Bing fact check label added search results signals a significant shift in how we consume online information. This new feature aims to improve the reliability of search results by clearly identifying potentially inaccurate content. It will be interesting to see how users react to this addition and how it affects their trust in online sources. The label’s design and placement within search results will be crucial for its effectiveness.
This blog post will explore the Bing fact check label, delving into its purpose, functionality, and potential impact on user behavior and information consumption. We’ll analyze various scenarios, discuss user trust and information accuracy, and examine the technical aspects of label implementation. The post will also compare Bing’s approach with those of other search engines, highlighting unique features and potential challenges.
Introduction to Bing Fact Check Label
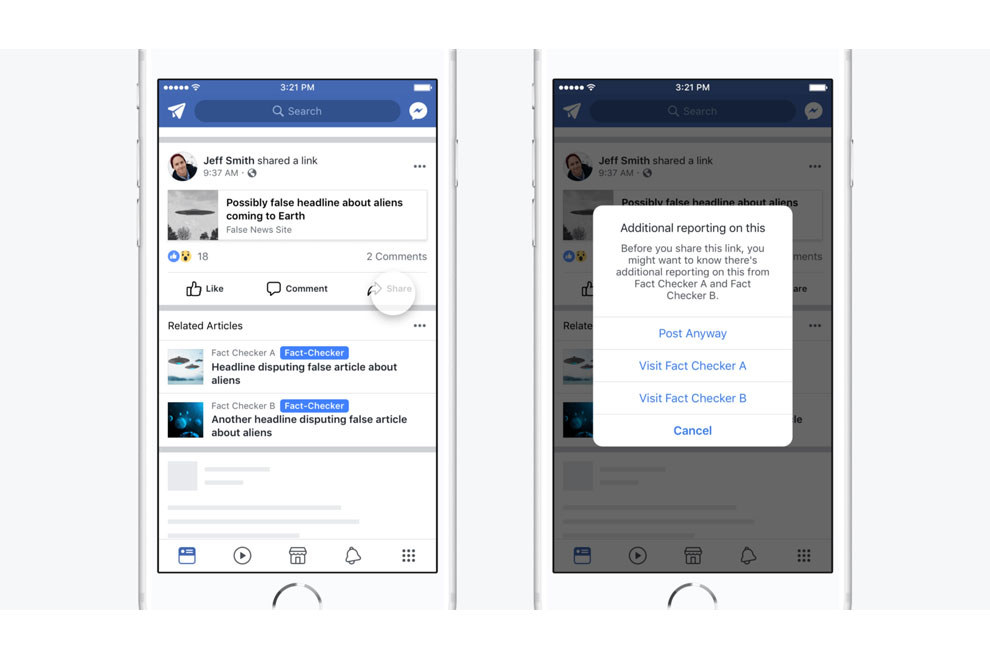
Bing’s new fact-check label in search results aims to enhance the reliability of information presented to users. This feature is designed to provide a clear indication of whether a search result has been verified by a reputable fact-checking organization. It empowers users to critically evaluate the information they encounter, potentially reducing the spread of misinformation.The core functionality of the label is to flag results that have been independently verified as accurate or inaccurate by a trusted fact-checking source.
This allows users to quickly assess the trustworthiness of the information presented and make informed decisions based on reliable sources. This approach is crucial in today’s information landscape, where the proliferation of false or misleading content is a significant concern.
Display of the Fact-Check Label
The fact-check label is visually distinct, typically appearing as a small icon or badge alongside the search result. This icon or badge will clearly communicate the verification status, whether it’s a confirmation of accuracy or a warning of inaccuracy. Its placement within the search results should be consistent and easily noticeable, ensuring that users don’t miss the important information.
Bing’s new fact-check label in search results is definitely interesting. It’s a step toward greater transparency, but it also raises questions about potential bias. This reminds me of the recent Google leaked research, specifically on the topic of censorship and freedom of speech in China, which highlights the complexities of information control and the delicate balance between accuracy and freedom of expression.
This research really sparked debate about the role of tech giants in shaping information access, and the potential for bias in search results. Ultimately, Bing’s fact-check label seems like a good start to help users better assess the reliability of information.
