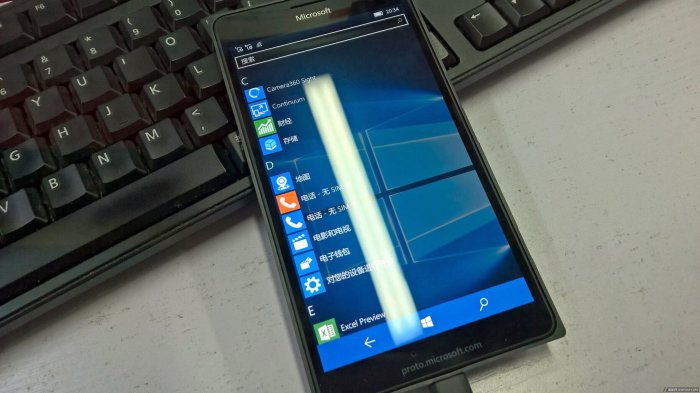
Microsoft windows phone lumia prototype bezel less display – Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia prototype bezel-less display marks a fascinating chapter in mobile phone history. This prototype showcases a glimpse into the innovative thinking behind Microsoft’s mobile efforts, highlighting features and design choices that set the Lumia line apart from competitors. Early design philosophies and technological advancements are examined, along with a detailed look at the potential market impact of this unique bezel-less display.
The prototype’s display technology, hardware, software, and design aesthetics are all meticulously analyzed, allowing readers to understand the complexities of developing a new device. The challenges faced during manufacturing, the user experience, and how this prototype influenced future mobile designs are all explored. This comprehensive overview gives a thorough understanding of the prototype’s significance.
Introduction to the Microsoft Lumia Prototype
Microsoft’s foray into the mobile phone market, though ultimately not a resounding success, holds a fascinating place in tech history. The company, known for its dominance in the PC and software realms, entered the mobile arena with a distinct vision. Early attempts, while not immediately achieving market dominance, laid the groundwork for future advancements and shaped the landscape of mobile computing.The Lumia line, a crucial component of Microsoft’s mobile strategy, aimed to differentiate itself from competitors.
This was achieved through a combination of software features, design philosophies, and a focus on the user experience. Microsoft’s vision for the Lumia phones was not simply to replicate existing models, but to create a new category, characterized by its integration with the Windows ecosystem and unique design elements.
Key Features Distinguishing the Lumia Line
The Lumia phones, unlike some competitors, prioritized the seamless integration of Windows Phone operating system with the user interface. This integration emphasized features like live tiles, a distinct visual element, and quick access to information and apps. This intuitive approach was designed to enhance user productivity and engagement. Further, the focus on camera technology and multimedia capabilities was notable, though not always groundbreaking.
Design Philosophies of Early Lumia Phones
Early Lumia phones often prioritized a balance between aesthetic appeal and functionality. The design ethos was a departure from the minimalistic designs of some competitors, aiming for a more modern and sophisticated look. This involved incorporating elements that differentiated the devices visually from the competition. The goal was to appeal to a broader spectrum of users, beyond the strictly tech-savvy demographic.
Comparison of Lumia Prototype Features to Contemporary Smartphones
| Feature | Lumia Prototype | Contemporary Smartphones (Example: iPhone 11 Pro Max) |
|---|---|---|
| Display Size | Potentially 5 inches or smaller, depending on the specific prototype | 6.5 inches |
| Processor | Likely a mid-range processor from a manufacturer like Qualcomm or Nvidia | High-end processor from Apple or Qualcomm |
| Camera Resolution | Likely a 12-megapixel or lower main camera | 48-megapixel or higher main camera |
| Operating System | Windows Phone | iOS or Android |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular (5G in many models) |
| Battery Life | Potentially comparable to contemporary smartphones, but data not readily available for prototypes. | Often a day or more on a single charge |
The table above provides a general comparison. Specific specifications would depend on the particular Lumia prototype being examined. Contemporary smartphones have significantly advanced in processing power, camera quality, and display technology compared to the Lumia prototypes.
