Encryption | Specifies the requirements for encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit. |
| Incident Response | Artikels the procedures for responding to security incidents, including detection, containment, eradication, and recovery. |
| Compliance Requirements | Details the adherence to industry regulations and standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR. |
| Acceptable Use Policy | Defines the acceptable use of vSphere resources and applications. |
Security Procedure for Incident Response
A well-defined incident response procedure is crucial for managing security incidents effectively. It provides a structured framework for responding to security breaches, minimizing damage, and restoring operations. This process involves several key stages, from initial detection and containment to eradication and recovery. A flow chart illustrates the steps involved in responding to a security incident.
“A clear incident response plan is vital for minimizing the impact of security incidents and restoring operations as quickly as possible.”
 The flow chart illustrates the sequence of actions to be taken during an incident response. Starting with incident identification, it proceeds to containment, analysis, eradication, recovery, and finally, post-incident review. Each step Artikels specific actions and responsibilities to ensure a coordinated and effective response.
The flow chart illustrates the sequence of actions to be taken during an incident response. Starting with incident identification, it proceeds to containment, analysis, eradication, recovery, and finally, post-incident review. Each step Artikels specific actions and responsibilities to ensure a coordinated and effective response.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, securing applications within a VMware vSphere virtualized data center requires a multi-faceted approach. This guide provides a comprehensive framework for understanding and addressing the unique security challenges of virtualized environments. By implementing the strategies Artikeld, organizations can significantly enhance the security posture of their applications and data, mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity. This design guide empowers you to build a secure and resilient virtualized data center.