This prominent display aims to draw users’ attention to the fact-checking status without hindering their ability to easily browse the search results.
Potential Impact on User Behavior
The introduction of a fact-check label has the potential to significantly influence user behavior. Users may become more discerning in their selection of information sources, prioritizing results with fact-checking validation. Increased awareness of the reliability of information could lead to a more critical approach to online content, fostering a more informed and discerning audience. This could result in a shift towards a greater reliance on verified information and a decreased vulnerability to misinformation.
Types of Search Results and Fact-Check Labels
| Search Result Type | Potential Fact-Check Label |
|---|---|
| News Article | A green checkmark or “Verified” label indicating accuracy or a red “Disputed” label if the news article has been disputed by a fact-checking organization. |
| Social Media Post | A “Misleading” or “Unverified” label if the social media post is deemed inaccurate or a “Confirmed” label if the post is confirmed to be accurate by a fact-checking source. |
| Wikipedia Page | A “Fact-Checked” label indicating the page has been reviewed and validated, or a “Needs Review” label for pages needing additional scrutiny. |
| Website Article | A “Reliable Source” label for verified sources, or a “Questionable Source” label if the article is flagged for lacking verification. |
User Interactions with the Fact-Check Label
The fact-check label should encourage various user interactions. Users might click on the label to learn more about the fact-checking process, the specific verification performed, or the fact-checking organization involved. This click-through functionality would provide transparency and further context to the verification. Alternatively, users might use the label as a filter to prioritize verified results, allowing them to quickly identify reliable information within the search results.
Impact on User Trust and Information Accuracy: Bing Fact Check Label Added Search Results
The introduction of a Bing fact-check label alongside search results represents a significant step towards improving information accuracy and user trust. This label aims to provide users with a clearer indication of the reliability of the information presented, potentially mitigating the spread of misinformation. However, the implementation of such a system necessitates careful consideration of its potential impact on user behavior and the overall information landscape.The label’s effectiveness hinges on its ability to foster trust and encourage critical evaluation of information sources.
Users will need to understand the criteria behind the fact-checking process to fully leverage the label’s value. Misinterpretations or perceived biases could erode user confidence in the system, necessitating transparency and consistent application of the fact-checking standards.
Potential Effects on User Trust
The presence of a fact-check label can significantly impact user trust in search results. Positive reception relies on user perception of the label’s objectivity and accuracy. If users perceive the label as reliable and trustworthy, it can enhance their confidence in the presented information. Conversely, if users perceive the label as biased or unreliable, it could lead to a decline in trust in the entire search engine.
Bing’s new fact-check label in search results is a smart move, boosting user trust in information. This move is crucial in the current digital landscape, especially as remote work becomes more prevalent in fields like healthcare. Considering the security implications of telemedicine and the future of remote work in healthcare, securing telemedicine and the future of remote work in healthcare.viewer highlights the need for reliable information sources.
Ultimately, this Bing update will help users navigate the digital world more confidently, ensuring they’re getting the accurate information they need.
Furthermore, the label’s impact will depend on the clarity and prominence of its presentation within the search results.
Comparison with Other Fact-Checking Mechanisms
Existing online fact-checking mechanisms, such as those from independent organizations, often vary in their methodologies and coverage. A Bing fact-check label, integrated directly into search results, offers a more readily accessible and immediate evaluation of information. The comparison lies in the accessibility and the potential for broader impact compared to independent fact-checking websites. Users may find the integrated label more convenient for quick assessments, whereas independent fact-checkers may offer deeper analysis.
A crucial difference is the source of the fact-checking. Bing’s label derives from its own verification process, while independent fact-checkers operate independently.
Influence on User Decisions
The label can significantly influence user decisions about information sources. Users presented with fact-checked results might be more inclined to trust and utilize those sources. This could lead to a shift in user behavior, encouraging a greater reliance on verified information. Conversely, users might develop skepticism towards information lacking a fact-check label. Ultimately, the label’s impact will depend on user understanding and acceptance of the verification process.