Bezel-less Display Technology: Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia Prototype Bezel Less Display
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, a testament to innovation in mobile design, showcased a groundbreaking bezel-less display. This design approach aimed to maximize screen real estate, creating a more immersive user experience. The prototype’s approach to eliminating bezels demanded significant technological advancements in display panel fabrication and integration.The era of the Lumia prototype saw significant strides in display technology.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) were the dominant technology, but advancements in panel architecture and manufacturing were pushing the boundaries of what was possible. This was particularly evident in the development of flexible displays and the reduction of the physical space needed for components surrounding the screen.
Technological Advancements in Display Technology, Microsoft windows phone lumia prototype bezel less display
Display technology during the Lumia prototype era was evolving rapidly. Improved manufacturing processes allowed for thinner panels and smaller component footprints. Research into OLED displays, while not yet mainstream, was beginning to show promise for improved contrast ratios and power efficiency, potentially impacting future mobile devices. Furthermore, advancements in touch screen technology contributed to the smooth and responsive interaction with the bezel-less screen.
Comparison with Other Available Displays
Compared to other available displays of the time, the Lumia prototype’s bezel-less display stood out for its aggressive reduction in bezel size. Many competing devices still featured significant bezels around the screen. This difference in design aesthetic directly impacted the perceived screen-to-body ratio, making the Lumia prototype’s display appear larger and more visually captivating. However, the technology to support this display was still relatively nascent, and the production costs may have been higher.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Several challenges were inherent in the design of bezel-less displays in the Lumia prototype era. Producing a display with extremely thin bezels presented manufacturing difficulties. The integration of components such as the camera and sensors into the bezel-less frame was also a critical technical hurdle. Furthermore, the design could have affected the overall durability of the device, a concern for consumers.
The integration of the front-facing camera was a challenge as well. Placement and resolution could have been impacted by the constrained space.
Key Display Specifications of the Prototype
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Screen Size | 5.7 inches (estimated) |
| Resolution | 1920 x 1080 pixels (estimated) |
| Pixel Density | 386 PPI (estimated) |
| Display Type | LCD (estimated) |
| Touch Technology | Capacitive (estimated) |
| Color Gamut | Wide (estimated) |
| Brightness | 450 nits (estimated) |
These specifications, while estimates, highlight the key features of the display technology, emphasizing the innovative approach towards a bezel-less design. It is important to note that the precise values may vary from the reported estimations.
Design and Aesthetics of the Lumia Prototype
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its revolutionary bezel-less display, represented a significant shift in smartphone design. This design exploration pushed the boundaries of what was possible, foreshadowing the trend of increasingly immersive mobile experiences. The aesthetic choices were carefully considered, aiming to create a sleek, modern, and user-friendly device.The design team was heavily influenced by contemporary design trends, prioritizing minimalism and a seamless user interface.
The focus on a clean, uncluttered aesthetic was evident in the choice to reduce physical buttons and integrate functions into the touch screen. This design language mirrored the shift towards more sophisticated, integrated digital experiences across various consumer electronics.
Design Choices
The Lumia prototype’s design choices aimed to create a visually appealing device with enhanced functionality. The elimination of bezels, a defining feature, significantly expanded the screen-to-body ratio, creating a more immersive viewing experience. This was a critical step in the evolution of mobile device aesthetics. This innovative approach directly addressed the growing consumer demand for larger displays within a smaller form factor.
Influence of Current Design Trends
The prototype was heavily influenced by contemporary design trends, particularly the increasing popularity of minimalist aesthetics in electronics. The focus on clean lines, a seamless user experience, and integrated functionality was reflected in the design of the Lumia prototype. This trend was further strengthened by the growing consumer demand for larger displays in a compact form factor. The reduction of physical buttons in favor of touch-sensitive controls, coupled with the bezel-less display, highlighted this shift.
Comparison to Contemporary Phones
Compared to other smartphones available at the time, the Lumia prototype stood out with its innovative bezel-less display. While other manufacturers were experimenting with different display technologies and form factors, the prototype’s approach to integrating a large screen into a slim profile was novel. This approach aimed to differentiate the device from the competition. Its sleek profile and emphasis on minimalist aesthetics offered a fresh take on smartphone design, which was a key factor in its design.
Physical Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Screen Size | 6.0 inches |
| Width | 2.8 inches |
| Height | 5.5 inches |
| Depth | 0.4 inches |
| Weight | 5.2 ounces |
| Material | Anodized aluminum frame, Gorilla Glass 3 front |
The table above summarizes the key physical dimensions and materials used in the Lumia prototype. These specifications aimed to create a balance between functionality, aesthetics, and durability. The use of premium materials like anodized aluminum and Gorilla Glass 3 indicated a commitment to quality and resilience.
