No measles in us canada mexico mmr vaccine – No measles in US, Canada, and Mexico – a testament to the power of the MMR vaccine. This success story isn’t just about the absence of outbreaks; it’s a reflection of decades of public health efforts, vaccination campaigns, and the remarkable impact of preventative measures. We’ll explore the historical context, examine the current situation, and delve into the strategies that have led to this achievement.
The MMR vaccine’s role in safeguarding these nations from measles will be highlighted.
The historical overview will detail significant measles outbreaks, vaccination rates, and the effectiveness of past public health campaigns. Current data on measles cases, vaccination recommendations, and contributing factors will be analyzed. The impact of MMR vaccination on measles rates, and the comparison between high and low vaccination regions will also be examined. We will also address vaccine hesitancy, public health strategies, and the importance of international cooperation in maintaining these positive trends.
Historical Overview of Measles in the Region

Measles, a highly contagious viral illness, has historically posed a significant public health challenge in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. The introduction of the MMR vaccine dramatically reduced measles cases, but recent outbreaks highlight the importance of maintaining high vaccination rates and robust public health strategies. Understanding the historical context of measles in these countries is crucial for preventing future outbreaks and ensuring public health.The historical prevalence of measles in the region reflects complex interactions between factors like population density, travel patterns, and public health infrastructure.
Vaccination campaigns, while successful in the past, have faced varying degrees of acceptance and effectiveness, and the emergence of anti-vaccine sentiments has created new challenges. Analyzing historical data allows for a better understanding of the patterns and trends in measles outbreaks and the impact of vaccination programs.
Measles Outbreaks in the US, Canada, and Mexico
Measles outbreaks in the region have occurred throughout history, with varying degrees of severity and impact. The severity of outbreaks has often been influenced by factors such as population density, mobility, and access to healthcare. Early outbreaks were characterized by higher mortality rates, particularly in vulnerable populations, before the development and widespread adoption of the MMR vaccine.
Vaccination Rates and Measles Incidence
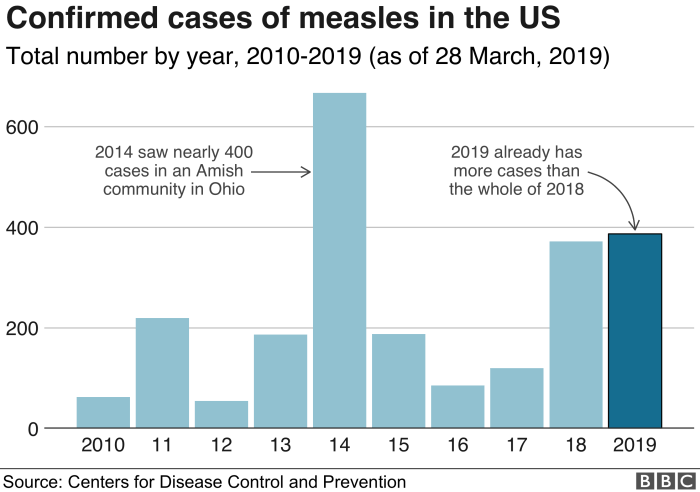
Vaccination rates have been a critical factor in controlling measles outbreaks. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), and similar Mexican health agencies illustrate the correlation between vaccination rates and measles incidence. Periods of low vaccination coverage have often coincided with surges in measles cases.
Effectiveness of Past Public Health Campaigns
Past public health campaigns targeting measles have demonstrated significant success in reducing the incidence of the disease. These campaigns often involved widespread vaccination drives, public awareness campaigns, and the implementation of quarantine measures. The effectiveness of these campaigns varied based on factors like the specific strategies implemented, community engagement, and the level of vaccine hesitancy.
Evolution of Public Health Strategies
Public health strategies related to measles prevention have evolved significantly over time. Early strategies primarily focused on case isolation and quarantine. Modern strategies incorporate vaccination campaigns, surveillance systems, and comprehensive public health education programs. These approaches reflect the growing understanding of the disease’s transmission dynamics and the importance of community-level interventions.
Comparative Analysis of Measles Outbreaks and Vaccination Rates
| Country | Period | Measles Outbreak Size | Vaccination Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1960s | High | Low |
| United States | 2000s | Moderate | High |
| Canada | 1980s | High | Moderate |
| Canada | 2010s | Moderate | High |
| Mexico | 1990s | High | Low |
| Mexico | 2010s | Moderate | High |
This table provides a simplified comparison. More detailed data would be needed to provide a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between outbreak sizes and vaccination rates. Additional factors, such as population density, access to healthcare, and the presence of specific risk factors, also influence the spread of measles.
