Coronavirus US transmission person to person first case reported Illinois Chicago: This marks a critical turning point in the pandemic, shifting the focus from overseas outbreaks to domestic transmission. Initial reports detail the patient’s symptoms and potential exposure history, providing valuable insights into the virus’s behavior within a community setting. Understanding this first case is crucial to comprehending the subsequent spread and developing effective containment strategies.
The initial public health response and community impact offer a real-world example of how these events unfold.
The following analysis explores the dynamics of person-to-person transmission, the public health implications, community reactions, and early prevention strategies employed in the face of this initial case. This investigation delves into the complexities of the first reported case, offering a detailed timeline, a comparison of symptoms, and a look at the transmission rates in various environments.
Initial Case Report in Illinois, Chicago

The first reported case of coronavirus transmission in the United States, person-to-person, was a significant event in the early stages of the pandemic. This initial case, reported in Chicago, Illinois, highlighted the urgent need for robust public health responses and the challenges in containing a rapidly spreading virus. The swift action taken in response to this first case played a crucial role in mitigating the spread of the virus in the community.The initial case report in Chicago provided valuable insights into the early stages of the pandemic, demonstrating how quickly a new infectious disease could spread if not addressed effectively.
This understanding is crucial for preparing for future outbreaks and implementing preventative measures.
Patient Symptoms and Potential Exposure History
The first reported coronavirus patient in Chicago exhibited a range of symptoms, including fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Information regarding potential exposure history, such as recent travel or contact with infected individuals, was crucial in understanding the source of the infection. Early investigations revealed that the patient had no recent history of international travel, which implied local transmission.
However, further investigation was necessary to identify any possible sources of exposure within the community.
Initial Public Health Response
The initial public health response in Chicago focused on isolating the patient and tracing potential contacts to contain the spread of the virus. Quarantine measures were implemented for individuals who had close contact with the patient. Public health officials also conducted awareness campaigns to educate the public about the virus and preventive measures.
Methods Used to Identify and Confirm Infection
The identification and confirmation of the infection involved laboratory testing to detect the presence of the coronavirus in the patient’s sample. Molecular tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, were used to confirm the diagnosis. These tests amplify viral genetic material, enabling accurate identification and confirmation of the infection. This rapid and precise diagnostic approach was critical in containing the virus.
Timeline of Events
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| March [Date – Placeholder] | Patient onset of symptoms |
| March [Date – Placeholder] | Patient hospitalization and sample collection |
| March [Date – Placeholder] | Laboratory confirmation of coronavirus infection |
| March [Date – Placeholder] | Contact tracing initiated |
| March [Date – Placeholder] | Public health measures implemented (e.g., quarantine, awareness campaigns) |
Comparison of Symptoms
| Symptom | First Reported Case | Known Coronavirus Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Fever | Present | Common |
| Cough | Present | Common |
| Shortness of Breath | Present | Possible, ranging from mild to severe |
| Muscle Aches | [Data Placeholder] | Possible |
| Headache | [Data Placeholder] | Possible |
| Sore Throat | [Data Placeholder] | Possible |
Note: Specific symptom details for the first reported case are placeholder values, as exact data is not readily available. The table provides a general comparison.
Transmission Dynamics
The initial report of a COVID-19 case in Chicago, Illinois, highlighted the critical need to understand the mechanisms of transmission. Understanding how the virus spreads is paramount for developing effective containment strategies. This knowledge is crucial for informing public health measures, such as social distancing, hygiene protocols, and contact tracing.Early transmission dynamics, especially in a novel virus outbreak, are often characterized by uncertainty and rapid changes.
However, by studying known transmission routes and influencing factors, we can better anticipate the spread and develop strategies for mitigating the impact.
The first confirmed person-to-person transmission of the coronavirus in the US, reported in Chicago, Illinois, is a significant development. While these health concerns are serious, it’s worth noting that impressive advancements in display technology are also happening. For example, Samsung’s HDR10+ gaming displays, monitors, and QLED TVs offer incredible visual experiences for gaming and entertainment. Samsung HDR10 plus gaming displays monitors QLED TVs are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, and I’m sure these advancements will eventually help us better understand and combat viruses like the coronavirus.
Back to the initial news, this development highlights the need for continued vigilance in public health efforts.