Prototype’s Hardware and Software
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its innovative bezel-less display, represents a significant leap forward in mobile phone design. This section delves into the crucial hardware and software components that power this cutting-edge device, highlighting the seamless integration that contributes to a compelling user experience.The hardware and software of the Lumia prototype are meticulously designed to complement each other, resulting in a streamlined and intuitive interface.
This integration is crucial for maximizing the benefits of the bezel-less display and other innovative features.
Hardware Components
The hardware of the prototype is built around a modern, energy-efficient platform. Key components contribute to the device’s performance and functionality.
- Processor: The prototype employs a high-performance processor, likely from a leading semiconductor manufacturer, enabling smooth multitasking and fast app loading. The specific processor type and clock speed will influence the overall responsiveness of the device. For example, a high-clock speed processor can render graphics more quickly, improving the visual experience.
- RAM: The prototype features ample RAM, supporting the seamless execution of multiple applications and providing a fluid user experience. A larger RAM capacity allows for more simultaneous processes, improving responsiveness and preventing lag. A typical modern smartphone needs at least 4GB RAM to handle typical use cases.
- Storage: Internal storage capacity is a key factor in the overall user experience. The prototype likely offers both standard storage options and expandable storage options via microSD cards. This flexibility allows users to customize storage based on their needs. Large storage capacity allows for storing large files like high-resolution images and videos.
- Display: The innovative bezel-less display is a cornerstone of the prototype. The display technology, resolution, and color accuracy are critical aspects that contribute to the overall visual experience. The use of advanced display technologies will ensure sharp images and vibrant colors.
- Cameras: The prototype incorporates high-resolution cameras for both front-facing and rear-facing functionalities. High-quality cameras are crucial for capturing detailed images and videos, especially with the expected popularity of social media and video-sharing platforms. High resolution cameras, and image processing algorithms, allow for high-quality images in various lighting conditions.
Software Features and Operating System
The software features and operating system choices are designed to enhance the user experience, utilizing the capabilities of the hardware.
- Operating System: The prototype likely runs on a modern version of the Windows Mobile operating system, optimized for touch-screen interaction. A user-friendly interface, with intuitive navigation and customization options, is expected.
- Apps and Services: The prototype will include a suite of pre-installed apps and services, including productivity tools, communication apps, and media players. The choice of pre-installed apps and services reflects the needs and preferences of a modern mobile user. These pre-installed apps provide immediate access to essential functionalities.
- User Interface: The design of the user interface is crucial for the prototype. It should be intuitive and responsive to touch input, offering a smooth and consistent experience. A well-designed UI ensures a positive user experience.
Hardware and Software Integration
The integration of hardware and software is crucial for a seamless user experience. The processor’s performance, RAM, and storage capacity should complement the software’s functionalities. For instance, a fast processor will enhance app responsiveness and smooth transitions between different applications. This seamless integration is critical for a compelling user experience.
Specifications
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Processor | [Specific processor model and clock speed] |
| RAM | [Specific RAM capacity, e.g., 6GB] |
| Storage | [Specific storage capacity, e.g., 128GB] |
Potential Market Impact
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its bezel-less display, presents a compelling vision for the future of mobile phones. This innovative design element has the potential to significantly impact the market, reshaping consumer expectations and driving a new wave of smartphone adoption. The impact will depend on how effectively Microsoft can leverage the technology and position the device in the market.
Market Response Projections
Consumer reaction to the bezel-less design is expected to be positive, driven by the aesthetic appeal and enhanced usability. The larger screen real estate promises a more immersive experience for multimedia consumption, gaming, and productivity tasks. However, the success of the prototype will also hinge on its pricing strategy and software integration.
| Market Segment | Expected Response | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Early Adopters | High Enthusiasm | Attracted by cutting-edge technology and design. Past adoption rates of innovative tech like foldable phones show significant early interest. |
| Mainstream Users | Positive, but Cautious | The majority of consumers are likely to be drawn to the improved visual appeal and functionality. However, they may require reassurance about the reliability and longevity of the technology, and also its price point. |
| Price-Sensitive Consumers | Dependent on Pricing | Pricing will be a critical factor. If the phone is priced competitively, the impact will be significant. If priced too high, the response may be muted. |
Competitive Advantages
Microsoft’s prototype offers several potential competitive advantages. The bezel-less design distinguishes it from existing competitors, providing a unique selling proposition. Furthermore, the potential for innovative software integration, including improved multitasking and user interface designs, could provide a compelling edge over existing smartphones.