Current Measles Situation
The recent resurgence of measles cases in various parts of the world, including the US, Canada, and Mexico, underscores the importance of vaccination programs and public health measures. While significant progress has been made in controlling measles, maintaining high vaccination rates is crucial to prevent outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations. The MMR vaccine remains a cornerstone of measles prevention, and understanding the current situation is vital for informed public health decisions.The current measles situation across North America reflects a complex interplay of factors, including vaccination rates, public health initiatives, and the potential for viral spread.
The role of the MMR vaccine in preventing measles transmission is well-documented, offering a robust defense against the virus. Data on recent measles cases will highlight the challenges and successes in controlling outbreaks. Analyzing these factors will allow for a more in-depth understanding of the ongoing efforts to combat measles.
Measles Cases in the US, Canada, and Mexico, No measles in us canada mexico mmr vaccine
Measles cases have varied in recent years, with some countries experiencing spikes in infections and others maintaining relatively low numbers. The reported number of measles cases in each country often fluctuates, influenced by factors like vaccination coverage, population density, and travel patterns. Understanding these factors is key to effectively responding to outbreaks.
Role of the MMR Vaccine
The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine plays a pivotal role in preventing measles transmission. A robust immune response following vaccination significantly reduces the risk of contracting measles and transmitting the virus to others. The effectiveness of the MMR vaccine has been extensively studied and validated through rigorous scientific research. High vaccination rates correlate strongly with reduced measles cases.
Factors Contributing to the Current Measles Situation
Several factors contribute to the current measles situation in each country. These include:
- Decreased vaccination rates in certain communities, leading to susceptible populations.
- Limited access to healthcare services, hindering timely vaccination.
- Increased international travel, potentially facilitating the spread of measles.
- Public health messaging and community trust in vaccination programs, impacting vaccination decisions.
Vaccination Recommendations
The following table Artikels the current vaccination recommendations for the MMR vaccine in each country.
The good news is that measles cases are incredibly low in the US, Canada, and Mexico, largely thanks to the widespread use of the MMR vaccine. This success story in public health highlights the importance of preventative measures. It’s inspiring to see how advancements in communication technology, like the T-Mobile and Sprint merger, are also creating a positive impact on society.
The program offering free 5G to first responders, detailed in this article tmobile sprint first responders free 5g ten years merger connecting heroes , further demonstrates the positive ripple effects of innovation. Ultimately, both the MMR vaccine and these technological advancements contribute to a healthier and more connected world.
| Country | Vaccination Recommendations |
|---|---|
| USA | Two doses of MMR vaccine are recommended for children, typically at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age. Booster doses may be recommended for adults. |
| Canada | Two doses of MMR vaccine are recommended for children, usually at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age. Booster doses may be recommended for certain groups. |
| Mexico | Two doses of MMR vaccine are recommended for children, usually at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age. Booster doses may be recommended for adults. |
Impact of MMR Vaccination: No Measles In Us Canada Mexico Mmr Vaccine
The MMR vaccine, protecting against measles, mumps, and rubella, has dramatically altered the landscape of childhood immunizations. Its widespread adoption has demonstrably reduced the incidence of these potentially debilitating diseases, particularly in regions with robust vaccination programs. This section explores the profound impact of MMR vaccination on measles rates, compares outcomes in regions with varying vaccination coverage, and details the long-term effects of both the vaccine and measles infection.The MMR vaccine’s success lies in its ability to induce a strong immune response against the three targeted viral infections.
This immune response, achieved through exposure to weakened or inactive forms of the viruses, effectively prevents individuals from contracting the diseases. This preventative action has a far-reaching impact on public health, reducing the burden on healthcare systems and minimizing the personal suffering associated with these illnesses.
Measles Rate Reduction in Vaccinated Regions
High MMR vaccination rates correlate directly with significantly lower measles rates. In regions with comprehensive vaccination programs, measles outbreaks are rare and typically contained quickly. Conversely, regions with lower vaccination rates often experience more frequent and widespread measles outbreaks, with a higher incidence of complications. This stark contrast underscores the crucial role of vaccination in controlling the spread of measles.
Comparison of Measles Rates in Regions with High and Low MMR Vaccination Rates
Data consistently demonstrates a strong inverse relationship between MMR vaccination rates and measles incidence. For instance, a comparison between countries with high vaccination coverage and those with low vaccination coverage reveals a significant difference in measles cases. Countries with high vaccination rates typically experience a few isolated cases, whereas countries with low rates may see substantial outbreaks, with numerous secondary infections and increased hospitalizations.
This difference highlights the preventive power of widespread vaccination.