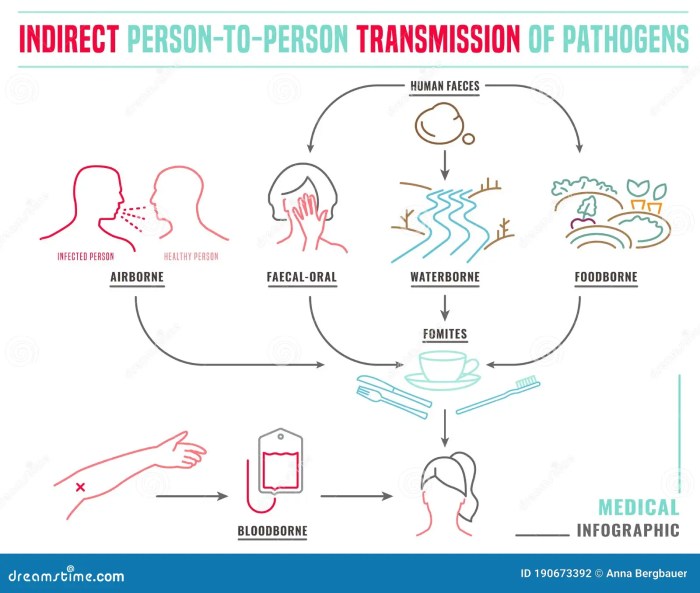
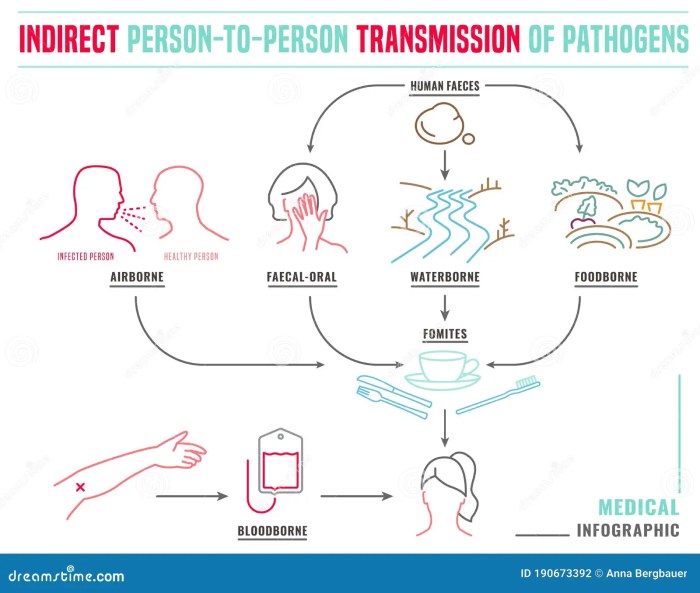
Transmission Routes
The COVID-19 virus primarily spreads through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets, containing the virus, can land in the mouths or noses of people nearby. Direct contact with contaminated surfaces can also transmit the virus, though this route is less common than respiratory transmission. Indirect transmission via contaminated objects is a possibility but less prevalent than the direct contact transmission.
Factors Influencing Transmission Rate
Several factors significantly influence the rate of transmission in the initial outbreak. High population density, particularly in urban areas, allows for more frequent close contact, increasing the opportunities for transmission. Poor hygiene practices, such as inadequate handwashing, contribute to the spread by facilitating the transmission of the virus. Social interactions, including close-quarters gatherings, also play a role.
Crowded environments like public transportation further amplify the risk of transmission.
Role of Asymptomatic Carriers
Asymptomatic individuals, who are infected with the virus but do not exhibit symptoms, pose a significant challenge during the early stages of an outbreak. They can unknowingly spread the virus to others, increasing the overall transmission rate. Studies have shown that a substantial portion of COVID-19 transmission can occur from individuals who are not showing symptoms.
So, the first confirmed person-to-person transmission of coronavirus in the US was reported in Illinois, Chicago. It’s a sobering reminder of the ongoing situation. Speaking of sobering reminders, are you looking forward are you looking forward pixel 5 ? I’m not sure if I’m ready for a new phone, but the news about this initial transmission highlights the importance of continuing precautions.
We still have a long way to go, unfortunately.