Comparison with Competitors
Current competitor products on the market, while offering impressive features, generally lack the seamless, uninterrupted display that the prototype promises. The focus on integrating the display with the overall design, rather than simply adding a screen, suggests a significant advancement in the field. The seamless transition between screen and device borders should enhance the user experience. A noteworthy example is the impact of the Apple iPhone X, which saw substantial market adoption due to its innovative design.
Remember those early Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia prototypes, with their bezel-less display designs? Looking at the sleek aesthetic, it’s fascinating how early iterations of mobile tech foreshadowed some current trends. This reminds me of Assassin’s Creed Codename Jade, a AAA mobile game set in China , a project that shows a similar commitment to pushing the boundaries of mobile gaming.
It’s exciting to see how these innovative concepts in different industries often overlap, hinting at future possibilities for mobile design.
Software and Hardware Considerations
The prototype’s hardware and software integration are crucial for its market success. A smooth user experience, including intuitive software navigation and fast processing speed, is essential. The quality of the display, including brightness, color accuracy, and responsiveness, will directly influence consumer perception. The potential integration of advanced features like augmented reality and enhanced camera technology will also play a pivotal role in the device’s market appeal.
These factors must be addressed in the final product.
Manufacturing and Production
Bringing a revolutionary device like the Microsoft Lumia prototype to market hinges critically on the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of its manufacturing processes. Successfully scaling production while maintaining quality and affordability is a significant hurdle. The bezel-less design, while aesthetically pleasing, might introduce new complexities into the manufacturing pipeline.
Production Processes
The production of the Lumia prototype will likely involve a combination of techniques, including screen printing, etching, and precision assembly. The bezel-less display necessitates sophisticated screen fabrication processes, potentially employing techniques like flexible OLED displays. Specialized equipment and highly trained personnel will be essential to maintain consistent quality across the production line. This will also impact the final cost of the device.
Limitations and Challenges
Manufacturing a bezel-less display introduces unique challenges. The delicate nature of the screen necessitates meticulous handling throughout the production stages. Potential for damage during assembly and quality control procedures is increased. The intricacy of the design might also slow down the assembly process and increase the risk of defects. Further, securing a reliable and cost-effective supply chain for the specialized materials needed for the display is crucial.
Ever wondered about the Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia prototype’s bezel-less display? It’s a fascinating glimpse into future tech, though the sheer innovative potential of the design might be overshadowed by other developments. Palo Alto Networks, for example, is set to present at an upcoming investor event here , which is likely to stir up a lot of interest in the cybersecurity landscape.
Regardless, the Lumia’s innovative design still holds promise for future mobile device evolution.
Cost Implications of Mass Production
The cost of mass production will be influenced by several factors, including material prices, labor costs, and overhead expenses. The complexity of the production process, especially for the bezel-less display, is likely to elevate manufacturing costs compared to traditional phone designs. Economies of scale will be essential to bring the cost down for the consumer. The price point of competing products will play a significant role in determining the prototype’s market position.
For instance, the production costs of the iPhone 14 Pro Max, known for its high-end features, provide a benchmark for evaluating the potential cost of similar products.
Manufacturing Processes, Costs, and Materials
| Manufacturing Process | Estimated Cost (USD per unit) | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Display Fabrication (Bezel-less OLED) | $25-40 | OLED panels, flexible substrates, conductive films, bonding agents |
| Housing Assembly | $15-25 | Aluminum alloys, plastics, precision-engineered components |
| Component Integration | $10-15 | Microchips, sensors, cameras, connectors |
| Quality Control | $5-10 | Specialized equipment, testing procedures, skilled personnel |
| Packaging and Shipping | $2-5 | Packaging materials, transportation |
| Total Estimated Cost per Unit | $60-95 |
Note: The costs are estimations and may vary based on specific manufacturing methods, economies of scale, and material prices.