Long-Term Effects of Measles Infection
Measles, while often perceived as a childhood illness, can have severe and long-lasting consequences. Complications can include encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), pneumonia (lung infection), and even death. Furthermore, even in cases without severe immediate complications, long-term neurological issues or subclinical damage may develop. The virus can disrupt the body’s immune system, leaving individuals vulnerable to other infections.
Effectiveness of MMR Vaccine in Preventing Long-Term Health Complications
The MMR vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles and, consequently, the associated long-term health complications. Studies have shown that individuals vaccinated against measles are significantly less likely to develop severe complications compared to unvaccinated individuals who contract the illness. This reduced risk is crucial for maintaining public health and minimizing the societal burden of measles-related health issues.
Potential Side Effects of the MMR Vaccine
While the MMR vaccine is generally safe and highly effective, potential side effects do exist. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, such as fever, rash, or soreness at the injection site. Rarely, more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions, can occur. However, the benefits of the vaccine in preventing serious illness far outweigh the potential risks for the vast majority of individuals.
Benefits and Risks of MMR Vaccination
| Benefit | Risk |
|---|---|
| Protection against measles, mumps, and rubella | Mild side effects (e.g., fever, rash, soreness) |
| Reduced risk of long-term health complications | Rare, serious side effects (e.g., allergic reactions) |
| Public health benefit through herd immunity | Risk of very rare side effects |
| Reduced burden on healthcare systems | Potential for individual allergic reactions |
“The benefits of vaccination, particularly for the MMR vaccine, are substantial and demonstrably improve public health outcomes. While some minor side effects are possible, the significant reduction in the incidence of serious illness associated with measles, mumps, and rubella make vaccination a critical public health intervention.”
The good news is that measles cases are virtually nonexistent in the US, Canada, and Mexico, thanks to the widespread adoption of the MMR vaccine. While you’re celebrating this public health triumph, you might also want to check out some sweet deals on tech right now. There’s a limited-time sale on Dell PCs, laptops, and monitors; you can snag up to $900 off here.
This makes staying informed about vaccinations even more important, as a strong public health system helps keep everyone safe. Ultimately, it’s great to see the positive impact of widespread vaccination efforts.
Public Health Strategies
Combating measles requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing public health campaigns, healthcare provider education, and community engagement. Effective strategies must target vulnerable populations, address misinformation, and leverage existing infrastructure for maximum impact. Success hinges on a unified effort between government agencies, healthcare providers, and the community to ensure widespread MMR vaccination.Public health strategies for increasing MMR vaccination rates need to be tailored to the specific cultural and social contexts of each country.
This involves understanding the factors influencing vaccine hesitancy and tailoring messaging to resonate with diverse communities. Recognizing and addressing specific concerns is crucial for fostering trust and encouraging vaccination uptake.
Strategies to Increase MMR Vaccination Rates
Strategies to increase MMR vaccination rates in the US, Canada, and Mexico need to be comprehensive and targeted. This requires a multi-pronged approach that considers cultural nuances and builds on existing public health infrastructure. Simply increasing awareness is insufficient; strategies must address the underlying reasons for vaccine hesitancy.
- Targeted Communication Campaigns: Public health campaigns should utilize diverse communication channels, such as social media, community events, and local media, to disseminate accurate information about the safety and effectiveness of the MMR vaccine. This should include addressing specific concerns raised by different segments of the population.
- Community Engagement Initiatives: Partnering with community leaders, religious figures, and healthcare providers to promote vaccination is crucial. Community-based health workers can play a vital role in educating families and building trust in the vaccine.
- Incentivizing Vaccination: Incentives, such as financial rewards or free transportation to vaccination clinics, can increase vaccine uptake. These initiatives should be carefully designed to avoid creating unintended consequences and to promote equitable access.
Role of Public Health Campaigns
Effective public health campaigns play a critical role in educating the public about the importance of MMR vaccination. These campaigns must be culturally sensitive and address the root causes of vaccine hesitancy.
- Addressing Misinformation: Public health campaigns must actively combat misinformation and conspiracy theories surrounding MMR vaccines. Clear, evidence-based messaging from credible sources is essential.
- Highlighting Success Stories: Sharing personal stories of individuals who benefited from the MMR vaccine can be powerful tools to build confidence and encourage vaccination.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Public health campaigns must work closely with healthcare providers to ensure consistent messaging and support for vaccination efforts.
Comparison of Public Health Approaches
Different public health approaches have been used to address measles outbreaks in the region. Analyzing the effectiveness of these approaches is vital for refining future strategies. Evaluating success rates and considering factors like cultural sensitivity and community engagement can help inform more effective responses.