Potential Biases
The implementation of a fact-check label carries the potential for inherent biases. The fact-checking methodology used by Bing could introduce biases based on the selection of sources, the criteria for verification, and the overall approach to evaluating information. For instance, the sources chosen for verification might reflect existing biases or preferences. Furthermore, the fact-checking process itself could be susceptible to bias, potentially leading to misjudgments.
Transparency and independent audits of the fact-checking process are crucial for mitigating these biases.
User Perspectives on Reliability
| User Perspective | Reliability of Fact-Checked Results | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Skeptical | Low | Suspects potential bias in Bing’s fact-checking process. |
| Neutral | Moderate | Recognizes the label but requires further evidence of its accuracy. |
| Positive | High | Trusts Bing’s fact-checking and considers it a reliable indicator of truth. |
| Cautious | Moderate-High | Acknowledges Bing’s label but still seeks independent verification. |
Technical Aspects of Label Implementation

The Bing fact-check label isn’t just a pretty badge; it’s a crucial part of a sophisticated system designed to help users navigate the often-complex landscape of online information. This system relies on a robust methodology for evaluating claims and ensuring accuracy. The implementation details, from claim evaluation to label placement, are complex, but transparent.This section dives into the technical machinery behind the scenes, revealing the processes used to determine the veracity of information and the methods employed to seamlessly integrate fact-checking labels into search results.
We’ll explore the criteria used to identify potentially inaccurate claims, the different types of claims evaluated, and the varying levels of confidence assigned to each fact check.
Methodology for Determining Accuracy
The accuracy of information is assessed through a multi-faceted approach involving several key components. This includes a combination of automated tools and human review. Automated tools perform initial screening, flagging potential inaccuracies based on pre-defined criteria. These tools analyze the text of claims, checking for inconsistencies, logical fallacies, and comparing the content against established facts and data sources.
This initial screening helps prioritize claims for human review.
Fact-Check Label Addition Process, Bing fact check label added search results
The process of adding the fact-check label to search results is streamlined and efficient. Once a claim is identified as potentially inaccurate, it undergoes a thorough review by a team of trained fact-checkers. This human review is crucial for nuanced understanding and evaluating complex claims that automated systems might miss. After the review, the fact-checker assigns a confidence level to the claim’s accuracy, and this is directly reflected in the label displayed.
Criteria for Identifying Potentially Inaccurate Information
Various criteria are used to identify potentially inaccurate information. These criteria include inconsistencies with existing data, discrepancies in multiple sources, logical fallacies in the argumentation, and lack of verifiable evidence. Claims that rely heavily on anecdotal evidence or unsupported assertions are also flagged. A comprehensive set of rules ensures consistency and fairness in identifying potential inaccuracies.
Evaluation of Different Types of Claims
The evaluation process adapts to the nature of the claim. Claims based on factual statements are evaluated differently from those containing opinions or interpretations. Claims involving complex scientific data require specialized expertise. For instance, claims about medical treatments are assessed using specific medical guidelines and verified against established scientific literature. The fact-checkers are trained to understand the nuances of different claim types.
Fact-Checking Confidence Levels
| Confidence Level | Description |
|---|---|
| High | The claim is accurate and supported by substantial evidence. |
| Medium | The claim is partially accurate or requires further investigation. |
| Low | The claim is inaccurate or unsupported. Further investigation is recommended. |
Label Design and User Experience
The design of the Bing Fact Check label is crucial for its effectiveness in communicating information reliability to users. A well-designed label should be easily understood, trustworthy, and seamlessly integrated into the search results page. A poor design can lead to confusion, distrust, and ultimately, a less valuable user experience. This section delves into the importance of visual cues, user interface elements, and accessibility considerations for optimal label design.