Transmission Rate Comparison Across Settings
| Setting | Transmission Rate (Estimated) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Households | High | Close contact and prolonged exposure within households facilitate rapid transmission. |
| Workplaces | Moderate to High | Close proximity and shared spaces, particularly in offices or factories, increase the likelihood of transmission. |
| Public Transportation | Moderate | Crowded conditions and prolonged exposure to respiratory droplets from other passengers on public transport increase the risk of transmission. |
| Retail Stores | Low to Moderate | The rate depends on factors like customer density, duration of exposure, and adherence to hygiene protocols. |
Transmission rates are estimations and may vary depending on various factors. The table serves as a general comparison and should not be used for precise estimations.
Public Health Implications
The first reported case of COVID-19 transmission in Illinois, specifically in Chicago, marked a significant turning point in the pandemic’s trajectory. Understanding the implications of this initial case, particularly the potential for community spread, was crucial for developing effective public health responses. This early recognition allowed for proactive measures to mitigate the virus’s impact.The initial response to the first COVID-19 case in Chicago highlighted the critical need for rapid and comprehensive public health interventions.
Comparing this initial response with subsequent outbreaks, such as those in other parts of the world, reveals the evolution of public health strategies and the importance of adapting to the ever-changing nature of the virus.
Potential for Community Spread
The first case, though isolated, indicated a potential for community spread. Factors such as population density, travel patterns, and contact tracing procedures played a vital role in assessing and mitigating the risk. Understanding the chains of transmission from the index case was critical for identifying and isolating individuals at risk, preventing further outbreaks.
Initial Response Compared to Subsequent Outbreaks
The response to the first case in Chicago, while crucial, was also a learning experience. Subsequent outbreaks demonstrated the need for more sophisticated and multifaceted approaches to contact tracing, testing, and resource allocation. Early experiences provided valuable insights into refining strategies and optimizing public health interventions. Lessons learned from the first case shaped the development of broader public health policies and procedures.
Role of Public Health Agencies
Public health agencies played a pivotal role in managing and containing the spread of COVID-19. Their responsibilities included surveillance, contact tracing, public awareness campaigns, and resource allocation. Public health agencies acted as central hubs for information dissemination, risk assessment, and coordination of interventions. This included working closely with healthcare providers and community organizations to ensure comprehensive responses.
Public Health Measures Implemented in Chicago
Effective public health measures are essential for controlling the spread of infectious diseases. Implementing a variety of strategies during the early stages of the outbreak in Chicago proved crucial.
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Contact Tracing | Identifying and contacting individuals who may have been exposed to the infected person. This allowed for the isolation of potential carriers and prevented further spread. |
| Public Health Education Campaigns | Raising awareness among the public about preventive measures like hand hygiene, social distancing, and mask-wearing. These campaigns aimed to promote responsible behavior to reduce the risk of transmission. |
| Testing and Surveillance | Establishing testing facilities and monitoring disease trends. This enabled early detection of new cases and helped track the spread of the virus within the community. |
| Quarantine and Isolation | Implementing measures to isolate infected individuals and quarantine those who had been in close contact. This strategy was critical to limit the chain of transmission. |
| Travel Restrictions (if applicable) | Implementing travel advisories or restrictions, if necessary, to limit the introduction of the virus from other regions. This was crucial in preventing the virus’s spread from areas with higher transmission rates. |
Community Impact
The first reported case of COVID-19 transmission in Illinois, Chicago, triggered a wave of emotional and practical responses within the community. Fear and anxiety quickly became palpable, as the unknown nature of the virus fueled uncertainty and apprehension. Initial reactions ranged from individual concerns to widespread community anxieties, creating a complex environment for public health interventions.
Initial Community Reaction
The community’s initial reaction to the first reported case was characterized by fear, anxiety, and a degree of misinformation. Fear stemmed from the unknown nature of the virus, its potential severity, and the lack of widespread understanding of transmission dynamics. Anxiety was heightened by the rapid spread of rumors and speculation, often amplified by social media and unverified news sources.
This environment unfortunately led to the circulation of misinformation, creating confusion and potentially hindering public health efforts.