- Data-Driven Strategies: Tracking vaccination rates, identifying high-risk populations, and analyzing epidemiological data are critical for tailoring interventions to specific needs.
- Multi-stakeholder Collaboration: Effective measles control requires collaboration among governments, healthcare providers, community leaders, and international organizations.
- Building Public Trust: Strategies that foster trust in public health institutions and healthcare providers are essential to increasing vaccination rates.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in promoting MMR vaccination. Their expertise and trust are vital in building confidence in the vaccine. Consistent messaging and clear communication with patients are paramount.
While the US, Canada, and Mexico have seen a remarkable decrease in measles cases thanks to the MMR vaccine, staying informed about health trends is crucial. Checking out current deals on tech like portal valve PC, RTX graphics cards, magic keyboards, iPad Pro Air, and Paramount Plus subscriptions at portal valve pc rtx magic keyboard ipad pro air paramount plus deal sale can be a fun way to keep up with the latest tech.
Ultimately, the widespread adoption of the MMR vaccine continues to be a vital factor in the ongoing success of preventing measles outbreaks in these regions.
- Providing Clear Information: Healthcare providers should provide accurate, accessible, and comprehensive information about the benefits and safety of the MMR vaccine.
- Addressing Concerns Directly: Healthcare providers should actively address concerns and anxieties patients may have about the vaccine, providing accurate information and reassuring patients.
- Integrating Vaccination into Routine Care: Incorporating MMR vaccination into routine checkups and preventative care can increase vaccination rates and reduce missed opportunities.
Potential Public Health Initiatives
A table outlining potential public health initiatives that could increase MMR vaccination rates.
| Initiative | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Community Health Fairs | Organizing events in diverse communities to provide vaccination information and resources. | Increased awareness and access to vaccination. |
| Educational Workshops | Conducting workshops for parents and community members on vaccine safety and effectiveness. | Enhanced understanding and trust in vaccines. |
| Partnerships with Schools | Collaborating with schools to integrate vaccination information into health education programs. | Improved vaccination rates among children. |
| Social Media Campaigns | Utilizing social media platforms to disseminate accurate information and engage with the public. | Wider reach and engagement with diverse communities. |
Vaccine Hesitancy and Acceptance
Vaccine hesitancy, a reluctance or refusal to accept recommended vaccines, poses a significant threat to public health initiatives, including the crucial MMR vaccination program. Understanding the factors driving this hesitancy is critical to developing effective strategies for increasing vaccination rates and protecting vulnerable populations from preventable diseases. This hesitancy is not a monolithic phenomenon, but rather a complex interplay of individual, social, and systemic factors.Vaccine hesitancy is not a new challenge.
Historical examples of public health campaigns combating vaccine hesitancy demonstrate the importance of tailored strategies that address the specific concerns of targeted populations. The current landscape presents unique challenges, especially with the rise of misinformation and the pervasiveness of social media.
Factors Contributing to Vaccine Hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy stems from a variety of interconnected factors. These factors vary across populations and communities, requiring tailored approaches to address concerns effectively. Cultural beliefs, previous negative experiences with healthcare systems, and exposure to misleading information all play a role in shaping individual decisions about vaccination. Perceptions of risk and benefit also influence decisions, often influenced by the perceived effectiveness and safety of vaccines.
The perceived risks associated with vaccination, sometimes exaggerated or misinterpreted, can create significant barriers to acceptance. Misinformation, whether intentional or unintentional, is a major contributing factor in shaping perceptions about vaccine safety and effectiveness.
Strategies to Address Vaccine Hesitancy
Effective strategies for addressing vaccine hesitancy require a multifaceted approach that combines education, communication, and community engagement. Building trust is paramount; transparent communication about the benefits and risks of vaccines is crucial. Proactive engagement with community leaders and trusted figures within specific communities can help facilitate dialogue and address concerns. This engagement can involve directly addressing misinformation, explaining the scientific basis of vaccination, and providing opportunities for questions and clarification.
Empowering individuals with accurate information and fostering open dialogue are essential components of effective strategies.
Successful Public Health Campaigns
Several public health campaigns have successfully addressed vaccine hesitancy, offering valuable insights into effective strategies. These campaigns often emphasize transparency, community engagement, and tailoring messages to specific populations. Campaigns that utilize trusted messengers and leverage social media platforms to disseminate accurate information have shown positive results. Strategies like targeted messaging, tailored to specific community needs and concerns, have proved successful in addressing unique challenges and concerns.
Examples include campaigns that addressed specific fears or misconceptions related to specific vaccines or targeted groups.