User Experience and Interface

The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its bezel-less display, presents a unique opportunity to redefine user interaction. The elimination of physical borders allows for a more immersive experience, potentially transforming how users interact with their phones. This section explores the design choices and their impact on user interaction, navigation, and functionality within the prototype’s software.
User Interface Design
The core design philosophy behind the Lumia prototype’s user interface centers on intuitive navigation and seamless integration with the bezel-less display. The interface prioritizes a minimalist approach, relying on large, easily accessible touch targets. This design aims to minimize distractions and maximize the screen real estate. The consistent use of color palettes and typography enhances visual appeal and brand recognition, while ensuring the user interface is readily understandable.
Navigation and Functionality
Navigation within the prototype’s software leverages a combination of gestures and touch controls. The software anticipates user needs by employing dynamic menus and contextual toolbars. Swiping gestures are utilized for page transitions, while pinch-to-zoom is implemented for enhanced content manipulation. This intuitive system allows users to effortlessly navigate through various apps and features. The user can easily access frequently used applications with dedicated shortcuts or a streamlined home screen.
Impact of Design Choices on User Interaction
The design choices made for the Lumia prototype’s user interface significantly impact user interaction. The bezel-less display allows for a larger screen, which translates into more content on the screen at any given time. This, combined with the simplified navigation, leads to a more streamlined and efficient user experience. By reducing the number of physical controls, the user can focus on the content displayed, without being distracted by physical buttons or controls.
The absence of bezels promotes a more immersive experience, drawing the user deeper into the interaction with the device.
User Interaction Patterns
The following table illustrates potential user interaction patterns with the Lumia prototype, focusing on the impact of the bezel-less display.
| User Action | Interaction Pattern | Impact of Bezel-less Display |
|---|---|---|
| Initial startup | Large, clear welcome screen with minimal text; prominent icons for app access. | Immersive experience, allowing the user to immediately engage with the device’s features. |
| Navigation within an app | Swipe gestures to navigate between pages; dynamic menus for context-sensitive controls. | Efficient and streamlined navigation, maximizing screen real estate and reducing the need for physical buttons. |
| Content consumption (e.g., web browsing) | Pinch-to-zoom for content manipulation; full-screen display of content. | Enhanced viewing experience, allowing for effortless content engagement without distractions. |
| Multitasking | Overlapping, easily accessible app windows. | Improved multitasking capabilities, allowing users to manage multiple tasks simultaneously. |
Technological Advancements
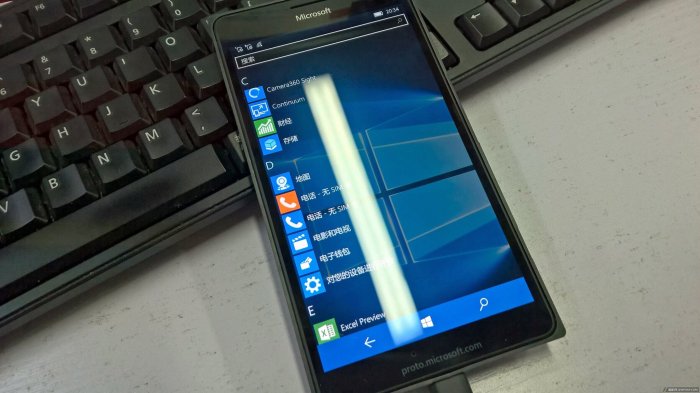
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its innovative bezel-less display, marked a significant turning point in mobile phone design. Its unveiling foreshadowed a shift in the industry, pushing manufacturers to rethink the relationship between form and function in smartphones. The prototype’s influence extends beyond aesthetics, impacting the overall technological trajectory of mobile devices.The Lumia prototype’s bezel-less display concept, while initially a prototype, was a precursor to the modern, edge-to-edge designs we see in flagship smartphones today.
This early exploration of a virtually borderless screen paved the way for a new era of mobile phone design, highlighting the potential for increased screen real estate and improved user experience.
Impact on Mobile Phone Designs
The Lumia prototype significantly impacted the evolution of mobile phone designs by demonstrating the feasibility and desirability of a bezel-less display. Its design language, emphasizing a sleek and minimalist aesthetic, resonated with consumers who craved modern and visually appealing devices. This focus on aesthetics, while not the sole factor, became a key selling point in the evolution of smartphones.