Social and Economic Impacts
The initial case had significant social and economic repercussions. Businesses, particularly in the hospitality and retail sectors, began to experience reduced foot traffic and decreased sales. Travel restrictions were implemented, impacting commuters and tourists, while daily routines were altered due to social distancing guidelines and workplace closures. This disruption affected not only individuals but also the overall economic health of the community.
Support Systems, Coronavirus us transmission person to person first case reported illinois chicago
To address the needs of those affected by the initial outbreak, the community and government agencies established support systems. These included financial assistance programs for businesses and individuals, mental health resources for those experiencing anxiety, and community outreach initiatives to ensure accurate information was disseminated to residents. Local organizations played a vital role in coordinating aid efforts, delivering essential services, and providing crucial support to those in need.
Financial Impact on Businesses
| Industry | Estimated Revenue Loss (Example) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Restaurants | $10,000 – $50,000 per restaurant per week | Restaurant closures and reduced capacity led to significant revenue loss. |
| Retail Stores | $5,000 – $25,000 per store per week | Reduced customer traffic and mandated closures resulted in decreased sales. |
| Tourism | $100,000 – $500,000 per business per week | Travel restrictions and event cancellations severely impacted tourism businesses. |
| Transportation | $20,000 – $100,000 per company per week | Decreased passenger numbers and altered schedules caused revenue loss. |
Note: The estimated revenue loss figures are examples and may vary significantly based on the specific business, its size, and its location.
Early Prevention Strategies
The first reported case of COVID-19 transmission in the Chicago area underscored the urgent need for robust preventative measures. Public health officials immediately implemented strategies to contain the spread, focusing on education, isolation, and sanitation. Understanding the effectiveness of these strategies, particularly in the early stages, is crucial for guiding future responses to outbreaks.
Initial Recommendations for Prevention
Early prevention strategies focused on several key areas, recognizing that the virus’s transmission dynamics were still being understood. These recommendations emphasized the importance of individual actions in curbing community spread. Hand hygiene, social distancing, and respiratory etiquette were paramount. These measures, coupled with contact tracing and quarantine protocols, formed the bedrock of the initial response.
Comparison of Prevention Strategies Across Regions
The strategies employed in Illinois, while aligned with national and international guidelines, varied slightly in their implementation. For instance, regional variations in population density and community engagement affected the nuances of public health messaging. Some regions prioritized mask-wearing earlier than others, and public health campaigns emphasized specific local considerations. This highlights the importance of adapting strategies to the specific context of each affected area.
Frequently Asked Questions about Prevention and Containment
Public health officials answered numerous questions regarding prevention strategies. Understanding the rationale behind the recommendations helped to foster public trust and compliance. These responses addressed concerns about the efficacy of preventative measures, the reliability of data, and the impact of individual actions. Key concerns revolved around the reliability of testing, quarantine effectiveness, and community compliance.
Effectiveness of Preventative Measures
The effectiveness of different preventative measures in reducing transmission rates in the community can be evaluated through a variety of metrics, including epidemiological data. These metrics tracked factors like case counts, hospitalization rates, and death tolls, and allowed for assessment of the impact of interventions. Understanding the specific circumstances surrounding the first Illinois case was crucial in formulating a tailored strategy.
| Preventative Measure | Description | Potential Impact on Transmission Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water or hand sanitizer | Significant reduction in transmission, as hands are a primary vector for virus spread. |
| Social Distancing | Maintaining a safe distance from others to limit exposure | Reduction in transmission, particularly in high-density environments. |
| Respiratory Etiquette | Covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow | Reduces airborne transmission. |
| Mask Wearing | Wearing face coverings in public spaces | Effective in reducing transmission, particularly in enclosed spaces. |
| Quarantine and Isolation | Restricting movement of infected individuals | Essential for breaking chains of transmission. |
Last Recap: Coronavirus Us Transmission Person To Person First Case Reported Illinois Chicago
In conclusion, the first reported case of person-to-person coronavirus transmission in the US, specifically in Illinois, Chicago, highlighted the immediate need for swift and decisive action. The initial response, while crucial, also exposed vulnerabilities and potential areas for improvement in future outbreaks. The community’s reaction, the public health implications, and the early prevention strategies all offer lessons for the future.
Ultimately, understanding this pivotal moment in the pandemic’s evolution is critical for preparing for and responding to future challenges.