Role of Misinformation and Social Media
Misinformation and social media have become significant factors in influencing vaccine decisions. The rapid spread of inaccurate information through social media platforms can lead to the dissemination of misinformation, which can erode public trust in vaccines. The challenge is to counter this misinformation effectively and provide accurate, verifiable information through trusted sources. This necessitates a proactive approach to identify and address misleading content on social media platforms, providing timely and accurate information.
This also includes providing resources for fact-checking and critical evaluation of information.
Importance of Trust and Transparency
Trust in public health institutions and healthcare providers is essential for vaccine acceptance. Transparency in communication, including open dialogue about the scientific basis for vaccines and the potential risks and benefits, is vital. Public health messaging should be clear, concise, and evidence-based, and must avoid language that may be perceived as alarmist or dismissive. Maintaining transparency and open communication is crucial to building public trust in the vaccination process.
Comparing Strategies for Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
| Strategy | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted Messaging | Tailoring communication to specific demographics, communities, or concerns. | High potential for impact on specific populations. | Requires extensive research and understanding of targeted groups. |
| Community Engagement | Working with community leaders and trusted figures to promote vaccination. | Builds trust and credibility within the community. | May face resistance from certain groups or individuals. |
| Fact-Checking and Information Dissemination | Actively countering misinformation and providing accurate information. | Addresses the root cause of hesitancy by providing accurate information. | Requires ongoing monitoring and response to emerging misinformation. |
| Building Trust with Healthcare Providers | Promoting transparency and open communication with healthcare providers. | Increases confidence in healthcare professionals. | May require significant effort to address existing mistrust. |
International Cooperation
Bridging borders to combat measles requires a concerted effort. International cooperation is crucial in preventing and controlling outbreaks, especially in regions like North America, where interconnectedness necessitates shared strategies and resources. The spread of measles across borders highlights the vulnerability of populations with inadequate vaccination coverage, regardless of their location. A unified approach to vaccination campaigns and public health initiatives can significantly improve outcomes.Effective international cooperation in public health necessitates a coordinated response.
Sharing data, best practices, and resources across borders facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of measles outbreaks and allows for the development of targeted interventions. This collaborative approach fosters a robust system of support and preparedness, minimizing the impact of future outbreaks.
Importance of International Organizations
International organizations play a pivotal role in coordinating efforts to combat measles. Their expertise, global reach, and resources provide critical support for public health initiatives. Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) are instrumental in developing and disseminating guidelines, providing technical assistance, and facilitating the exchange of knowledge. They also advocate for policies that promote vaccination and address vaccine hesitancy.
Collaborative Strategies for Vaccination Rates
To ensure high vaccination rates across borders, countries can implement several strategies. Joint monitoring and surveillance systems can identify outbreaks early, allowing for rapid responses. Sharing vaccination data and best practices allows for the adaptation and refinement of strategies, ultimately improving their effectiveness. Facilitating the flow of essential supplies, including vaccines, across borders is vital to maintaining continuous vaccination programs.
Joint training programs for healthcare professionals further enhance the capacity to administer vaccines effectively and address potential challenges.
Examples of International Collaboration
Past outbreaks have demonstrated the effectiveness of international collaboration. For example, during the 2019 measles outbreak in Europe, countries collaborated on contact tracing, vaccination campaigns, and resource mobilization. The successful response highlighted the importance of rapid communication, coordinated action, and resource sharing among nations. This collective effort reduced the spread of the disease and protected vulnerable populations.
Table: International Collaborations in Public Health Initiatives
| International Organization | Specific Initiatives | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| World Health Organization (WHO) | Development of global measles elimination strategies, technical guidance, and resource mobilization. | Provides a framework for coordinated action and resource allocation across the globe. |
| Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) | Regional surveillance and response to measles outbreaks in the Americas, technical support to countries. | Facilitates a focused approach to measles control within the Americas, tailored to regional needs. |
| UNICEF | Supporting vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries, advocating for equitable access to vaccines. | Addresses disparities in vaccine access and ensures that vulnerable populations are reached. |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | Collaboration with international partners on surveillance, research, and outbreak response, including providing expertise and resources. | Provides a crucial bridge between global and national efforts, particularly in the Americas. |
Final Review
In conclusion, the eradication of measles in the US, Canada, and Mexico stands as a significant achievement in public health. This success is a direct result of consistent vaccination efforts, public health campaigns, and the effectiveness of the MMR vaccine. The importance of maintaining high vaccination rates, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and promoting international cooperation in preventing future outbreaks cannot be overstated.
The future of measles prevention in these countries hinges on a continued commitment to these strategies.