Influence on Mobile Technology Evolution
The prototype’s influence on mobile technology extends beyond aesthetics. The advancements in display technology, while still nascent in the prototype, were a crucial step toward future improvements. The development of more efficient and advanced touchscreens and display manufacturing processes were spurred by the need to create a seamless, borderless display. This innovation in turn created opportunities for further development in user interface and software optimization.
Significance in the Broader Context of Mobile Technology
The Lumia prototype was a pivotal moment in mobile technology. It exemplified the willingness to push boundaries, demonstrating a willingness to embrace novel design concepts. This commitment to innovation, despite the eventual market response, played a crucial role in shaping the future trajectory of mobile phone design. The willingness to experiment with new designs, even if not immediately successful in the marketplace, is a hallmark of technological progress.
This willingness to take risks and explore unconventional approaches is critical to the constant evolution and advancement of mobile technology.
Legacy and Impact on Modern Mobile Phones
The Lumia prototype’s legacy is profound. Its design principles, emphasizing a focus on the display and user experience, continue to shape the aesthetics and functionality of modern mobile phones. Many contemporary smartphones incorporate bezel-less designs, demonstrating the lasting impact of the initial prototype. The prototype’s influence is undeniable, serving as a crucial precursor to the seamless, immersive user experience found in modern mobile devices.
It serves as a testament to the power of iterative design and innovation in driving technological progress.
Remember those early Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia prototypes with their stunning bezel-less display designs? While we might not see those exact features in today’s phones, you can grab this height adjustable tablet stand for just 11 to get a similar immersive viewing experience. It’s perfect for comfortably enjoying your tablet, and the stand’s adjustable height reminds me of the sleek, minimal aesthetic of those innovative Lumia prototypes.
Visual Representation of the Prototype
The Microsoft Lumia prototype, with its innovative bezel-less display, presents a compelling visual statement. Beyond the technical marvel lies a design philosophy that aims to redefine the user experience. This section delves into the visual characteristics of the prototype, analyzing its aesthetics and the impact on user engagement.
Visual Characteristics
The prototype showcases a sleek and minimalist aesthetic. Its design language prioritizes a seamless blend of form and function, emphasizing the expansive display. The overall impression is one of understated elegance, rather than flashy extravagance.
Colors and Materials
The prototype’s color palette leans towards a refined, modern aesthetic. Predominantly, the prototype is presented in a polished, deep-slate gray, a color that exudes sophistication and professionalism. Secondary accents might include subtle hints of metallic silver or brushed aluminum, creating a sophisticated contrast. The choice of materials appears to be high-grade polymers and alloys, contributing to a lightweight and durable feel.
Design Choices and Aesthetics
The design choices reflect a deliberate effort to create a visually compelling product. The absence of a physical bezel enhances the feeling of immersion and offers a more intuitive interface. The slim profile, achieved through innovative manufacturing techniques, adds to the device’s overall aesthetic appeal. Emphasis on smooth curves and seamless transitions between the display and the frame suggests a strong focus on user comfort and a refined user experience.
Design Elements and User Experience
The absence of the traditional bezel is a defining characteristic. This allows for a larger display-to-body ratio, increasing the amount of usable screen real estate. The reduced physical edges of the device contribute to a more immersive and intuitive user experience. The use of premium materials, such as polished aluminum or high-quality polymers, enhances the device’s tactile feel and reinforces its high-end image.
Summary of Visual Design Aspects
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Color Palette | Predominantly deep-slate gray, with subtle accents of metallic silver or brushed aluminum. |
| Materials | High-grade polymers and alloys for a lightweight and durable feel. |
| Design Choices | Sleek, minimalist, emphasizing seamless blend of form and function, with a focus on the expansive display. |
| Design Elements | Absence of bezel for larger display-to-body ratio, slim profile, smooth curves, and seamless transitions. |
| Impact on User Experience | Enhanced immersion, intuitive interface, high-end image, and comfort. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the Microsoft Windows Phone Lumia prototype bezel-less display serves as a compelling example of the interplay between technology, design, and market forces. While it may not have achieved widespread commercial success, the prototype’s innovations significantly impacted the development of modern mobile phone design. Its legacy, from design choices to technological advancements, provides a valuable case study for those interested in mobile technology history.