Label Design Comparison
Different label designs can significantly impact user perception. A consistent design approach across Bing search results is vital for establishing trust and clarity.
| Label Design | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Icon | A small, easily recognizable icon (e.g., a shield or a magnifying glass) next to the result. | Simple, fast to process, takes up minimal space. | Might not be informative enough about the level of fact-checking. |
| Color-Coded Badge | A small badge with a distinct color (e.g., green for verified, red for disputed) next to the result. | Visually highlights the result’s trustworthiness, clear distinction between fact-checked and unverified results. | May become visually overwhelming if used excessively. Colorblind users might have difficulty. |
| Pop-up Explanation | A small, informative pop-up that appears when the user hovers over the label. | Provides detailed information, reduces ambiguity. | May interrupt the user’s flow if triggered unexpectedly. Can take up more screen space. |
| Detailed Fact-Check Summary | A short summary of the fact-check directly below the search result. | Provides clear evidence of fact-checking, more in-depth analysis for users. | May be too lengthy, and can overwhelm the user with details. |
Improving Clarity and Comprehension
To enhance user comprehension, the label should be concise and informative. Using clear visual cues, like contrasting colors and easily recognizable icons, is key. Avoid overly technical language and jargon. The label should clearly indicate the nature of the fact-check (e.g., “Verified,” “Disputed,” “Needs Further Review”). A concise summary of the fact-check’s findings, presented in an easily digestible format, would greatly enhance clarity.
Visual Cues and User Interface Elements
Visual cues, such as color and iconography, play a significant role in conveying information quickly and effectively. Consistent use of these cues across all fact-checked results creates a recognizable pattern. Proper spacing and typography also contribute to a clean and user-friendly experience. Visual elements should be intuitive and aligned with established design patterns for internet search results.
Interactive Elements
Integrating interactive elements, such as pop-up explanations or links to the original fact-check, can enhance user engagement and understanding. Users can gain more context and confidence in the information presented by exploring further details. Interactive elements should be seamlessly integrated into the existing design. For instance, a brief, clickable summary of the fact-check can be displayed below the result.
Accessibility for Users with Disabilities
Ensuring the label is accessible to users with disabilities is paramount. This includes providing alternative text for screen readers, using sufficient color contrast, and adhering to web accessibility guidelines. Ensuring that the label is functional with assistive technologies is critical to avoid excluding a significant segment of users.
Table Structure for Label Styles
A well-structured table should include clear column headings (Label Design, Description, Pros, Cons) to aid in understanding. Rows should present distinct label styles, with concise descriptions and highlighting key advantages and disadvantages. The table should be visually appealing, using clear formatting and appropriate font sizes. Consider including examples of each style to provide a tangible demonstration.
Potential Challenges and Future Considerations
Implementing a fact-check label in search results presents numerous challenges, extending beyond the initial design and implementation phases. Maintaining accuracy, consistency, and user trust requires a proactive and adaptable approach. The potential impact on the future of online information verification is significant, demanding careful consideration of long-term implications.
Maintaining Accuracy and Consistency
Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of fact-check labels is crucial for maintaining user trust. A single error in labeling can damage credibility and erode user confidence in the entire verification process. Human error, conflicting expert opinions, and evolving information necessitate ongoing review and refinement of the labeling criteria. Automated systems, while helpful, cannot fully replace human judgment and interpretation in complex situations.
Rigorous review processes, involving multiple experts and diverse perspectives, are essential for maintaining accuracy. The process should also incorporate a system for tracking and addressing corrections and updates to ensure that outdated information is promptly corrected.
Addressing Bias and Conflicts of Interest
Fact-checking organizations themselves can face accusations of bias or conflicts of interest. This potential for bias must be mitigated through transparent disclosure of the fact-checking organization’s affiliations, funding sources, and methodology. Establishing clear guidelines for conflict resolution and independent oversight mechanisms will help maintain objectivity and public trust. For example, the use of multiple, independent fact-checking organizations to verify the same claims can provide a more robust and less biased evaluation.
Bing’s new fact-check label in search results is a welcome addition, but recent security concerns with ShareIt, like those highlighted in shareits security flaws are good reason switch nearby share , prompt me to think about the importance of secure file sharing options. It’s great to see Bing taking steps to improve the reliability of information presented, which will help users to better evaluate results.
Hopefully, this will encourage a greater level of user trust in search results overall.
Tracking and Measuring Label Effectiveness
Measuring the effectiveness of the fact-check label is essential for understanding its impact on user behavior and information consumption. Metrics such as click-through rates on fact-checked articles, user engagement with the label itself, and changes in users’ perceived reliability of information can provide valuable insights. A/B testing different label designs and placements can also help determine the optimal approach for maximizing user engagement and the impact of the label.
Analyzing user feedback and comments regarding the label’s effectiveness can further inform adjustments and improvements.
Future Enhancements
The fact-check label can be further enhanced to improve user experience and provide more comprehensive information.
| Enhancement | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-lingual support | Providing the fact-check label in multiple languages to cater to a broader audience. | Fact-check label available in Spanish, French, and Mandarin. |
| Interactive explanations | Providing more detailed explanations of the fact-check process and rationale behind the label. | Clickable links to detailed analyses or supporting evidence. |
| Integration with other platforms | Integrating the fact-check label with social media and other online platforms. | Displaying the label in social media posts sharing news articles. |
| Historical context | Providing historical context for claims and their evolution. | Links to previous fact-checks on the same or related claims. |
Ongoing Improvements and Adaptations
The online information landscape is constantly evolving, requiring ongoing improvements and adaptations to the fact-check label. Staying abreast of new misinformation tactics, incorporating feedback from users, and adapting to changing user needs are crucial for maintaining the label’s effectiveness and relevance. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential for adapting to emerging challenges and ensuring the label remains a valuable tool for users.
Comparison with Other Search Engines’ Approaches
Bing’s fact-checking label represents a significant step in the evolution of online search, prompting a critical examination of how other search engines approach the issue of information accuracy. This comparison reveals valuable insights into the potential impact of such initiatives on user trust and the overall information ecosystem. A comprehensive understanding of existing approaches allows us to appreciate the nuances and strengths of Bing’s specific implementation.
Different Fact-Checking Approaches
Various search engines employ different strategies for flagging potentially unreliable information. Some focus on partnerships with fact-checking organizations, while others rely on algorithms to identify potentially misleading content. The varying approaches reflect the complexities inherent in discerning factual accuracy in the vast expanse of online information. Understanding these variations is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of Bing’s unique approach.
Examples of Other Search Engines’ Approaches
- Google’s approach primarily involves incorporating information from third-party fact-checking sources into its search results. It relies heavily on a combination of algorithms and human review to identify and label potentially misleading content. This multifaceted approach reflects Google’s commitment to comprehensive information accuracy.
- DuckDuckGo, known for its privacy-focused approach, currently does not have a dedicated fact-checking label. Their strategy centers on prioritizing unbiased and comprehensive search results, rather than directly labeling specific content as “fact-checked”.
- Yahoo, in the past, utilized a similar approach to Google, emphasizing partnerships with fact-checking organizations. The current state of Yahoo’s fact-checking mechanisms, however, warrants further investigation.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Search Engine | Fact-Checking Approach | Unique Features | Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bing | Direct labeling of fact-checked content, highlighting the source. | Clear visual distinction, immediate feedback. | Enhanced transparency, improved user understanding of source reliability. |
| Integration of fact-checking information from partners. | Leveraging a vast network of sources. | Wider coverage, potential for broader reach and impact. | |
| DuckDuckGo | Focus on unbiased results, no direct labeling. | Privacy-centric approach, no direct labeling. | Preservation of user privacy, neutrality. |
| Yahoo | Past use of fact-checking partnerships. | Past involvement with fact-checking organizations. | Past efforts to enhance information accuracy. |
Potential Impact on User Behavior
The comparison highlights the diverse strategies employed by different search engines. Bing’s clear, direct labeling could potentially improve user trust and encourage critical evaluation of information. Conversely, a lack of clear labeling, as seen in DuckDuckGo, might result in users relying more heavily on their own judgment. The varied approaches underscore the need for ongoing research into how users interact with these labeling systems.
The impact of these labeling strategies on user behavior will require careful monitoring and analysis.
Final Review
In conclusion, Bing’s introduction of a fact-check label represents a step towards more reliable online information. While challenges and potential biases exist, the label has the potential to significantly influence user behavior and information consumption. Ultimately, the success of this feature hinges on its user-friendliness, accuracy, and ongoing improvement. Future considerations regarding the label’s methodology and potential enhancements will be crucial to its lasting impact on the digital landscape.




